|
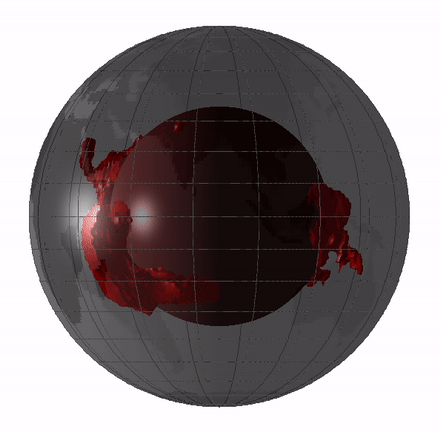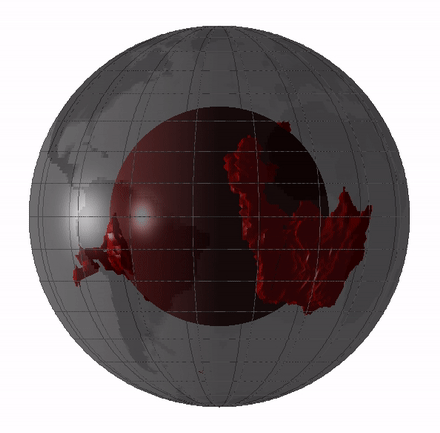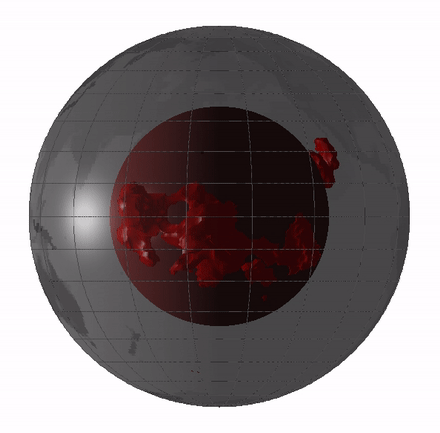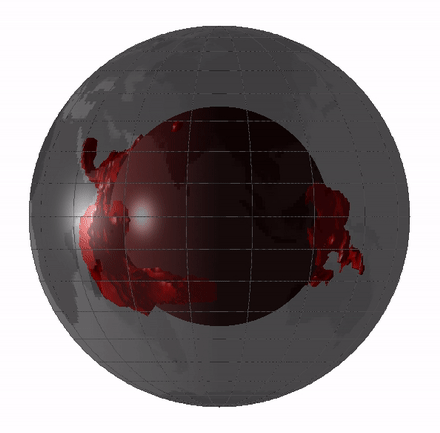
Superplume
Large low-shear-velocity provinces, LLSVPs, also called LLVPs or superplumes, are characteristic structures of parts of the lowermost mantle (the region surrounding the outer core) of Earth. These provinces are characterized by slow shear wave velocities and were discovered by seismic tomography of deep Earth. There are two main provinces: the African LLSVP and the Pacific LLSVP. Both extend laterally for thousands of kilometers and possibly up to vertically from the core–mantle boundary. The Pacific LLSVP is across, and underlies four hotspots that suggest multiple mantle plumes underneath. These zones represent around 8% of the volume of the mantle (6% of Earth). Other names for LLSVPs include " superswells", "thermo-chemical piles", or "hidden reservoirs". Most of these names, however, are more interpretive of their proposed geodynamical or geochemical effects. For example, the name "thermo-chemical pile" interprets LLSVPs as lower-mantle piles of thermally hot and/or chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Superswell
A superswell is a large area of anomalously high topography and shallow ocean regions. These areas of anomalous topography are byproducts of large upwelling of Mantle (geology), mantle material from the core–mantle boundary, referred to as superplumes. Two present day superswells have been identified: the African superswell and the South Pacific superswell. In addition to these, the Darwin Rise in the south central Pacific Ocean is thought to be a paleosuperswell, showing evidence of being uplifted compared to surrounding ancient ocean topography. Superplume Data shows a dramatic increase in Crust (geology), crustal production from 125-120 Ma. (million years) to 70 Ma, largely in East Pacific Rise areas, although the marked increase in production rates of crustal material was also seen in the Gondwana ridges, as well as in oceanic plateaus. This period of increased crustal production is interpreted as a superplume event. This "pulse" of increased crustal production peaked soo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LLSVP
Large low-shear-velocity provinces, LLSVPs, also called LLVPs or superplumes, are characteristic structures of parts of the lowermost mantle (the region surrounding the outer core) of Earth. These provinces are characterized by slow shear wave velocities and were discovered by seismic tomography of deep Earth. There are two main provinces: the African LLSVP and the Pacific LLSVP. Both extend laterally for thousands of kilometers and possibly up to vertically from the core–mantle boundary. The Pacific LLSVP is across, and underlies four hotspots that suggest multiple mantle plumes underneath. These zones represent around 8% of the volume of the mantle (6% of Earth). Other names for LLSVPs include " superswells", "thermo-chemical piles", or "hidden reservoirs". Most of these names, however, are more interpretive of their proposed geodynamical or geochemical effects. For example, the name "thermo-chemical pile" interprets LLSVPs as lower-mantle piles of thermally hot and/or chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Core–mantle Boundary
The core–mantle boundary (CMB) of Earth lies between the planet's silicate mantle and its liquid iron-nickel outer core. This boundary is located at approximately 2,891 km (1,796 miles) depth beneath Earth's surface. The boundary is observed via the discontinuity in seismic wave velocities at that depth due to the differences between the acoustic impedances of the solid mantle and the molten outer core. P-wave velocities are much slower in the outer core than in the deep mantle while S-waves do not exist at all in the liquid portion of the core. Recent evidence suggests a distinct boundary layer directly above the CMB possibly made of a novel phase of the basic perovskite mineralogy of the deep mantle named post-perovskite. Seismic tomography studies have shown significant irregularities within the boundary zone and appear to be dominated by the African and Pacific Large Low-Shear-Velocity Provinces (LLSVP). The uppermost section of the outer core is thought to be about 500� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mantle Plume
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of convection within the Earth's mantle, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspots, such as Hawaii or Iceland, and large igneous provinces such as the Deccan and Siberian Traps. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism near plate boundaries. Concepts Mantle plumes were first proposed by J. Tuzo Wilson in 1963 and further developed by W. Jason Morgan in 1971 and 1972. A mantle plume is posited to exist where super-heated material forms ( nucleates) at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle. Rather than a continuous stream, plumes should be viewed as a series of hot bubbles of material. Reaching the brittle upper Earth's crust they form diapirs. These diapirs are "hotspots" in the crust. In particular, the conc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a divergent plate boundary. The rate of seafloor spreading determines the morphology of the crest of the mid-ocean ridge and its width in an ocean basin. The production of new seafloor and oceanic lithosphere results from mantle upwelling in response to plate separation. The melt rises as magma at the linear weakness between the separating plates, and emerges as lava, creating new oceanic crust and lithosphere upon cooling. The first discovered mid-ocean ridge was the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is a spreading center that bisects the North and South Atlantic basins; hence the origin of the name 'mid-ocean ridge'. Most oceanic spreading centers are not in the middle of their hosting ocean basis but regardless, are traditionally called mid-ocean rid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra Low Velocity Zone
Ultra low velocity zones (ULVZs) are patches on the core-mantle boundary that have extremely low seismic velocities. The zones are mapped to be hundreds of kilometers in diameter and tens of kilometers thick. Their shear wave velocities can be up to 30% lower than surrounding material. The composition and origin of the zones remain uncertain. The zones appear to correlate with edges of the African and Pacific Large low-shear-velocity provinces (LLSVPs) as well as the location of hotspots. Discovery and constraints ULVZs are discovered by the delay and scattering of body waves that reflect and diffract on or are refracted by the core-mantle boundary. Different body waves types give different constraints on the dimensions or velocity contrasts of the ULVZ. Even though ULVZs are discovered in places, it remains difficult to map out their extent and constrain their density and velocity. Usually trade-offs between various parameters exist. In general though, ULVZs appear to be a h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or more. The crust and upper mantle (Earth), upper mantle are distinguished on the basis of chemistry and mineralogy. Earth's lithosphere Earth's lithosphere, which constitutes the hard and rigid outer vertical layer of the Earth, includes the crust and the uppermost mantle. The lithosphere is underlain by the asthenosphere which is the weaker, hotter, and deeper part of the upper mantle. The lithosphere–asthenosphere boundary is defined by a difference in response to stress. The lithosphere remains rigid for very long periods of geologic time in which it deforms elastically and through brittle failure, while the asthenosphere deforms viscously and accommodates strain through plasticity (physics), pl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago. were probably the first to recognise a Precambrian supercontinent, which they named 'Pangaea I'. It was renamed 'Rodinia' by who also were the first to produce a reconstruction and propose a temporal framework for the supercontinent. Rodinia formed at c. 1.23 Ga by accretion and collision of fragments produced by breakup of an older supercontinent, Columbia, assembled by global-scale 2.0–1.8 Ga collisional events.; Rodinia broke up in the Neoproterozoic with its continental fragments reassembled to form Pannotia 633–573 million years ago. In contrast with Pannotia, little is known yet about the exact configuration and geodynamic history of Rodinia. Paleomagnetic evidence provides some clues to the paleolatitude of individual pieces of the Ea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Geophysical Union
The American Geophysical Union (AGU) is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization of Earth, atmospheric, ocean, hydrologic, space, and planetary scientists and enthusiasts that according to their website includes 130,000 people (not members). AGU's activities are focused on the organization and dissemination of scientific information in the interdisciplinary and international fields within the Earth and space sciences. The geophysical sciences involve four fundamental areas: atmospheric and ocean sciences; solid-Earth sciences; hydrologic sciences; and space sciences. The organization's headquarters is located on Florida Avenue in Washington, D.C. History The AGU was established in December 1919 by the National Research Council (NRC) to represent the United States in the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG), and its first chairman was William Bowie of the United States Coast and Geodetic Survey (USCGS). For more than 50 years, it operated as an unincorporated affili ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crustal Recycling
Crustal recycling is a tectonic process by which surface material from the lithosphere is recycled into the mantle by subduction erosion or delamination. The subducting slabs carry volatile compounds and water into the mantle, as well as crustal material with an isotopic signature different from that of primitive mantle. Identification of this crustal signature in mantle-derived rocks (such as mid-ocean ridge basalts or kimberlites) is proof of crustal recycling. Historical and theoretical context Between 1906 and 1936 seismological data were used by R.D. Oldham, A. Mohorovičić, B. Gutenberg and I. Lehmann to show that the earth consisted of a solid crust and mantle, a fluid outer core and a solid innermost core. The development of seismology as a modern tool for imaging the Earth's deep interior occurred during the 1980s, and with it developed two camps of geologists: whole-mantle convection proponents and layered-mantle convection proponents. Layered-mantle convection pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiogenic Nuclide
A radiogenic nuclide is a nuclide that is produced by a process of radioactive decay. It may itself be radioactive (a radionuclide) or stable (a stable nuclide). Radiogenic nuclides (more commonly referred to as radiogenic isotopes) form some of the most important tools in geology. They are used in two principal ways: #In comparison with the quantity of the radioactive 'parent isotope' in a system, the quantity of the radiogenic 'daughter product' is used as a radiometric dating tool (e.g. uranium–lead geochronology). #In comparison with the quantity of a non-radiogenic isotope of the same element, the quantity of the radiogenic isotope is used to define its isotopic signature (e.g. 206Pb/204Pb). This technique is discussed in more detail under the heading isotope geochemistry. Examples Some naturally occurring isotopes are entirely radiogenic, but all these are isotopes that are radioactive, with half-lives too short to occur primordially. Thus, they are only present as ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elsevier Science Direct
ScienceDirect is a website which provides access to a large bibliographic database of scientific and medical publications of the Dutch publisher Elsevier. It hosts over 18 million pieces of content from more than 4,000 academic journals and 30,000 e-books of this publisher. The access to the full-text requires subscription, while the bibliographic metadata is free to read. ScienceDirect is operated by Elsevier. It was launched in March 1997. Usage The journals are grouped into four main sections: ''Physical Sciences and Engineering'', ''Life Sciences'', ''Health Sciences'', and ''Social Sciences and Humanities''. Article abstracts are freely available, and access to their full texts (in PDF and, for newer publications, also HTML) generally requires a subscription or pay-per-view purchase unless the content is freely available in open access. Subscriptions to the overall offering hosted on ScienceDirect, rather than to specific titles it carries, are usually acquired through a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |