|
Shreekhand
Shrikhand is a traditional sweets of the Indian subcontinent, sweet of the Indian subcontinent made from strained yogurt. It is often served as part of a ''thali'' (platter) or with ''puris'' (puffed deep-fried whole wheat bread). It is a traditional dessert in Gujarati cuisine, Gujarati and Marathi cuisine, Marathi cuisine. History Both Gujaratis and Maharashtrians claim the invention of shrikhand. According to a popular legend, shrikhand was invented by traveling herders. To carry their yogurt more easily while traveling overnight, they strained out its whey. Since the strained yogurt became sour by morning, they mixed it with sugar and nuts to make it more palatable, and shrikhand was born. According to food historian K. T. Achaya, shrikhand was first made around 500 BC. His book ''Indian Food: A Historical Companion'' states, "To dewater curd, it was hung in a muslin bag for a few hours; sugar and spices added to the mass yielded shikharini (identical with modern day shrikhand ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marathi Cuisine
Maharashtrian or Marathi cuisine is the cuisine of the Marathi people from the Indian state of Maharashtra. It has distinctive attributes, while sharing much with other Indian cuisines. Traditionally, Maharashtrians have considered their food to be more austere than others. Maharashtrian cuisine includes mild and spicy dishes. Wheat, rice, ''jowar'', ''bajri'', vegetables, lentils and fruit are dietary staples. Peanuts and cashews are often served with vegetables. Meat was traditionally used sparsely or only by the well off until recently, because of economic conditions and culture. The urban population in metropolitan cities of the state has been influenced by cuisine from other parts of India and abroad. For example, the South Indian dishes ''idli'' and ''dosa,'' as well as Chinese and Western dishes such as pizza, are quite popular in home cooking, and in restaurants. Distinctly Maharashtrian dishes include ''ukdiche modak'', , Kande pohe and Thalipeeth. Regular meals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maharashtrian Cuisine
Maharashtrian or Marathi cuisine is the cuisine of the Marathi people from the Indian state of Maharashtra. It has distinctive attributes, while sharing much with other Indian cuisines. Traditionally, Maharashtrians have considered their food to be more austere than others. Maharashtrian cuisine includes mild and spicy dishes. Wheat, rice, ''jowar'', ''bajri'', vegetables, lentils and fruit are dietary staples. Peanuts and cashews are often served with vegetables. Meat was traditionally used sparsely or only by the well off until recently, because of economic conditions and culture. The urban population in metropolitan cities of the state has been influenced by cuisine from other parts of India and abroad. For example, the South Indian dishes ''idli'' and ''dosa,'' as well as Chinese and Western dishes such as pizza, are quite popular in home cooking, and in restaurants. Distinctly Maharashtrian dishes include ''ukdiche modak'', , Kande pohe and Thalipeeth. Regular meals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pistachios
The pistachio (, ''Pistacia vera''), a member of the cashew family, is a small tree originating from Central Asia and the Middle East. The tree produces seeds that are widely consumed as food. ''Pistacia vera'' is often confused with other species in the genus ''Pistacia'' that are also known as pistachio. These other species can be distinguished by their geographic distributions (in the wild) and their seeds which are much smaller and have a soft shell. Etymology Pistachio is from late Middle English ''pistace'', from Old French, superseded in the 16th century by forms from Italian ''pistacchio'', via Latin from Greek ''pistákion'', and from Middle Persian ''pistakē''. History The pistachio tree is native to regions of Central Asia, including present-day Iran and Afghanistan. Archaeology shows that pistachio seeds were a common food as early as 6750 BC. So far, the earliest evidence of pistachio consumption goes back to the Bronze Age Central Asia and comes from Djarkuta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herders
A herder is a pastoral worker responsible for the care and management of a herd or flock of domestic animals, usually on open pasture. It is particularly associated with nomadic or transhumant management of stock, or with common land grazing. The work is often done either on foot or mounted. Depending on the type of animal being herd, the english language can give different professional names, for example, cowboy for cows, shepherd for sheep, or goatherd for goat. Terminology Herders may be distinguished by sex (''e.g.'', herdsman, herdswoman or herdboy) or by the type of livestock, for example camelherd, cowherd, duckherd, goatherd or shepherd. By country China Tibetan herding communities living in the Tibetan Plateau in the Sichuan Province of southwest China continued to graze herds on common lands even after the 1982 Household responsibility system. Several reasons have been given for the endurance of the traditional pastoral lifestyle: *complex topography prevent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Desserts
Mithai (sweets) are the confectionery and desserts of the Indian subcontinent.The Sweet Side of the Subcontinent Raison d'Etre, New York City (September 20, 2012) Thousands of dedicated shops in India, Bangladesh, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka sell nothing but sweets. Sugarcane has been grown in the Indian subcontinent for thousands of years, and the art of refining sugar was invented there 8000 years ago (6000 BCE) by the Indus Valley civilisation. The English word "sugar" comes from a Sanskrit word for refined sugar, while the word "candy" comes from Sanskrit word for the unrefined sugar – one of the simplest raw forms of sweet. Over its long history, cuisines of the Indian subcontinent developed a diverse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Yogurt-based Dishes And Beverages
This is a list of yogurt-based dishes and beverages. Yogurt is a food produced by bacterial fermentation of milk. The bacteria used to make yogurt are known as "yogurt cultures". Fermentation of lactose by these bacteria produces lactic acid, which acts on milk protein to give yogurt its texture and its characteristic tang. Worldwide, cow's milk, the protein of which is mainly casein, is most commonly used to make yogurt. Milk from water buffalo, goats, ewes, mares, camels, and yaks is also used to produce yogurt in various parts of the world. Dishes * Churri – a spicy Indian side dish * Çılbır – Turkish egg dish * Jameed – Jordanian yogurt strained cheese * * Labanie * * * Soups * Ash-e doogh – Iranian Azerbaijani thick yogurt soup * Cacık – cold yogurt soup from Turkey * Dovga – Azeribijani yogurt soup * Tarator – Bulgarian cold yogurt soup with cucumbers and garlic * Toyga soup – Turkish yogurt soup * Shakriya – Levantine stew with la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
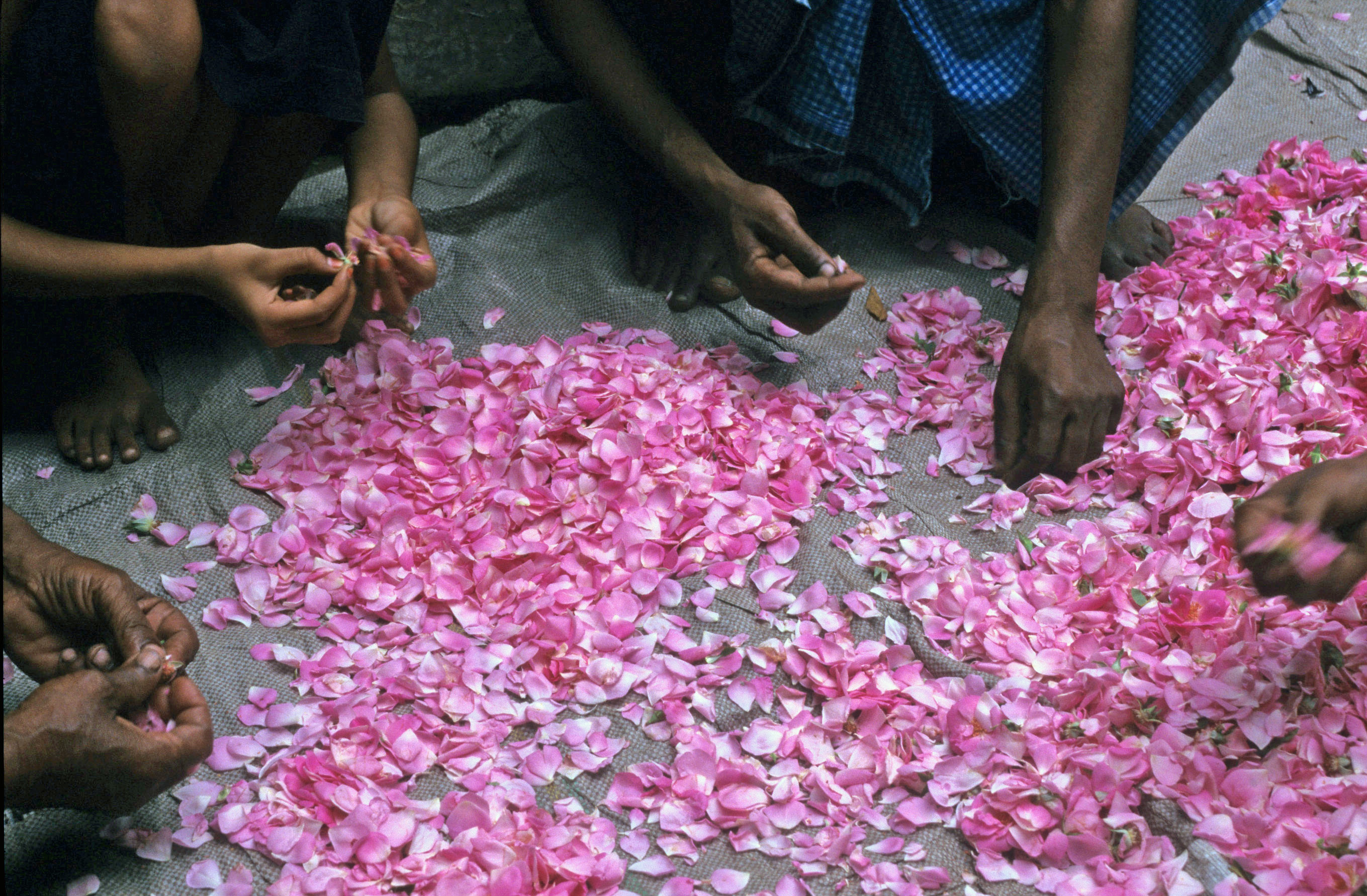
Gulkand
Gulkand (also written gulqand or gulkhand) is a sweet preserve of rose petals originating in the Indian subcontinent. The term is derived from Persian; ''gul'' (rose) and ''qand'' (sugar/sweet). Preparation Traditionally, gulkand has been prepared with Damask roses. Other common types of roses used include China rose, French rose, and Cabbage rose. It is prepared using special pink rose petals and is mixed with sugar. Rose petals are slow-cooked with sugar, which reduces the juices into a thick consistency. Uses in holistic medicine Gulkand is used in the Unani Unani or Yunani medicine (Urdu: ''tibb yūnānī'') is Perso-Arabic traditional medicine as practiced in Muslim culture in South Asia and modern day Central Asia. Unani medicine is pseudoscientific. The Indian Medical Association describes U ... system of medicine as a cooling tonic. It is also used in Ayurvedic and Persian medicine to help with bodily imbalances. References Indian condiments Pakist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mango
A mango is an edible stone fruit produced by the tropical tree ''Mangifera indica''. It is believed to have originated in the region between northwestern Myanmar, Bangladesh, and northeastern India. ''M. indica'' has been cultivated in South and Southeast Asia since ancient times resulting in two types of modern mango cultivars: the "Indian type" and the "Southeast Asian type". Other species in the genus ''Mangifera'' also produce edible fruits that are also called "mangoes", the majority of which are found in the Malesian ecoregion. Worldwide, there are several hundred cultivars of mango. Depending on the cultivar, mango fruit varies in size, shape, sweetness, skin color, and flesh color which may be pale yellow, gold, green, or orange. Mango is the national fruit of India, Pakistan and the Philippines, while the mango tree is the national tree of Bangladesh. Etymology The English word ''mango'' (plural "mangoes" or "mangos") originated in the 16th century from the Por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cheesecloth
Cheesecloth is a loose-woven gauze-like carded cotton cloth used primarily in cheesemaking and cooking. Grades Cheesecloth is available in at least seven different grades, from open to extra-fine weave. Grades are distinguished by the number of threads per inch in each direction. Uses Food preparation The primary use of cheesecloth is in some styles of cheesemaking, where it is used to remove whey from cheese curds, and to help hold the curds together as the cheese is formed. Cheesecloth is also used in straining stocks and custards, bundling herbs, making tofu and ghee, and thickening yogurt. Queso blanco and queso fresco are Spanish and Mexican cheeses that are made from whole milk using cheesecloth. Quark is a type of German unsalted cheese that is sometimes formed with cheesecloth. Paneer is a kind of Indian fresh cheese that is commonly made with cheesecloth. Fruitcake is wrapped in rum-infused cheesecloth during the process of "feeding" the fruitcake as it ripens. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jain
Jainism ( ), also known as Jain Dharma, is an Indian religion. Jainism traces its spiritual ideas and history through the succession of twenty-four tirthankaras (supreme preachers of ''Dharma''), with the first in the current time cycle being Rishabhadeva, whom the tradition holds to have lived millions of years ago, the twenty-third ''tirthankara'' Parshvanatha, whom historians date to the 9th century BCE, and the twenty-fourth ''tirthankara'' Mahavira, around 600 BCE. Jainism is considered to be an eternal ''dharma'' with the ''tirthankaras'' guiding every time cycle of the cosmology. The three main pillars of Jainism are ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), ''anekāntavāda'' (non-absolutism), and '' aparigraha'' (asceticism). Jain monks, after positioning themselves in the sublime state of soul consciousness, take five main vows: ''ahiṃsā'' (non-violence), '' satya'' (truth), '' asteya'' (not stealing), ''brahmacharya'' (chastity), and '' aparigraha'' (non-possessiveness). Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Cookbooks
Indian cookbooks are cookbooks written in India, or about Indian cooking. Some of the oldest cookbooks were written in India Indian cooking varies regionally and has evolved over the centuries due to various influences. Vegetarianism has made a significant impact on Indian cooking. Spices play a major role in Indian cooking. Early Indian texts and cookbooks Ayurvedic Samhitas (4th century BCE) suggests foods are used to support and bring out the three qualities of mind, namely sattvic foods, rajasic foods, and tamasic foods. Several Samhitas from Ayurveda texts describe and discusses methods to cook food and recipes, it mentions recipes for cooking rice in different ways, khichadi (rice-lentil dish), takra (curd dish), yusha (lentil dish), vesavara (minced meat dish), different methods to cook grains and pulses in various ways etc. Texts further discusses different ways to use meats, milk and milk products, vegetables, fruits, leafy greens, roots, oils, sugarcane products to prepar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kannada
Kannada (; ಕನ್ನಡ, ), originally romanised Canarese, is a Dravidian language spoken predominantly by the people of Karnataka in southwestern India, with minorities in all neighbouring states. It has around 47 million native speakers, and was additionally a second or third language for around 13 million non-native speakers in Karnataka. Kannada was the court language of some of the most powerful dynasties of south and central India, namely the Kadambas, Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas, Yadava Dynasty or Seunas, Western Ganga dynasty, Wodeyars of Mysore, Nayakas of Keladi Hoysalas and the Vijayanagara empire. The official and administrative language of the state of Karnataka, it also has scheduled status in India and has been included among the country's designated classical languages.Kuiper (2011), p. 74R Zydenbos in Cushman S, Cavanagh C, Ramazani J, Rouzer P, ''The Princeton Encyclopedia of Poetry and Poetics: Fourth Edition'', p. 767, Princeton Unive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |






.jpg)
