|
Sequential Equilibrium
Sequential equilibrium is a refinement of Nash equilibrium for extensive form games due to David M. Kreps and Robert Wilson. A sequential equilibrium specifies not only a strategy for each of the players but also a ''belief'' for each of the players. A belief gives, for each information set of the game belonging to the player, a probability distribution on the nodes in the information set. A profile of strategies and beliefs is called an ''assessment'' for the game. Informally speaking, an assessment is a perfect Bayesian equilibrium if its strategies are sensible given its beliefs ''and'' its beliefs are confirmed on the outcome path given by its strategies. The definition of sequential equilibrium further requires that there be arbitrarily small perturbations of beliefs and associated strategies with the same property. Consistent assessments The formal definition of a strategy being sensible given a belief is straightforward; the strategy should simply maximize expec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subgame Perfect Equilibrium
In game theory, a subgame perfect equilibrium (SPE), or subgame perfect Nash equilibrium (SPNE), is a refinement of the Nash equilibrium concept, specifically designed for dynamic games where players make sequential decisions. A strategy profile is an SPE if it represents a Nash equilibrium in every possible subgame of the original game. Informally, this means that at any point in the game, the players' behavior from that point onward should represent a Nash equilibrium of the continuation game (i.e. of the subgame), no matter what happened before. This ensures that strategies are credible and rational throughout the entire game, eliminating non-credible threats. Every finite extensive game with complete information (all players know the complete state of the game) and perfect recall (each player remembers all their previous actions and knowledge throughout the game) has a subgame perfect equilibrium. A common method for finding SPE in finite games is backward induction, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
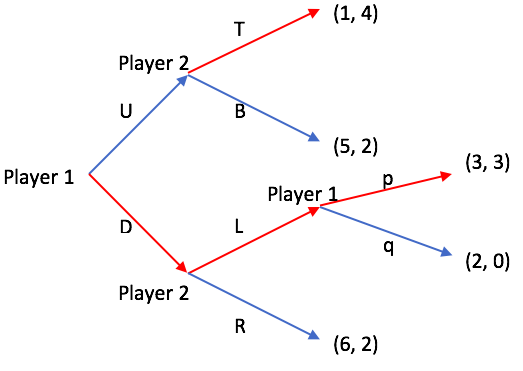
Perfect Bayesian Equilibrium
In game theory, a Bayesian game is a strategic decision-making model which assumes players have incomplete information. Players may hold private information relevant to the game, meaning that the payoffs are not common knowledge. Bayesian games model the outcome of player interactions using aspects of Bayesian probability. They are notable because they allowed the specification of the solutions to games with incomplete information for the first time in game theory. Hungarian economist John C. Harsanyi introduced the concept of Bayesian games in three papers from 1967 and 1968: He was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for these and other contributions to game theory in 1994. Roughly speaking, Harsanyi defined Bayesian games in the following way: players are assigned a set of characteristics by nature at the start of the game. By mapping probability distributions to these characteristics and by calculating the outcome of the game using Bayesian probability, the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Quasi-perfect Equilibrium
Quasi-perfect equilibrium is a refinement of Nash Equilibrium for extensive form games due to Eric van Damme. Informally, a player playing by a strategy from a quasi-perfect equilibrium takes observed as well as potential future mistakes of his opponents into account but assumes that he himself will not make a mistake in the future, even if he observes that he has done so in the past. Quasi-perfect equilibrium is a further refinement of sequential equilibrium. It is itself refined by normal form proper equilibrium. Mertens' voting game It has been argued by Jean-François MertensJean-François Mertens. "Two examples of strategic equilibrium." ''Games and Economic Behavior'', 8:378--388, 1995. that quasi-perfect equilibrium is superior to Reinhard Selten Reinhard Justus Reginald Selten (; 5 October 1930 – 23 August 2016) was a German economics, economist, who won the 1994 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences (shared with John Harsanyi and John Forbes Nash, J ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Admissible Decision Rule
In statistical decision theory, an admissible decision rule is a rule for making a decision such that there is no other rule that is always "better" than it (or at least sometimes better and never worse), in the precise sense of "better" defined below. This concept is analogous to Pareto efficiency. Definition Define sets \Theta\,, \mathcal and \mathcal, where \Theta\, are the states of nature, \mathcal the possible observations, and \mathcal the actions that may be taken. An observation of x \in \mathcal\,\! is distributed as F(x\mid\theta)\,\! and therefore provides evidence about the state of nature \theta\in\Theta\,\!. A decision rule is a function \delta:\rightarrow , where upon observing x\in \mathcal, we choose to take action \delta(x)\in \mathcal\,\!. Also define a loss function L: \Theta \times \mathcal \rightarrow \mathbb, which specifies the loss we would incur by taking action a \in \mathcal when the true state of nature is \theta \in \Theta. Usually we will tak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Proper Equilibrium
Proper equilibrium is a refinement of Nash Equilibrium by Roger B. Myerson. Proper equilibrium further refines Reinhard Selten's notion of a trembling hand perfect equilibrium by assuming that more costly trembles are made with significantly smaller probability than less costly ones. Definition Given a normal form game and a parameter \epsilon > 0, a totally mixed strategy profile \sigma is defined to be \epsilon-proper if, whenever a player has two pure strategies s and s' such that the expected payoff of playing s is smaller than the expected payoff of playing s' (that is u(s,\sigma_) Example The game to the right is a varia ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trembling Hand Perfect Equilibrium
In game theory, trembling hand perfect equilibrium is a type of refinement of a Nash equilibrium that was first proposed by Reinhard Selten. A trembling hand perfect equilibrium is an equilibrium that takes the possibility of off-the-equilibrium play into account by assuming that the players, through a "slip of the hand" or tremble, may choose unintended strategies, albeit with negligible probability. Definition First define a perturbed game. A perturbed game is a copy of a base game, with the restriction that only totally mixed strategies are allowed to be played. A totally mixed strategy is a mixed strategy in an n-player strategic game where ''every'' pure strategy is played with positive probability. This is the "trembling hands" of the players; they sometimes play a different strategy, other than the one they intended to play. Then define a mixed strategy profile \sigma=(\sigma_1,\ldots,\sigma_n) as being trembling hand perfect if there is a sequence of perturbed game ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Subgame Perfect Equilibrium
In game theory, a subgame perfect equilibrium (SPE), or subgame perfect Nash equilibrium (SPNE), is a refinement of the Nash equilibrium concept, specifically designed for dynamic games where players make sequential decisions. A strategy profile is an SPE if it represents a Nash equilibrium in every possible subgame of the original game. Informally, this means that at any point in the game, the players' behavior from that point onward should represent a Nash equilibrium of the continuation game (i.e. of the subgame), no matter what happened before. This ensures that strategies are credible and rational throughout the entire game, eliminating non-credible threats. Every finite extensive game with complete information (all players know the complete state of the game) and perfect recall (each player remembers all their previous actions and knowledge throughout the game) has a subgame perfect equilibrium. A common method for finding SPE in finite games is backward induction, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Mixed Strategy
In game theory, a move, action, or play is any one of the options which a player can choose in a setting where the optimal outcome depends ''not only'' on their own actions ''but'' on the actions of others. The discipline mainly concerns the action of a player in a game affecting the behavior or actions of other players. Some examples of "games" include chess, bridge, poker, monopoly, diplomacy or battleship. The term strategy is typically used to mean a complete algorithm for playing a game, telling a player what to do for every possible situation. A player's strategy determines the action the player will take at any stage of the game. However, the idea of a strategy is often confused or conflated with that of a move or action, because of the correspondence between moves and pure strategies in most games: for any move ''X'', "always play move ''X''" is an example of a valid strategy, and as a result every move can also be considered to be a strategy. Other authors treat strate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Limit Point
In mathematics, a limit point, accumulation point, or cluster point of a set S in a topological space X is a point x that can be "approximated" by points of S in the sense that every neighbourhood of x contains a point of S other than x itself. A limit point of a set S does not itself have to be an element of S. There is also a closely related concept for sequences. A cluster point or accumulation point of a sequence (x_n)_ in a topological space X is a point x such that, for every neighbourhood V of x, there are infinitely many natural numbers n such that x_n \in V. This definition of a cluster or accumulation point of a sequence generalizes to nets and filters. The similarly named notion of a (respectively, a limit point of a filter, a limit point of a net) by definition refers to a point that the sequence converges to (respectively, the filter converges to, the net converges to). Importantly, although "limit point of a set" is synonymous with "cluster/accumulation poi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Information Set (game Theory)
In game theory, an information set is the basis for decision making in a game, which includes the actions available to players and the potential outcomes of each action. It consists of a collection of decision nodes that a player cannot distinguish between when making a move, due to incomplete information about previous actions or the current state of the game. In other words, when a player's turn comes, they may be uncertain about which exact node in the game tree they are currently at, and the information set represents all the possibilities they must consider. Information sets are a fundamental concept particularly important in games with imperfect information. In games with perfect information (such as chess or Go (game), Go), every information set contains exactly one decision node, as each player can observe all previous moves and knows the exact game state. However, in games with imperfect information—such as most Card game, card games like poker or Bridge (card game), bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bayesian Game
In game theory, a Bayesian game is a strategic decision-making model which assumes players have incomplete information. Players may hold private information relevant to the game, meaning that the payoffs are not common knowledge. Bayesian games model the outcome of player interactions using aspects of Bayesian probability. They are notable because they allowed the specification of the solutions to games with incomplete information for the first time in game theory. Hungarian economist John C. Harsanyi introduced the concept of Bayesian games in three papers from 1967 and 1968: He was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for these and other contributions to game theory in 1994. Roughly speaking, Harsanyi defined Bayesian games in the following way: players are assigned a set of characteristics by nature at the start of the game. By mapping probability distributions to these characteristics and by calculating the outcome of the game using Bayesian probability, the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Extensive Form Game
In game theory, an extensive-form game is a specification of a game allowing for the explicit representation of a number of key aspects, like the sequencing of players' possible moves, their choices at every decision point, the (possibly imperfect) information each player has about the other player's moves when they make a decision, and their payoffs for all possible game outcomes. Extensive-form games also allow for the representation of incomplete information in the form of chance events modeled as " moves by nature". Extensive-form representations differ from normal-form in that they provide a more complete description of the game in question, whereas normal-form simply boils down the game into a payoff matrix. Finite extensive-form games Some authors, particularly in introductory textbooks, initially define the extensive-form game as being just a game tree with payoffs (no imperfect or incomplete information), and add the other elements in subsequent chapters as refinements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |