|
Spawn (computing)
Spawn in computing refers to a function that loads and executes a new child process. The current process may wait for the child to terminate or may continue to execute concurrent computing. Creating a new subprocess requires enough memory in which both the child process and the current program can execute. There is a family of spawn functions in DOS, inherited by Microsoft Windows. There is also a different family of spawn functions in an optional extension of the POSIX standards . DOS/Windows spawn functions The DOS/Windows spawn functions are inspired by Unix functions fork and exec; however, as these operating systems do not support fork,Windows Subsystem for Linux implements fork. Other POSIX environments such as Cygwin may have an implementation, but using it is not recommended due to the differences in the process model between POSIX and Windows. Fork is not part of the Windows API and most Windows programs do not use these environments, so do not have access to fork. t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computer, computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and the development of both computer hardware, hardware and software. Computing has scientific, engineering, mathematical, technological, and social aspects. Major computing disciplines include computer engineering, computer science, cybersecurity, data science, information systems, information technology, and software engineering. The term ''computing'' is also synonymous with counting and calculation, calculating. In earlier times, it was used in reference to the action performed by Mechanical computer, mechanical computing machines, and before that, to Computer (occupation), human computers. History The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper (or for chalk and slate) with or without the aid of tables. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Path (variable)
PATH is an environment variable on Unix-like operating systems, DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows, specifying a set of directories where executable programs are located. In general, each executing process or user session has its own PATH setting. History Multics originated the idea of a search path. The early Unix shell only looked for program names in /bin, but by Version 3 Unix the directory was too large and /usr/bin, and a search path, became part of the operating system. Unix and Unix-like On POSIX and Unix-like operating systems, the $PATH variable is specified as a list of one or more directory names separated by colon (:) characters. Directories in the PATH-string are not meant to be escaped, making it impossible to have directories with : in their name. The /bin, /usr/bin, and /usr/local/bin directories are typically included in most users' $PATH setting (although this varies from implementation to implementation). The superuser also typically has /sbin and /usr/sbin en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Process (computing)
In computing, a process is the Instance (computer science), instance of a computer program that is being executed by one or many thread (computing), threads. There are many different process models, some of which are light weight, but almost all processes (even entire virtual machines) are rooted in an operating system (OS) process which comprises the program code, assigned system resources, physical and logical access permissions, and data structures to initiate, control and coordinate execution activity. Depending on the OS, a process may be made up of multiple threads of execution that execute instructions Concurrency (computer science), concurrently. While a computer program is a passive collection of Instruction set, instructions typically stored in a file on disk, a process is the execution of those instructions after being loaded from the disk into memory. Several processes may be associated with the same program; for example, opening up several instances of the same progra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Process
A process is a series or set of activities that interact to produce a result; it may occur once-only or be recurrent or periodic. Things called a process include: Business and management * Business process, activities that produce a specific service or product for customers * Business process modeling, activity of representing processes of an enterprise in order to deliver improvements * Manufacturing process management, a collection of technologies and methods used to define how products are to be manufactured. * Process architecture, structural design of processes, applies to fields such as computers, business processes, logistics, project management * Process area, related processes within an area which together satisfies an important goal for improvements within that area * Process costing, a cost allocation procedure of managerial accounting * Process management (project management), a systematic series of activities directed towards planning, monitoring the performance a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
PATH (variable)
PATH is an environment variable on Unix-like operating systems, DOS, OS/2, and Microsoft Windows, specifying a set of directories where executable programs are located. In general, each executing process or user session has its own PATH setting. History Multics originated the idea of a search path. The early Unix shell only looked for program names in /bin, but by Version 3 Unix the directory was too large and /usr/bin, and a search path, became part of the operating system. Unix and Unix-like On POSIX and Unix-like operating systems, the $PATH variable is specified as a list of one or more directory names separated by colon (:) characters. Directories in the PATH-string are not meant to be escaped, making it impossible to have directories with : in their name. The /bin, /usr/bin, and /usr/local/bin directories are typically included in most users' $PATH setting (although this varies from implementation to implementation). The superuser also typically has /sbin and /usr/sbin en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Windows NT
Windows NT is a Proprietary software, proprietary Graphical user interface, graphical operating system produced by Microsoft as part of its Windows product line, the first version of which, Windows NT 3.1, was released on July 27, 1993. Originally made for the workstation, office, and Server (computing), server markets, the Windows NT line was made available to consumers with the release of Windows XP in 2001. The underlying technology of Windows NT continues to exist to this day with incremental changes and improvements, with the latest version of Windows based on Windows NT being Windows Server 2025 announced in 2024. The name "Windows NT" originally denoted the major technological advancements that it had introduced to the Windows product line, including eliminating the 16-bit computing, 16-bit memory access limitations of earlier Windows releases such as Windows 3.1 and the Windows 9x series. Each Windows release built on this technology is considered to be based on, if not a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
OpenVMS
OpenVMS, often referred to as just VMS, is a multi-user, multiprocessing and virtual memory-based operating system. It is designed to support time-sharing, batch processing, transaction processing and workstation applications. Customers using OpenVMS include banks and financial services, hospitals and healthcare, telecommunications operators, network information services, and industrial manufacturers. During the 1990s and 2000s, there were approximately half a million VMS systems in operation worldwide. It was first announced by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) as VAX/VMS (''Virtual Address eXtension/Virtual Memory System'') alongside the VAX-11/780 minicomputer in 1977. OpenVMS has subsequently been ported to run on DEC Alpha systems, the Itanium-based HPE Integrity Servers, and select x86-64 hardware and hypervisors. Since 2014, OpenVMS is developed and supported by VMS Software Inc. (VSI). OpenVMS offers high availability through computer cluster, clustering—the ability t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X, *nix or *NIX) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-like Application software, application is one that behaves like the corresponding List of POSIX commands, Unix command or Unix shell, shell. Although there are general Unix philosophy, philosophies for Unix design, there is no technical standard defining the term, and opinions can differ about the degree to which a particular operating system or application is Unix-like. Some well-known examples of Unix-like operating systems include Linux, FreeBSD and OpenBSD. These systems are often used on servers as well as on personal computers and other devices. Many popular applications, such as the Apache HTTP Server, Apache web server and the Bash (Unix shell), Bash shell, are also designed to be used on Unix-like systems. Definition The Open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Virtual Memory
In computing, virtual memory, or virtual storage, is a memory management technique that provides an "idealized abstraction of the storage resources that are actually available on a given machine" which "creates the illusion to users of a very large (main) memory". The computer's operating system, using a combination of hardware and software, maps memory addresses used by a program, called '' virtual addresses'', into ''physical addresses'' in computer memory. Main storage, as seen by a process or task, appears as a contiguous address space or collection of contiguous segments. The operating system manages virtual address spaces and the assignment of real memory to virtual memory. Address translation hardware in the CPU, often referred to as a memory management unit (MMU), automatically translates virtual addresses to physical addresses. Software within the operating system may extend these capabilities, utilizing, e.g., disk storage, to provide a virtual address space ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
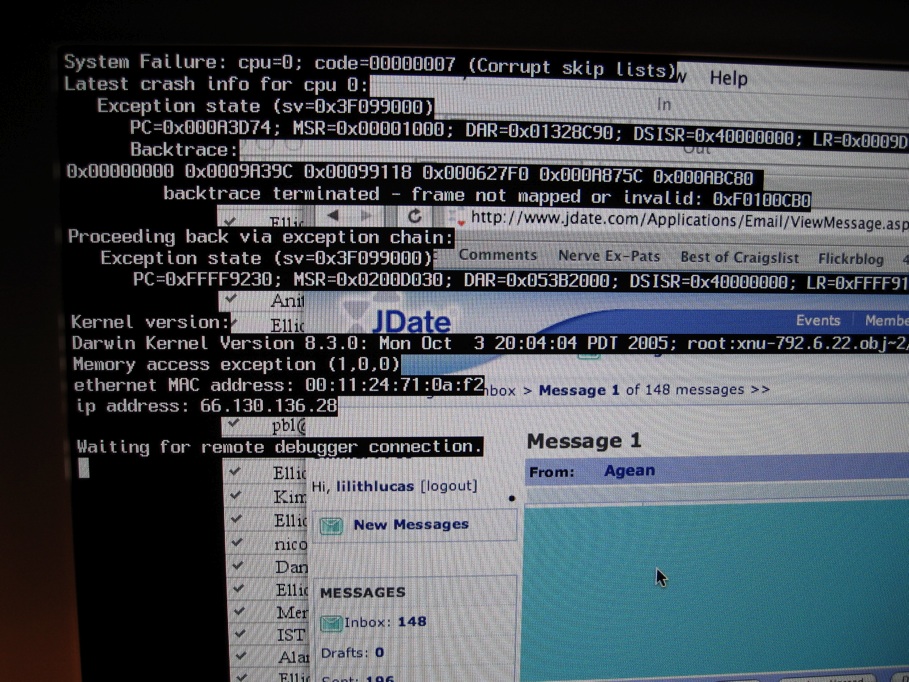
Abnormal End
In computing, a crash, or system crash, occurs when a computer program such as a software application or an operating system stops functioning properly and exits. On some operating systems or individual applications, a crash reporting service will report the crash and any details relating to it (or give the user the option to do so), usually to the developer(s) of the application. If the program is a critical part of the operating system, the entire system may crash or hang, often resulting in a kernel panic or fatal system error. Most crashes are the result of a software bug. Typical causes include accessing invalid memory addresses, incorrect address values in the program counter, buffer overflow, overwriting a portion of the affected program code due to an earlier bug, executing invalid machine instructions (an illegal or unauthorized opcode), or triggering an unhandled exception. The original software bug that started this chain of events is typically considered t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |