|
Streptomyces
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Streptomycetes are characterised by a complex secondary metabolism. They produce over two-thirds of the clinically useful antibiotics of natural origin (e.g., neomycin, streptomycin, cypemycin, grisemycin, bottromycins and chloramphenicol). The antibiotic streptomycin takes its name directly from ''Streptomyces''. Streptomycetes are infrequent pathogens, though infections in humans, such as mycetoma, can be caused by '' S. somaliensis'' and '' S. sudanensis'', and in plants can be caused by '' S. cavi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Mycelial Sheets
''Streptomyces'' is the largest genus of Actinomycetota and the type genus of the family Streptomycetaceae. Over 500 species of ''Streptomyces'' bacteria have been described. As with the other Actinomycetota, streptomycetes are gram-positive, and have genomes with high GC-content, GC content. Found predominantly in soil and decaying vegetation, most streptomycetes produce spores, and are noted for their distinct "earthy" odor that results from production of a volatile metabolite, geosmin. Streptomycetes are characterised by a complex secondary metabolism. They produce over two-thirds of the clinically useful antibiotics of natural origin (e.g., neomycin, streptomycin, cypemycin, grisemycin, bottromycins and chloramphenicol). The antibiotic streptomycin takes its name directly from ''Streptomyces''. Streptomycetes are infrequent pathogens, though infections in humans, such as Eumycetoma, mycetoma, can be caused by ''Streptomyces somaliensis, S. somaliensis'' and ''Streptomyces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Scabies
''Streptomyces scabies'' or ''Streptomyces scabiei'' is a streptomycete bacterium species found in soils around the world. Unlike most of the 500 or so ''Streptomyces'' species it is a plant pathogen causing corky lesions to form on tuber and root crops as well as decreasing the growth of seedlings. Along with other closely related species it causes the potato disease common scab, which is an economically important disease in many potato growing areas. It was first described in 1892, being classified as a fungus, before being renamed in 1914 and again in 1948. Several other species of ''Streptomyces'' cause similar diseases to ''S. scabies'' but other, more closely related species, do not. The genome of ''S. scabies'' has been sequenced and is the largest ''Streptomyces'' genome known so far. The genome contains a pathogenicity island containing the genes required for ''S. scabies'' to infect plants, and which can be transferred between different species. ''S. scabies'' can produ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Caviscabies
''Streptomyces griseus'' is a species of bacteria in the genus ''Streptomyces'' commonly found in soil. A few strains have been also reported from deep-sea sediments. It is a Gram-positive bacterium with high GC content. Along with most other streptomycetes, ''S. griseus'' strains are well known producers of antibiotics and other such commercially significant secondary metabolites. These strains are known to be producers of 32 different structural types of bioactive compounds. Streptomycin, the first antibiotic ever reported from a bacterium, comes from strains of ''S. griseus''. Recently, the whole genome sequence of one of its strains had been completed. The taxonomic history of ''S. griseus'' and its phylogenetically related strains has been turbulent. ''S. griseus'' was first described in 1914 by Krainsky, who called the species ''Actinomyces griseus''. The name was changed in 1948 by Waksman and Henrici to ''Streptomyces griseus''. The interest in these strains stems from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomycetaceae
The ''Streptomycetaceae'' are a family of ''Actinomycetota'', making up the monotypic order ''Streptomycetales''. It includes the important genus ''Streptomyces''. This was the original source of many antibiotics, namely streptomycin, the first antibiotic against tuberculosis. Genomics Sequence alignments of actinomycetotal genomes have led to the identification of three conserved signature indels which are unique to the order Streptomycetales. The enzyme PBGD contains a four-amino-acid insertion which is present in all ''Streptomyces'' species and ''Kitasatospora setae'', but not any other Actinomycetota. Similarly, a one- amino-acid insertion is present in a conserved region of adenylate kinase and is found in all ''Streptomyces'' species and '' K. setae'', but is not found in any other Actinomycetota. Five conserved signature proteins have also been identified which are present in various sequenced ''Streptomyces'' species, but not in ''K. setae''; however, as the complete ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Somaliensis
''Streptomyces somaliensis'' is a protelytic bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces'' which has been isolated from a mycetoma from the foot of a man in Somalia. ''Streptomyces somaliensis'' is a human pathogen and can cause actinomycosis Actinomycosis is a rare infectious bacterial disease caused by ''Actinomyces'' species. The name refers to ray-like appearance of the organisms in the granules. About 70% of infections are due to either ''Actinomyces israelii'' or '' A. gerencseria .... See also * List of ''Streptomyces'' species References Further reading * * * * * * External linksType strain of ''Streptomyces somaliensis'' at Bac''Dive'' - the Bacterial Diversity Metadatabase somaliensis Bacteria described in 1948 {{Streptomyces-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Sudanensis
''Streptomyces sudanensis'' is a bacterium species from the genus of ''Streptomyces'' which has been isolated from patients with actinomycosis infections in Sudan Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic t .... See also * List of ''Streptomyces'' species References sudanensis Bacteria described in 2008 {{Streptomyces-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Turgidiscabies
''Streptomyces turgidiscabies'' is a streptomycete bacterium species, causing scab in potatoes. It has flexuous spore In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, f ..., the latter which are cylindrical and smooth. The type strain is SY9113T (= ATCC 700248T = IFO 16080T). It is almost identical to '' Streptomyces reticuliscabiei''; however, they are considered distinct species given the diseases they cause are different. References Further reading *Joshi, Madhumita V., and Rosemary Loria. "Streptomyces turgidiscabies possesses a functional cytokinin biosynthetic pathway and produces leafy galls." Molecular plant-microbe interactions 20.7 (2007): 751–758. * *Thwaites, R., et al. "Streptomyces turgidiscabies and S. acidiscabies: two new causal agents of common scab of potato (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streptomyces Acidiscabies
''Streptomyces acidiscabies'' is a streptomycete bacterium species, causing a scab disease of potatoes. Its type strain is RL-110 (= ATCC 49003). References Further reading * *Zhao, W. Q., X. M. Yu, and D. Q. Liu. "First report of Streptomyces acidiscabies causing potato scab in China." New Disease Reports 19 (2009): 29. * * External links *LPSN acidiscabies Bacteria described in 1989 {{Streptomyces-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
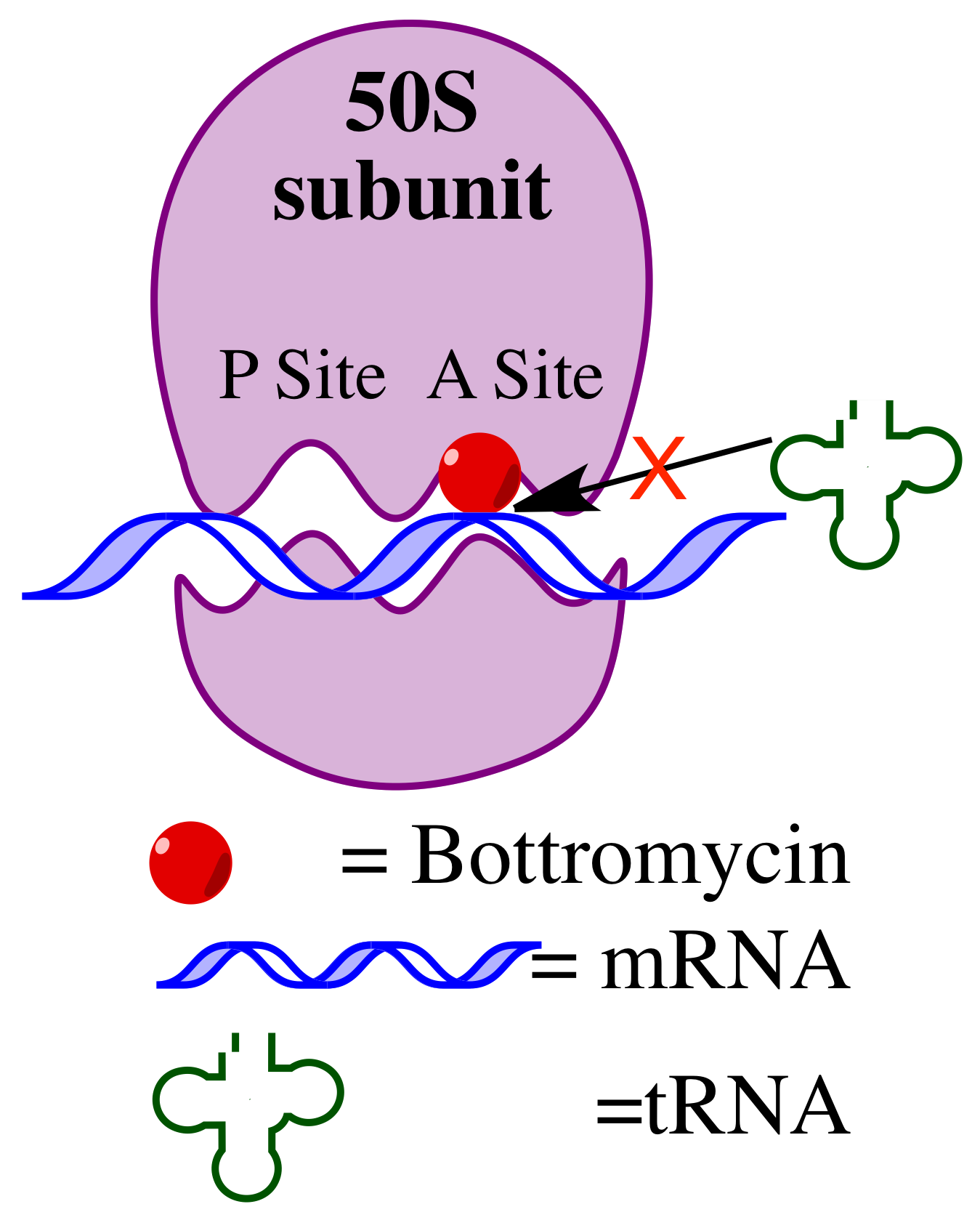
Bottromycin
Bottromycin is a macrocyclic peptide with antibiotic activity. It was first discovered in 1957 as a natural product isolated from ''Streptomyces bottropensis''. It has been shown to inhibit methicillin-resistant ''Staphylococcus aureus'' (MRSA) and vancomycin-resistant Enterococci ( VRE) among other Gram-positive bacteria and mycoplasma. Bottromycin is structurally distinct from both vancomycin, a glycopeptide antibiotic, and methicillin, a beta-lactam antibiotic. Bottromycin binds to the A site of the ribosome and blocks the binding of aminoacyl-''t''RNA, therefore inhibiting bacterial protein synthesis. Although bottromycin exhibits antibacterial activity ''in vitro'', it has not yet been developed as a clinical antibiotic, potentially due to its poor stability in blood plasma. To increase its stability ''in vivo'', some bottromycin derivatives have been explored. The structure of bottromycin contains a macrocyclic amidine as well as a thiazole ring. The absolute stereochemist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one biological cell. They constitute a large domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometres in length, bacteria were among the first life forms to appear on Earth, and are present in most of its habitats. Bacteria inhabit soil, water, acidic hot springs, radioactive waste, and the deep biosphere of Earth's crust. Bacteria are vital in many stages of the nutrient cycle by recycling nutrients such as the fixation of nitrogen from the atmosphere. The nutrient cycle includes the decomposition of dead bodies; bacteria are responsible for the putrefaction stage in this process. In the biological communities surrounding hydrothermal vents and cold seeps, extremophile bacteria provide the nutrients needed to sustain life by converting dissolved compounds, such as hydrogen sulphide and methane, to energy. Bacteria also live in symbiotic and parasitic relationsh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neomycin
Neomycin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that displays bactericidal activity against gram-negative aerobic bacilli and some anaerobic bacilli where resistance has not yet arisen. It is generally not effective against gram-positive bacilli and anaerobic gram-negative bacilli. Neomycin comes in oral and topical formulations, including creams, ointments, and eyedrops. Neomycin belongs to the aminoglycoside class of antibiotics that contain two or more amino sugars connected by glycosidic bonds. Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. Neomycin received approval for medical use in 1952. Rutgers University was granted the patent for neomycin in 1957. Discovery Neomycin was discovered in 1949 by the microbiologist Selman Waksman and his student Hubert Lechevalier at Rutgers University. It is produced naturally by the bacterium '' Streptomyces fradiae''. Synthesis requires specific nutrient conditions i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actinomycetota
The ''Actinomycetota'' (or ''Actinobacteria'') are a phylum of all gram-positive bacteria. They can be terrestrial or aquatic. They are of great economic importance to humans because agriculture and forests depend on their contributions to soil systems. In soil they help to decompose the organic matter of dead organisms so the molecules can be taken up anew by plants. While this role is also played by fungi, ''Actinomycetota'' are much smaller and likely do not occupy the same ecological niche. In this role the colonies often grow extensive mycelia, like a fungus would, and the name of an important order of the phylum, '' Actinomycetales'' (the actinomycetes), reflects that they were long believed to be fungi. Some soil actinomycetota (such as ''Frankia'') live symbiotically with the plants whose roots pervade the soil, fixing nitrogen for the plants in exchange for access to some of the plant's saccharides. Other species, such as many members of the genus '' Mycobacterium'', ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |