|
Stripped Book
A stripped book is a mass market paperback that has been stripped of its cover in order to be recycled. The covers are returned to the publisher as evidence that the books have been destroyed and to obtain a credit on the purchase price. The books are meant to be destroyed by pulping but some find their way to street merchants, presumably by illegal means, and are resold. See also * Out-of-print book * Remaindered book Remaindered books or remainders are printed books that are no longer selling well, and whose remaining unsold copies are liquidated by the publisher at greatly reduced prices. While the publisher may take a net loss on the sales of these books, t ... References Book publishing Book terminology Books by type Industrial processes Pulp and paper industry {{Publishing-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Market Paperback
A paperback (softcover, softback) book is one with a thick paper or paperboard cover, and often held together with glue rather than stitches or staples. In contrast, hardcover (hardback) books are bound with cardboard covered with cloth, leather, paper, or plastic. Inexpensive books bound in paper have existed since at least the 19th century in such forms as pamphlets, yellowbacks, dime novels, and airport novels. Modern paperbacks can be differentiated from one another by size. In the United States, there are "mass-market paperbacks" and larger, more durable "trade paperbacks". In the United Kingdom, there are A-format, B-format, and the largest C-format sizes. Paperback editions of books are issued when a publisher decides to release a book in a low-cost format. Lower-quality paper, glued (rather than stapled or sewn) bindings, and the lack of a hard cover may contribute to the lower cost of paperbacks. Paperback can be the preferred medium when a book is not expected to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paper Recycling
The recycling of paper is the process by which waste paper is turned into new paper products. It has a number of important benefits: It saves waste paper from occupying homes of people and producing methane as it breaks down. Because paper fibre contains carbon (originally absorbed by the tree from which it was produced), recycling keeps the carbon locked up for longer and out of the atmosphere. Around two-thirds of all paper products in the US are now recovered and recycled, although it does not all become new paper. After repeated processing the fibres become too short for the production of new paper, which is why virgin fibre (from sustainably farmed trees) is frequently added to the pulp recipe. There are three categories of paper that can be used as feedstocks for making ''recycled paper'': mill broke, pre-consumer waste, and post-consumer waste. ''Mill broke'' is paper trimmings and other paper scrap from the manufacture of paper, and is recycled in a paper mill. ''Pre-c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
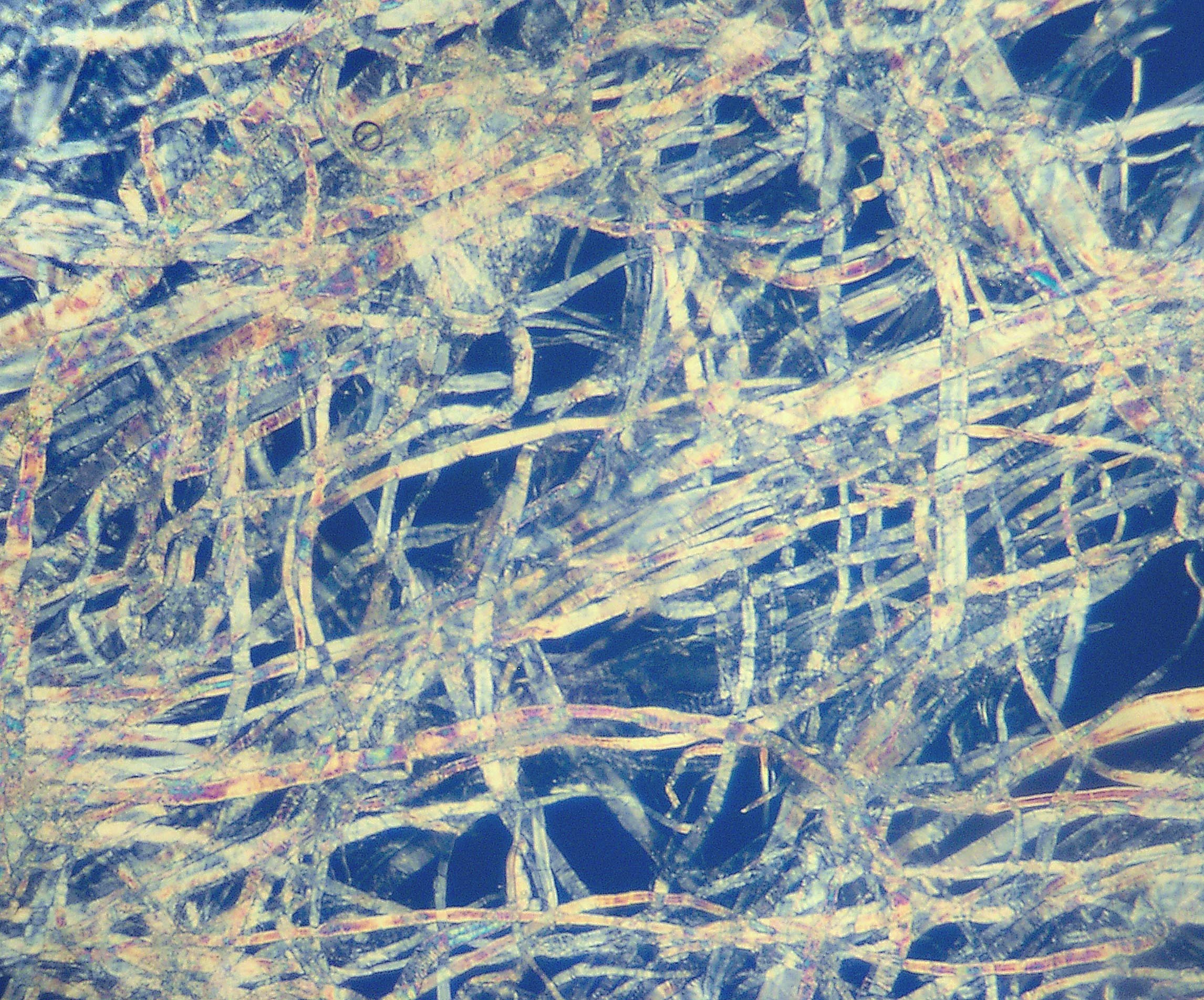
Pulping
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products. History Before the widely acknowledged invention of papermaking by Cai Lun in China around 105 AD, paper-like writing materials such as papyrus and amate were produced by ancient civilizations using plant materials which were largely unprocessed. Strips of bark or bast material were woven together, beaten into rough sheets, dried, and polished by hand. Pulp used in modern and traditional papermaking is distinguished by the process which produces a finer, more regular slurry of cellulose fibers which are pulled out of solution by a screen and dried to form sheets or rolls. The earliest paper produced in China consisted of bast fibers from the paper mul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Out-of-print Book
__NOTOC__ An out-of-print (OOP) or out-of-commerce item or work is something that is no longer being published. The term applies to all types of printed matter, visual media, sound recordings, and video recordings. An out-of-print book is a book that is no longer being published. The term can apply to specific editions of more popular works, which may then go in and out of print repeatedly, or to the sole printed edition of a work, which is not picked up again by any future publishers for reprint. Most works that have ever been published are out of print at any given time, while certain highly popular books, such as the Bible, are always "in print". Less popular out-of-print books are often rare and may be difficult to acquire unless scanned or electronic copies of the books are available. With the advent of book scanning, and print-on-demand technology, fewer and fewer works are now considered truly out of print. A publisher creates a print run of a fixed number of copies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Remaindered Book
Remaindered books or remainders are printed books that are no longer selling well, and whose remaining unsold copies are liquidated by the publisher at greatly reduced prices. While the publisher may take a net loss on the sales of these books, they are able to recover at least some of their sunken costs on the sale and clear out space in the warehouses. Copies of remaindered books may be marked by the publisher, distributor, or bookseller to prevent them from being returned. "Remainder marks" have varied over the years, but today most remainders are marked with a stroke with a felt-tipped marker across the top or bottom of the book's pages, near the spine. Only hardcovers and trade paperbacks (paperback books, often larger than "pocket" paperbacks, sold "to the trade" or directly to sales outlets) are typically remaindered. Mass market paperbacks ("pocket" paperback books sold through a third-party distributor) usually become stripped books rather than remaindered books. A boo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Publishing
Publishing is the activity of making information, literature, music, software and other content available to the public for sale or for free. Traditionally, the term refers to the creation and distribution of printed works, such as books, newspapers, and magazines. With the advent of digital information systems, the scope has expanded to include electronic publishing such as E-book, ebooks, academic journals, micropublishing, Electronic publishing, websites, blogs, video game publisher, video game publishing, and the like. Publishing may produce private, club, commons or public goods and may be conducted as a commercial, public, social or community activity. The commercial publishing industry ranges from large multinational conglomerates such as Bertelsmann, RELX, Pearson plc, Pearson and Thomson Reuters to thousands of small independents. It has various divisions such as trade/retail publishing of fiction and non-fiction, educational publishing K–12, (k-12) and Academic publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Book Terminology
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physical arrangement is ''codex'' (plural, ''codices''). In the history of hand-held physical supports for extended written compositions or records, the codex replaces its predecessor, the scroll. A single sheet in a codex is a leaf and each side of a leaf is a page. As an intellectual object, a book is prototypically a composition of such great length that it takes a considerable investment of time to compose and still considered as an investment of time to read. In a restricted sense, a book is a self-sufficient section or part of a longer composition, a usage reflecting that, in antiquity, long works had to be written on several scrolls and each scroll had to be identified by the book it contained. Each part of Aristotle's ''Physics'' is called a bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Books By Type
A book is a medium for recording information in the form of writing or images, typically composed of many pages (made of papyrus, parchment, vellum, or paper) bound together and protected by a cover. The technical term for this physical arrangement is ''codex'' (plural, ''codices''). In the history of hand-held physical supports for extended written compositions or records, the codex replaces its predecessor, the scroll. A single sheet in a codex is a leaf and each side of a leaf is a page. As an intellectual object, a book is prototypically a composition of such great length that it takes a considerable investment of time to compose and still considered as an investment of time to read. In a restricted sense, a book is a self-sufficient section or part of a longer composition, a usage reflecting that, in antiquity, long works had to be written on several scrolls and each scroll had to be identified by the book it contained. Each part of Aristotle's ''Physics'' is called a bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Industrial Processes
Industrial processes are procedures involving chemical, physical, electrical or mechanical steps to aid in the manufacturing of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry. Chemical processes by main basic material Certain chemical process yield important basic materials for society, e.g., (cement, steel, aluminum, and fertilizer). However, these chemical reactions contribute to climate change by emitting carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, through chemical reactions, as well as through the combustion of fossil fuels to generate the high temperatures needed to reach the activation energies of the chemical reactions. Cement (the paste within concrete) * Calcination – Limestone, which is largely composed of fossilized calcium carbonate (CaCO3), breaks down at high temperatures into useable calcium oxide (CaO) and carbon dioxide gas (), which gets released as a by-product. This chemical reaction, call ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |