|
Solar Conversion Efficiency
Solar-cell efficiency refers to the portion of energy in the form of sunlight that can be converted via photovoltaics into electricity by the solar cell. The efficiency of the solar cells used in a photovoltaic system, in combination with latitude and climate, determines the annual energy output of the system. For example, a solar panel with 20% efficiency and an area of 1 m2 will produce 200 kWh/yr at Standard Test Conditions if exposed to the Standard Test Condition solar irradiance value of 1000 W/m2 for 2.74 hours a day. Usually solar panels are exposed to sunlight for longer than this in a given day, but the solar irradiance is less than 1000 W/m2 for most of the day. A solar panel can produce more when the sun is high in the sky and will produce less in cloudy conditions or when the sun is low in the sky, usually the sun is lower in the sky in the winter. Two location dependant factors that affect solar PV efficiency are the dispersion and intensity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NREL PV Cell Record Efficiency Chart
The National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the US specializes in the research and development of renewable energy, energy efficiency, energy systems integration, and sustainable transportation. NREL is a federally funded research and development center sponsored by the Department of Energy and operated by the Alliance for Sustainable Energy, a joint venture between MRIGlobal and Battelle. Located in Golden, Colorado, NREL is home to the National Center for Photovoltaics, the National Bioenergy Center, and the National Wind Technology Center. History The Solar Energy Research, Development and Demonstration Act of 1974 established the Solar Energy Research Institute, which opened in 1977 and was operated by MRIGlobal. Under the Jimmy Carter administration, its activities went beyond research and development in solar energy as it tried to popularize knowledge about already existing technologies, like passive solar. During the Ronald Reagan administration the institute ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Shockley
William Bradford Shockley Jr. (February 13, 1910 – August 12, 1989) was an American physicist and inventor. He was the manager of a research group at Bell Labs that included John Bardeen and Walter Brattain. The three scientists were jointly awarded the 1956 Nobel Prize in Physics for "their researches on semiconductors and their discovery of the transistor effect". Partly as a result of Shockley's attempts to commercialize a new transistor design in the 1950s and 1960s, California's Silicon Valley became a hotbed of electronics innovation. In his later life, while a professor of electrical engineering at Stanford University and afterward, Shockley became widely known for his racist views and advocacy of eugenics. Early life and education Shockley was born to American parents in London on February 13, 1910, and was raised in his family's hometown of Palo Alto, California, from the age of three. His father, William Hillman Shockley, was a mining engineer who speculated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Current (electricity)
An electric current is a stream of charged particles, such as electrons or ions, moving through an electrical conductor or space. It is measured as the net rate of flow of electric charge through a surface or into a control volume. The moving particles are called charge carriers, which may be one of several types of particles, depending on the conductor. In electric circuits the charge carriers are often electrons moving through a wire. In semiconductors they can be electrons or holes. In an electrolyte the charge carriers are ions, while in plasma, an ionized gas, they are ions and electrons. The SI unit of electric current is the ampere, or ''amp'', which is the flow of electric charge across a surface at the rate of one coulomb per second. The ampere (symbol: A) is an SI base unit. Electric current is measured using a device called an ammeter. Electric currents create magnetic fields, which are used in motors, generators, inductors, and transformers. In ordinary conduct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to move a test charge between the two points. In the International System of Units, the derived unit for voltage is named ''volt''. The voltage between points can be caused by the build-up of electric charge (e.g., a capacitor), and from an electromotive force (e.g., electromagnetic induction in generator, inductors, and transformers). On a macroscopic scale, a potential difference can be caused by electrochemical processes (e.g., cells and batteries), the pressure-induced piezoelectric effect, and the thermoelectric effect. A voltmeter can be used to measure the voltage between two points in a system. Often a common reference potential such as the ground of the system is used as one of the points. A voltage can represent either a source ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dust On The A Solar Panel
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in homes is composed of about 20–50% dead skin cells. The rest, and in offices, and other human environments is composed of small amounts of plant pollen, human hairs, animal fur, textile fibers, paper fibers, minerals from outdoor soil, burnt meteorite particles, and many other materials which may be found in the local environment. Atmospheric Atmospheric or wind-borne fugitive dust, also known as ''aeolian dust'', comes from arid and dry regions where high velocity winds are able to remove mostly silt-sized material, deflating susceptible surfaces. This includes areas where grazing, ploughing, vehicle use, and other human behaviors have further destabilized the land, though not all source areas have been largely affected by anthropo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
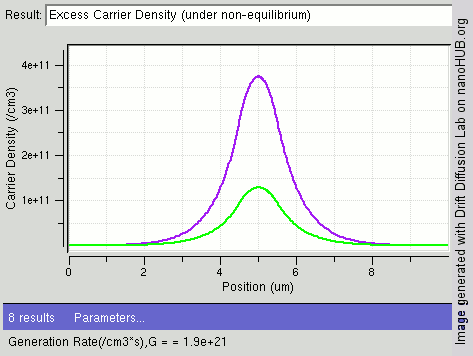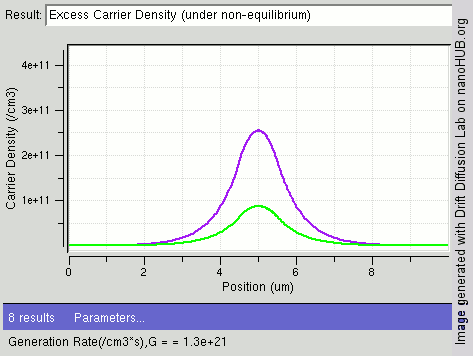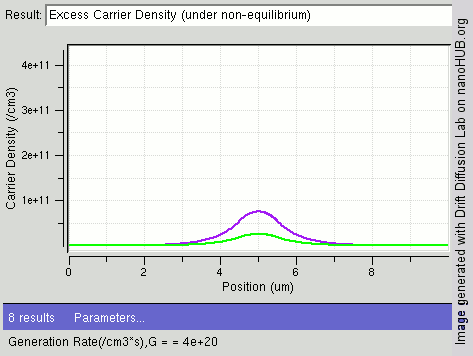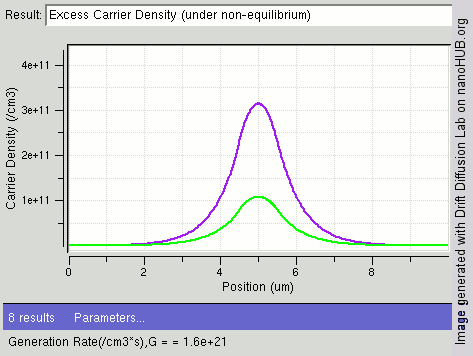
Carrier Generation And Recombination
In the solid-state physics of semiconductors, carrier generation and carrier recombination are processes by which mobile charge carriers (electrons and electron holes) are created and eliminated. Carrier generation and recombination processes are fundamental to the operation of many optoelectronic semiconductor devices, such as photodiodes, light-emitting diodes and laser diodes. They are also critical to a full analysis of p-n junction devices such as bipolar junction transistors and p-n junction diodes. The electron–hole pair is the fundamental unit of generation and recombination in inorganic semiconductors, corresponding to an electron transitioning between the valence band and the conduction band where generation of electron is a transition from the valence band to the conduction band and recombination leads to a reverse transition. Overview Like other solids, semiconductor materials have an electronic band structure determined by the crystal properties of the material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Band Gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference (in electron volts) between the top of the valence band and the bottom of the conduction band in insulators and semiconductors. It is the energy required to promote a valence electron bound to an atom to become a conduction electron, which is free to move within the crystal lattice and serve as a charge carrier to conduct electric current. It is closely related to the HOMO/LUMO gap in chemistry. If the valence band is completely full and the conduction band is completely empty, then electrons cannot move within the solid because there are no available states. If the electrons are not free to move within the crystal lattice, then there is no generated current due to no net charge carrier mobility. However, if some electrons transfer from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, Elasticity (physics), elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter physics, condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phonon is an excited state in the quantum mechanical Quantization (physics), quantization of the mode of vibration, modes of vibrations for elastic structures of interacting particles. Phonons can be thought of as quantized sound waves, similar to photons as quantized light waves. The study of phonons is an important part of condensed matter physics. They play a major role in many of the physical properties of condensed matter systems, such as thermal conductivity and electrical conductivity, as well as in models of neutron scattering and related effects. The concept of phonons was introduced in 1932 by Soviet Union, Soviet physicist Igor Tamm. The name ''phonon'' comes from the Ancient Greek language, Greek word (), which translates to ''so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
P–n Junction
A p–n junction is a boundary or interface between two types of semiconductor materials, p-type and n-type, inside a single crystal of semiconductor. The "p" (positive) side contains an excess of holes, while the "n" (negative) side contains an excess of electrons in the outer shells of the electrically neutral atoms there. This allows electrical current to pass through the junction only in one direction. The p-n junction is created by doping, for example by ion implantation, diffusion of dopants, or by epitaxy (growing a layer of crystal doped with one type of dopant on top of a layer of crystal doped with another type of dopant). If two separate pieces of material were used, this would introduce a grain boundary between the semiconductors that would severely inhibit its utility by scattering the electrons and holes. p–n junctions are elementary "building blocks" of semiconductor electronic devices such as diodes, transistors, solar cells, light-emitting diodes (LEDs) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blackbody Radiation
Black-body radiation is the thermal electromagnetic radiation within, or surrounding, a body in thermodynamic equilibrium with its environment, emitted by a black body (an idealized opaque, non-reflective body). It has a specific, continuous spectrum of wavelengths, inversely related to intensity, that depend only on the body's temperature, which is assumed, for the sake of calculations and theory, to be uniform and constant., Chapter 13. A perfectly insulated enclosure which is in thermal equilibrium internally contains black-body radiation, and will emit it through a hole made in its wall, provided the hole is small enough to have a negligible effect upon the equilibrium. The thermal radiation spontaneously emitted by many ordinary objects can be approximated as black-body radiation. Of particular importance, although planets and stars (including the Earth and Sun) are neither in thermal equilibrium with their surroundings nor perfect black bodies, black-body radiation is sti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carnot Heat Engine
A Carnot heat engine is a heat engine that operates on the Carnot cycle. The basic model for this engine was developed by Nicolas Léonard Sadi Carnot in 1824. The Carnot engine model was graphically expanded by Benoît Paul Émile Clapeyron in 1834 and mathematically explored by Rudolf Clausius in 1857, work that led to the fundamental thermodynamic concept of entropy. The Carnot engine is the most efficient heat engine which is theoretically possible. The efficiency depends only upon the absolute temperatures of the hot and cold heat reservoirs between which it operates. A heat engine acts by transferring energy from a warm region to a cool region of space and, in the process, converting some of that energy to mechanical work. The cycle may also be reversed. The system may be worked upon by an external force, and in the process, it can transfer thermal energy from a cooler system to a warmer one, thereby acting as a refrigerator or heat pump rather than a heat engine. Every th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |