|
Square Trisection
In geometry, a square trisection is a type of dissection problem which consists of cutting a square into pieces that can be rearranged to form three identical squares. History The dissection of a square in three congruent partitions is a geometrical problem that dates back to the Islamic Golden Age. Craftsman who mastered the art of zellige needed innovative techniques to achieve their fabulous mosaics with complex geometric figures. The first solution to this problem was proposed in the 10th century AD by the Persian mathematician Abu'l-Wafa' (940-998) in his treatise ''"On the geometric constructions necessary for the artisan"''. Abu'l-Wafa' also used his dissection to demonstrate the Pythagorean theorem. This geometrical proof of Pythagoras' theorem would be rediscovered in the years 1835 - 1840 by Henry Perigal and published in 1875. Search of optimality The beauty of a dissection depends on several parameters. However, it is usual to search for solutions with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
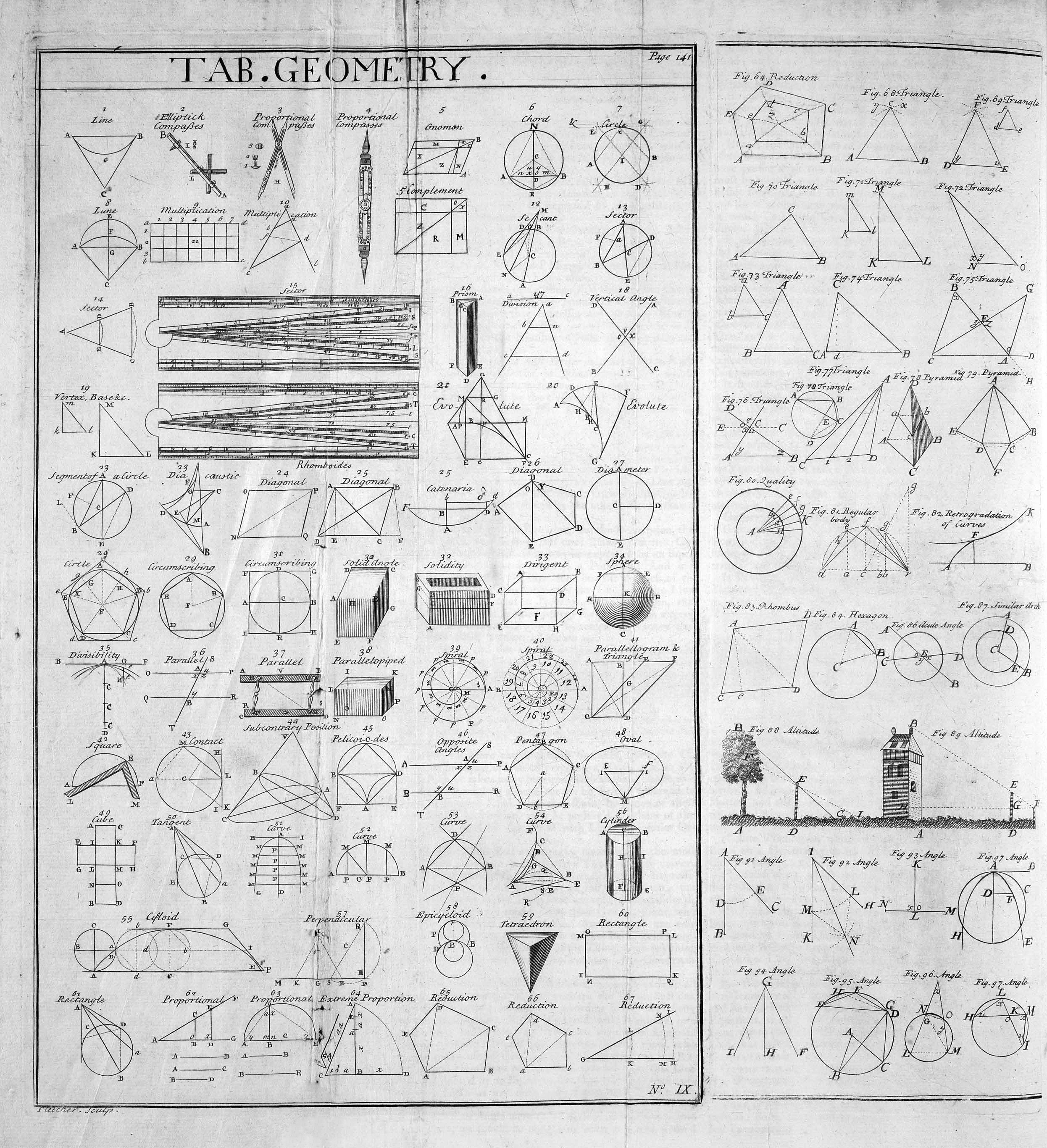
Geometry
Geometry (; ) is, with arithmetic, one of the oldest branches of mathematics. It is concerned with properties of space such as the distance, shape, size, and relative position of figures. A mathematician who works in the field of geometry is called a ''geometer''. Until the 19th century, geometry was almost exclusively devoted to Euclidean geometry, which includes the notions of point, line, plane, distance, angle, surface, and curve, as fundamental concepts. During the 19th century several discoveries enlarged dramatically the scope of geometry. One of the oldest such discoveries is Carl Friedrich Gauss' ("remarkable theorem") that asserts roughly that the Gaussian curvature of a surface is independent from any specific embedding in a Euclidean space. This implies that surfaces can be studied ''intrinsically'', that is, as stand-alone spaces, and has been expanded into the theory of manifolds and Riemannian geometry. Later in the 19th century, it appeared that geome ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Édouard Lucas
__NOTOC__ François Édouard Anatole Lucas (; 4 April 1842 – 3 October 1891) was a French mathematician. Lucas is known for his study of the Fibonacci sequence. The related Lucas sequences and Lucas numbers are named after him. Biography Lucas was born in Amiens and educated at the École Normale Supérieure. He worked in the Paris Observatory and later became a professor of mathematics at the Lycée Saint Louis and the Lycée Charlemagne in Paris. Lucas served as an artillery officer in the French Army during the Franco-Prussian War of 1870–1871. In 1875, Lucas posed a challenge to prove that the only solution of the Diophantine equation: :\sum_^ n^2 = M^2\; with ''N'' > 1 is when ''N'' = 24 and ''M'' = 70. This is known as the cannonball problem, since it can be visualized as the problem of taking a square arrangement of cannonballs on the ground and building a square pyramid out of them. It was not until 1918 that a proof (using elliptic functions) was found for this ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Geometry
Geometry (from the grc, γεωμετρία; '' geo-'' "earth", '' -metron'' "measurement") arose as the field of knowledge dealing with spatial relationships. Geometry was one of the two fields of pre-modern mathematics, the other being the study of numbers (arithmetic). Classic geometry was focused in compass and straightedge constructions. Geometry was revolutionized by Euclid, who introduced mathematical rigor and the axiomatic method still in use today. His book, '' The Elements'' is widely considered the most influential textbook of all time, and was known to all educated people in the West until the middle of the 20th century. In modern times, geometric concepts have been generalized to a high level of abstraction and complexity, and have been subjected to the methods of calculus and abstract algebra, so that many modern branches of the field are barely recognizable as the descendants of early geometry. (See Areas of mathematics and Algebraic geometry.) Early geometry T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematical Problems
A mathematical problem is a problem that can be represented, analyzed, and possibly solved, with the methods of mathematics. This can be a real-world problem, such as computing the orbits of the planets in the solar system, or a problem of a more abstract nature, such as Hilbert's problems. It can also be a problem referring to the nature of mathematics itself, such as Russell's Paradox. Real-world problems Informal "real-world" mathematical problems are questions related to a concrete setting, such as "Adam has five apples and gives John three. How many has he left?". Such questions are usually more difficult to solve than regular mathematical exercises like "5 − 3", even if one knows the mathematics required to solve the problem. Known as word problems, they are used in mathematics education to teach students to connect real-world situations to the abstract language of mathematics. In general, to use mathematics for solving a real-world problem, the first s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclidean Plane Geometry
Euclidean geometry is a mathematical system attributed to ancient Greek mathematician Euclid, which he described in his textbook on geometry: the '' Elements''. Euclid's approach consists in assuming a small set of intuitively appealing axioms (postulates) and deducing many other propositions (theorems) from these. Although many of Euclid's results had been stated earlier,. Euclid was the first to organize these propositions into a logical system in which each result is '' proved'' from axioms and previously proved theorems. The ''Elements'' begins with plane geometry, still taught in secondary school (high school) as the first axiomatic system and the first examples of mathematical proofs. It goes on to the solid geometry of three dimensions. Much of the ''Elements'' states results of what are now called algebra and number theory, explained in geometrical language. For more than two thousand years, the adjective "Euclidean" was unnecessary because no other sort of geomet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
:en:A K Peters
A K Peters, Ltd. was a publisher of scientific and technical books, specializing in mathematics and in computer graphics, robotics, and other fields of computer science. They published the journals ''Experimental Mathematics (journal), Experimental Mathematics'' and the ''Journal of Graphics Tools'', as well as mathematics books geared to children. Background Klaus Peters wrote a doctoral dissertation on complex manifolds at the University of Erlangen in 1962, supervised by Reinhold Remmert. He then joined Springer Verlag, becoming their first specialist mathematics editor. As a Springer director from 1971, he hired Alice Merker for Springer New York: they were married that year, and moved to Heidelberg. Leaving Springer, they founded Birkhäuser Boston in 1979; Birkhäuser ran into financial difficulties, and was taken over by Springer. Klaus and Alice then spent a period running a Boston office for Harcourt Brace Jovanovich and their imprint Academic Press. With the takeover of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |