|
Stratified Flow
The flow in many fluids varies with density and depends upon the gravity. Due to which the fluid with lower density is always above the fluid with higher density. Stratified flows are very common such as the Earth's ocean and its atmosphere. Stratified fluid A stratified fluid may be defined as the fluid with density variations in the vertical direction. For example, air and water; both are fluids and if we consider them together then they can be seen as a stratified fluid system. Density variations in the atmosphere profoundly affect the motion of water and air. Wave phenomena in air flow over the mountains and occurrence of smog are the examples of stratification effect in the atmosphere. When a fluid system having a condition in which fluid density decreases with height, is disturbed, then the gravity and friction restore the undisturbed conditions. If however the fluid tends to be stable if density decreases with height. Upstream motions in stratified flow It is known that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratified Fluid
The flow in many fluids varies with density and depends upon the gravity. Due to which the fluid with lower density is always above the fluid with higher density. Stratified flows are very common such as the Earth's ocean and its atmosphere. Stratified fluid A stratified fluid may be defined as the fluid with density variations in the vertical direction. For example, air and water; both are fluids and if we consider them together then they can be seen as a stratified fluid system. Density variations in the atmosphere profoundly affect the motion of water and air. Wave phenomena in air flow over the mountains and occurrence of smog are the examples of stratification effect in the atmosphere. When a fluid system having a condition in which fluid density decreases with height, is disturbed, then the gravity and friction restore the undisturbed conditions. If however the fluid tends to be stable if density decreases with height. Upstream motions in stratified flow It is known that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
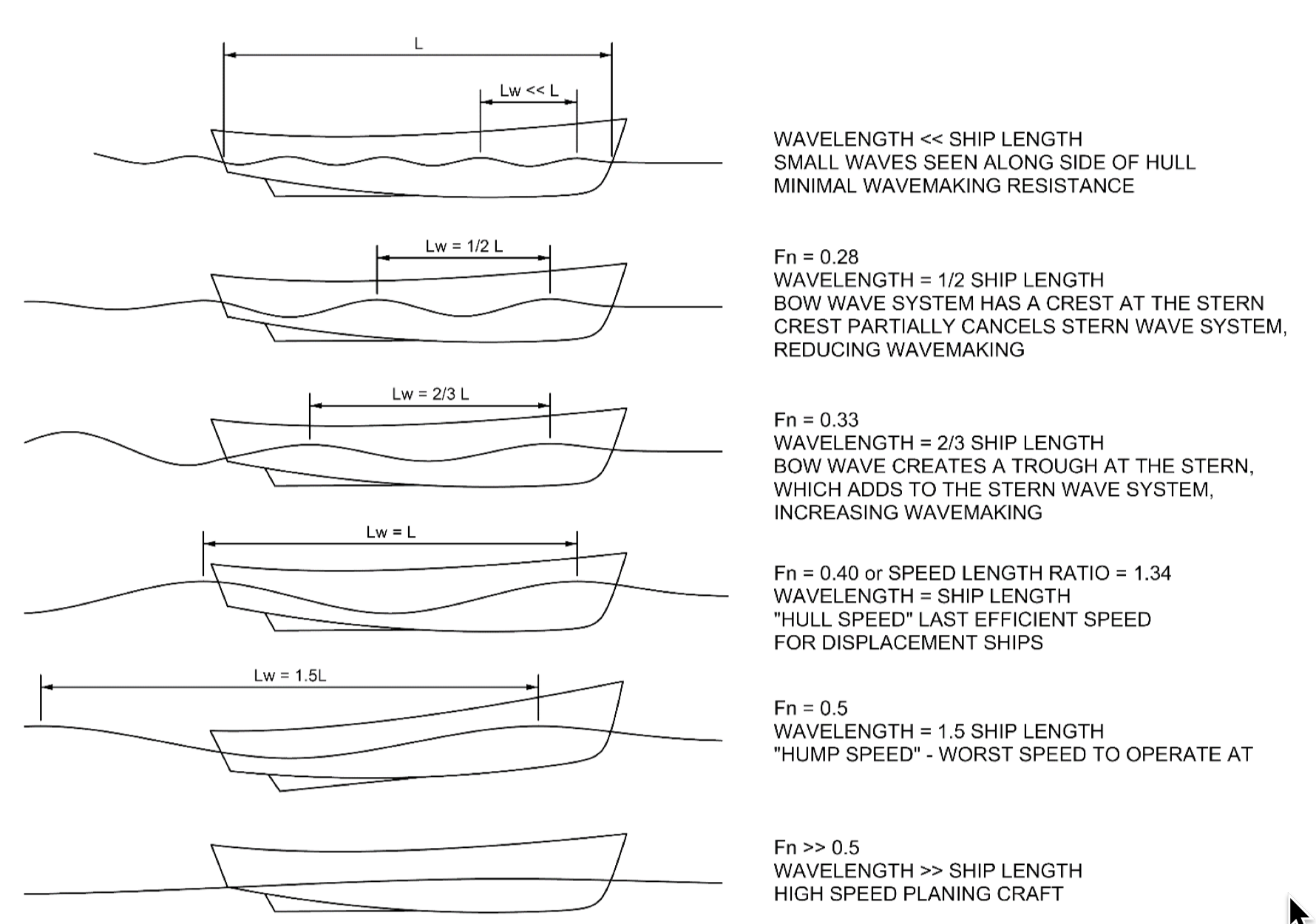
Froude Number
In continuum mechanics, the Froude number (, after William Froude, ) is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the flow inertia to the external field (the latter in many applications simply due to gravity). The Froude number is based on the speed–length ratio which he defined as: \mathrm = \frac where is the local flow velocity, is the local external field, and is a characteristic length. The Froude number has some analogy with the Mach number. In theoretical fluid dynamics the Froude number is not frequently considered since usually the equations are considered in the high Froude limit of negligible external field, leading to homogeneous equations that preserve the mathematical aspects. For example, homogeneous Euler equations are conservation equations. However, in naval architecture the Froude number is a significant figure used to determine the resistance of a partially submerged object moving through water. Origins In open channel flows, introduced first th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lee Waves
In meteorology, lee waves are atmospheric stationary waves. The most common form is mountain waves, which are atmospheric internal gravity waves. These were discovered in 1933 by two German glider pilots, Hans Deutschmann and Wolf Hirth, above the Krkonoše. They are periodic changes of atmospheric pressure, temperature and orthometric height in a current of air caused by vertical displacement, for example orographic lift when the wind blows over a mountain or mountain range. They can also be caused by the surface wind blowing over an escarpment or plateau, or even by upper winds deflected over a thermal updraft or cloud street. The vertical motion forces periodic changes in speed and direction of the air within this air current. They always occur in groups on the lee side of the terrain that triggers them. Sometimes, mountain waves can help to enhance precipitation amounts downwind of mountain ranges. Usually a turbulent vortex, with its axis of rotation parallel to the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columnar
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercellular matrix. Epithelial tissues line the outer surfaces of organs and blood vessels throughout the body, as well as the inner surfaces of cavities in many internal organs. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. There are three principal shapes of epithelial cell: squamous (scaly), columnar, and cuboidal. These can be arranged in a singular layer of cells as simple epithelium, either squamous, columnar, or cuboidal, or in layers of two or more cells deep as stratified (layered), or ''compound'', either squamous, columnar or cuboidal. In some tissues, a layer of columnar cells may appear to be stratified due to the placement of the nuclei. This sort of tissue is called pseudostratified. All glands are made up of epithelia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinusoidal
A sine wave, sinusoidal wave, or just sinusoid is a mathematical curve defined in terms of the '' sine'' trigonometric function, of which it is the graph. It is a type of continuous wave and also a smooth periodic function. It occurs often in mathematics, as well as in physics, engineering, signal processing and many other fields. Formulation Its most basic form as a function of time (''t'') is: y(t) = A\sin(2 \pi f t + \varphi) = A\sin(\omega t + \varphi) where: * ''A'', ''amplitude'', the peak deviation of the function from zero. * ''f'', ''ordinary frequency'', the ''number'' of oscillations (cycles) that occur each second of time. * ''ω'' = 2''f'', ''angular frequency'', the rate of change of the function argument in units of radians per second. * \varphi, ''phase'', specifies (in radians) where in its cycle the oscillation is at ''t'' = 0. When \varphi is non-zero, the entire waveform appears to be shifted in time by the amount ''φ''/''ω'' seconds. A negative value rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inviscid
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water. Viscosity quantifies the internal frictional force between adjacent layers of fluid that are in relative motion. For instance, when a viscous fluid is forced through a tube, it flows more quickly near the tube's axis than near its walls. Experiments show that some stress (such as a pressure difference between the two ends of the tube) is needed to sustain the flow. This is because a force is required to overcome the friction between the layers of the fluid which are in relative motion. For a tube with a constant rate of flow, the strength of the compensating force is proportional to the fluid's viscosity. In general, viscosity depends on a fluid's state, such as its temperature, pressure, and rate of deformation. However, the dependence on some of these properties is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravitational Potential Energy
Gravitational energy or gravitational potential energy is the potential energy a massive object has in relation to another massive object due to gravity. It is the potential energy associated with the gravitational field, which is released (converted into kinetic energy) when the objects fall towards each other. Gravitational potential energy increases when two objects are brought further apart. For two pairwise interacting point particles, the gravitational potential energy U is given by U = -\frac, where M and m are the masses of the two particles, R is the distance between them, and G is the gravitational constant. Close to the Earth's surface, the gravitational field is approximately constant, and the gravitational potential energy of an object reduces to U = mgh where m is the object's mass, g = / is the gravity of Earth, and h is the height of the object's center of mass above a chosen reference level. Newtonian mechanics In classical mechanics, two or more masse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Energy
In Outline of physical science, physical sciences, mechanical energy is the sum of potential energy and kinetic energy. The principle of conservation of mechanical energy states that if an isolated system is subject only to conservative forces, then the mechanical energy is constant. If an object moves in the opposite direction of a conservative net force, the potential energy will increase; and if the speed (not the velocity) of the object changes, the kinetic energy of the object also changes. In all real systems, however, nonconservative forces, such as frictional forces, will be present, but if they are of negligible Magnitude (mathematics), magnitude, the mechanical energy changes little and its conservation is a useful approximation. In elastic collisions, the kinetic energy is conserved, but in inelastic collisions some mechanical energy may be converted into thermal energy. The equivalence between lost mechanical energy and an increase in temperature was discovered by Jame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-channel Flow
In fluid mechanics and hydraulics, open-channel flow is a type of liquid flow within a conduit with a free surface, known as a channel. The other type of flow within a conduit is pipe flow. These two types of flow are similar in many ways but differ in one important respect: open-channel flow has a free surface, whereas pipe flow does not. Classifications of flow Open-channel flow can be classified and described in various ways based on the change in flow depth with respect to time and space. The fundamental types of flow dealt with in open-channel hydraulics are: * Time as the criterion ** ''Steady flow'' *** The depth of flow does not change over time, or if it can be assumed to be constant during the time interval under consideration. ** ''Unsteady flow'' *** The depth of flow does change with time. * Space as the criterion ** ''Uniform flow'' *** The depth of flow is the same at every section of the channel. Uniform flow can be steady or unsteady, depending on whether or not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratified Flow
The flow in many fluids varies with density and depends upon the gravity. Due to which the fluid with lower density is always above the fluid with higher density. Stratified flows are very common such as the Earth's ocean and its atmosphere. Stratified fluid A stratified fluid may be defined as the fluid with density variations in the vertical direction. For example, air and water; both are fluids and if we consider them together then they can be seen as a stratified fluid system. Density variations in the atmosphere profoundly affect the motion of water and air. Wave phenomena in air flow over the mountains and occurrence of smog are the examples of stratification effect in the atmosphere. When a fluid system having a condition in which fluid density decreases with height, is disturbed, then the gravity and friction restore the undisturbed conditions. If however the fluid tends to be stable if density decreases with height. Upstream motions in stratified flow It is known that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Dynamics
Meteorology is a branch of the atmospheric sciences (which include atmospheric chemistry and physics) with a major focus on weather forecasting. The study of meteorology dates back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not begin until the 18th century. The 19th century saw modest progress in the field after weather observation networks were formed across broad regions. Prior attempts at prediction of weather depended on historical data. It was not until after the elucidation of the laws of physics, and more particularly in the latter half of the 20th century the development of the computer (allowing for the automated solution of a great many modelling equations) that significant breakthroughs in weather forecasting were achieved. An important branch of weather forecasting is marine weather forecasting as it relates to maritime and coastal safety, in which weather effects also include atmospheric interactions with large bodies of water. Meteorological phenom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematically, density is defined as mass divided by volume: : \rho = \frac where ''ρ'' is the density, ''m'' is the mass, and ''V'' is the volume. In some cases (for instance, in the United States oil and gas industry), density is loosely defined as its weight per unit volume, although this is scientifically inaccurate – this quantity is more specifically called specific weight. For a pure substance the density has the same numerical value as its mass concentration. Different materials usually have different densities, and density may be relevant to buoyancy, purity and packaging. Osmium and iridium are the densest known elements at standard conditions for temperature and pressure. To simplify comparisons of density across different s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |