|
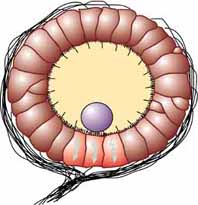
Statocysts
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, and crustaceans. A similar structure is also found in ''Xenoturbella''. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs (setae). The statolith's inertia causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity activates neurons, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained. In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance. It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians. Hearing In cephalopods like squids, statocy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statocyst
The statocyst is a balance sensory receptor present in some aquatic invertebrates, including bivalves, cnidarians, ctenophorans, echinoderms, cephalopods, and crustaceans. A similar structure is also found in ''Xenoturbella''. The statocyst consists of a sac-like structure containing a mineralised mass (statolith) and numerous innervated sensory hairs (setae). The statolith's inertia causes it to push against the setae when the animal accelerates. Deflection of setae by the statolith in response to gravity activates neurons, providing feedback to the animal on change in orientation and allowing balance to be maintained. In other words, the statolith shifts as the animal moves. Any movement large enough to throw the organism off balance causes the statolith to brush against tiny bristles which in turn send a message to the brain to correct its balance. It may have been present in the common ancestor of cnidarians and bilaterians. Hearing In cephalopods like squids, statocysts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squid
True squid are molluscs with an elongated soft body, large eyes, eight arms, and two tentacles in the superorder Decapodiformes, though many other molluscs within the broader Neocoleoidea are also called squid despite not strictly fitting these criteria. Like all other cephalopods, squid have a distinct head, bilateral symmetry, and a mantle. They are mainly soft-bodied, like octopuses, but have a small internal skeleton in the form of a rod-like gladius (cephalopod), gladius or pen, made of chitin. Squid diverged from other cephalopods during the Jurassic and occupy a similar role to teleost fish as open water predators of similar size and behaviour. They play an important role in the open water food web. The two long tentacles are used to grab prey and the eight arms to hold and control it. The beak then cuts the food into suitable size chunks for swallowing. Squid are rapid swimmers, moving by Aquatic locomotion#Jet propulsion, jet propulsion, and largely locate their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensory Organs Of Gastropods
The sensory organs of gastropods (snails and slugs) include olfactory organs, eyes, statocysts and mechanoreceptors. Gastropods have no sense of hearing.Chase R.: ''Sensory Organs and the Nervous System''. in Barker G. M. (ed.): ''The biology of terrestrial molluscs''. CABI Publishing, Oxon, UK, 2001, . 1–146, cited pages: 179–211. Olfactory organs In terrestrial gastropods the most important sensory organs are the olfactory organs which are located on the tips of the 4 tentacles. Some terrestrial gastropods can track the odor of food using their tentacles ( tropotaxis) and the wind ( anemotaxis). In opisthobranch marine gastropods, the chemosensory organs are two protruding structures on top of the head. These are known as rhinophores. An opisthobranch sea slug ''Navanax inermis'' has chemoreceptors on the sides of its mouth to track mucopolysaccharides in the slime trails of prey, and of potential mates. The freshwater snail '' Bithynia tentaculata'' is capabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otolith
An otolith ( grc-gre, ὠτο-, ' ear + , ', a stone), also called statoconium or otoconium or statolith, is a calcium carbonate structure in the saccule or utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular system of vertebrates. The saccule and utricle, in turn, together make the ''otolith organs''. These organs are what allows an organism, including humans, to perceive linear acceleration, both horizontally and vertically (gravity). They have been identified in both extinct and extant vertebrates. Counting the annual growth rings on the otoliths is a common technique in estimating the age of fish. Description Endolymphatic infillings such as otoliths are structures in the saccule and utricle of the inner ear, specifically in the vestibular labyrinth of all vertebrates (fish, amphibians, reptiles, mammals and birds). In vertebrates, the saccule and utricle together make the ''otolith organs''. Both statoconia and otoliths are used as gravity, balance, movement, and d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accelerometer
An accelerometer is a tool that measures proper acceleration. Proper acceleration is the acceleration (the rate of change of velocity) of a body in its own instantaneous rest frame; this is different from coordinate acceleration, which is acceleration in a fixed coordinate system. For example, an accelerometer at rest on the surface of the Earth will measure an acceleration due to Earth's gravity, straight upwards (by definition) of g ≈ 9.81 m/s2. By contrast, accelerometers in free fall (falling toward the center of the Earth at a rate of about 9.81 m/s2) will measure zero. Accelerometers have many uses in industry and science. Highly sensitive accelerometers are used in inertial navigation systems for aircraft and missiles. Vibration in rotating machines is monitored by accelerometers. They are used in tablet computers and digital cameras so that images on screens are always displayed upright. In unmanned aerial vehicles, accelerometers help to stabilise flight. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cnidarian Anatomy
Cnidaria () is a phylum under kingdom Animalia containing over 11,000 species of aquatic animals found both in freshwater and marine environments, predominantly the latter. Their distinguishing feature is cnidocytes, specialized cells that they use mainly for capturing prey. Their bodies consist of mesoglea, a non-living jelly-like substance, sandwiched between two layers of epithelium that are mostly one cell thick. Cnidarians mostly have two basic body forms: swimming medusae and sessile polyps, both of which are radially symmetrical with mouths surrounded by tentacles that bear cnidocytes. Both forms have a single orifice and body cavity that are used for digestion and respiration. Many cnidarian species produce colonies that are single organisms composed of medusa-like or polyp-like zooids, or both (hence they are trimorphic). Cnidarians' activities are coordinated by a decentralized nerve net and simple receptors. Several free-swimming species of Cubozoa and Scyphozoa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestibular System
The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of the inner ear in most mammals. As movements consist of rotations and translations, the vestibular system comprises two components: the semicircular canals, which indicate rotational movements; and the otoliths, which indicate linear accelerations. The vestibular system sends signals primarily to the neural structures that control eye movement; these provide the anatomical basis of the vestibulo-ocular reflex, which is required for clear vision. Signals are also sent to the muscles that keep an animal upright and in general control posture; these provide the anatomical means required to enable an animal to maintain its desired position in space. The brain uses information from the vestibular system in the head and fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statocyte
Statocytes are gravity-sensing (gravitropic) cells in higher plants. They contain amyloplasts-statoliths – starch-filled amyloplastic organelles – which sediment at the lowest part of the cells. Statocytes are present in the elongating region of coleoptiles, shoots and inflorescence stems. In roots, the root cap is the only place where sedimentation is observed, and only the central columella cells of the root cap serve as gravity-sensing statocytes. They can initiate differential growth patterns, bending the root towards the vertical axis. References See also * Prolonged sine The law of the prolonged sine was observed when measuring strength of the reaction of the plant stems and roots in response to turning from their usual vertical orientation. Such organisms maintained their usual vertical growth, and, if turned, s ... Plant cells {{botany-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
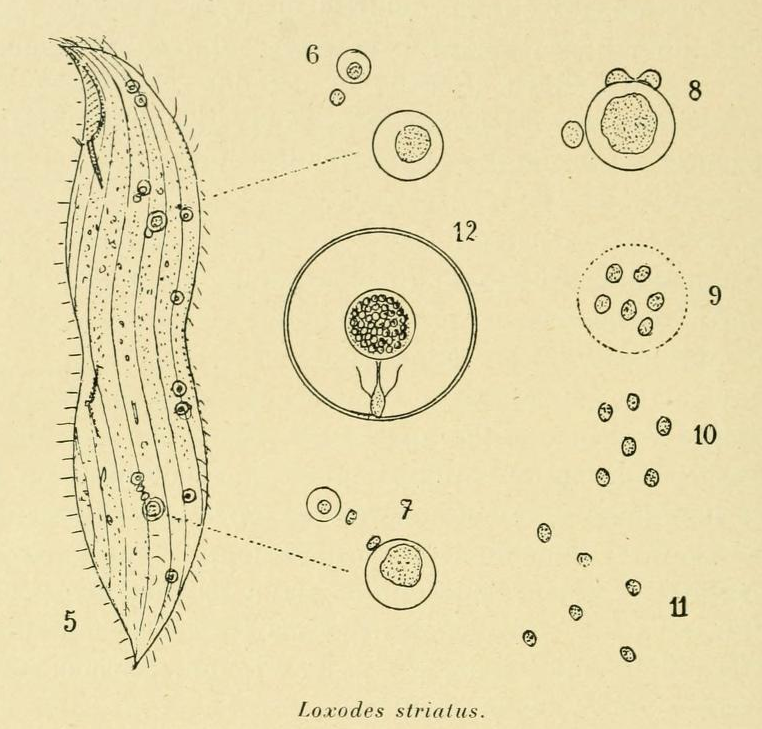
Loxodidae
Loxodidae is a family of karyorelict ciliates. Loxodidae members possess an elongated, laterally flattened shape. They share two key characters: a beak-like anterior rostrum interrupting the perioral kineties, and peculiar cytoplasmic organelles named Müller vesicles. The extensive development of lacunae of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum leads to strong vacuolization of the endoplasm. This feature is associated to a lack of contractile vacuoles in all loxodids. The term ''Loxodidae'' derives from the ancient Greek (), meaning "oblique, tilted". Gravitaxis Loxodidae members possess the ability to orient themselves in oxygen gradients. They use gravity as a stimulus for this spatial orientation, a phenomenon called gravitaxis or geotaxis. Loxodid ciliates must therefore have developed mechanoreceptors informing them about what is up or down. A likely candidate structure for their gravitaxis is the Müller vesicle. Müller vesicle Müller vesicles (also known as Müller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Müllerian Vesicle
Loxodidae is a family of karyorelict ciliates. Loxodidae members possess an elongated, laterally flattened shape. They share two key characters: a beak-like anterior rostrum interrupting the perioral kineties, and peculiar cytoplasmic organelles named Müller vesicles. The extensive development of lacunae of the smooth endoplasmic reticulum leads to strong vacuolization of the endoplasm. This feature is associated to a lack of contractile vacuoles in all loxodids. The term ''Loxodidae'' derives from the ancient Greek (), meaning "oblique, tilted". Gravitaxis Loxodidae members possess the ability to orient themselves in oxygen gradients. They use gravity as a stimulus for this spatial orientation, a phenomenon called gravitaxis or geotaxis. Loxodid ciliates must therefore have developed mechanoreceptors informing them about what is up or down. A likely candidate structure for their gravitaxis is the Müller vesicle. Müller vesicle Müller vesicles (also known as Müller ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertial Guidance
An inertial navigation system (INS) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors ( gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning the position, the orientation, and the velocity (direction and speed of movement) of a moving object without the need for external references. Often the inertial sensors are supplemented by a barometric altimeter and sometimes by magnetic sensors ( magnetometers) and/or speed measuring devices. INSs are used on mobile robots and on vehicles such as ships, aircraft, submarines, guided missiles, and spacecraft. Other terms used to refer to inertial navigation systems or closely related devices include inertial guidance system, inertial instrument, inertial measurement unit (IMU) and many other variations. Older INS systems generally used an inertial platform as their mounting point to the vehicle and the terms are sometimes considered synonymous. Overview Inertial navigation is a self-cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Longfin Inshore Squid
The longfin inshore squid (''Doryteuthis pealeii'') is a species of squid of the family Loliginidae. Description This species of squid is often seen with a reddish hue, but like many types of squid can manipulate its color, varying from a deep red to a soft pink. The dorsal mantle length of some males can reach up to 50 cm, although most squid commercially harvested are smaller than 30 cm long. This species exhibits sexual dimorphism, with most males growing faster and reaching larger sizes than females. Distribution The longfin inshore squid is found in the North Atlantic, schooling in continental shelf and slope waters from Newfoundland to the Gulf of Venezuela. It is commercially exploited, especially in the range from the Southern Georges Bank to Cape Hatteras. The population makes seasonal migrations that appear to be related to bottom water temperatures; they move offshore during late autumn to overwinter along the edge of the continental shelf and return ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)