|
Self-replicating
Self-replication is any behavior of a dynamical system that yields construction of an identical or similar copy of itself. Biological cells, given suitable environments, reproduce by cell division. During cell division, DNA is replicated and can be transmitted to offspring during reproduction. Biological viruses can replicate, but only by commandeering the reproductive machinery of cells through a process of infection. Harmful prion proteins can replicate by converting normal proteins into rogue forms. Computer viruses reproduce using the hardware and software already present on computers. Self-replication in robotics has been an area of research and a subject of interest in science fiction. Any self-replicating mechanism which does not make a perfect copy (mutation) will experience genetic variation and will create variants of itself. These variants will be subject to natural selection, since some will be better at surviving in their current environment than others and will ou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abiogenesis
In biology, abiogenesis (from a- 'not' + Greek bios 'life' + genesis 'origin') or the origin of life is the natural process by which life has arisen from non-living matter, such as simple organic compounds. The prevailing scientific hypothesis is that the transition from non-living to living entities on Earth was not a single event, but an evolutionary process of increasing complexity that involved the formation of a habitable planet, the prebiotic synthesis of organic molecules, molecular self-replication, self-assembly, autocatalysis, and the emergence of cell membranes. Many proposals have been made for different stages of the process. The study of abiogenesis aims to determine how pre-life chemical reactions gave rise to life under conditions strikingly different from those on Earth today. It primarily uses tools from biology and chemistry, with more recent approaches attempting a synthesis of many sciences. Life functions through the specialized chemistry of carbon and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Von Neumann
John von Neumann (; hu, Neumann János Lajos, ; December 28, 1903 – February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest coverage of any mathematician of his time and was said to have been "the last representative of the great mathematicians who were equally at home in both pure and applied mathematics". He integrated pure and applied sciences. Von Neumann made major contributions to many fields, including mathematics (foundations of mathematics, measure theory, functional analysis, ergodic theory, group theory, lattice theory, representation theory, operator algebras, matrix theory, geometry, and numerical analysis), physics (quantum mechanics, hydrodynamics, ballistics, nuclear physics and quantum statistical mechanics), economics ( game theory and general equilibrium theory), computing ( Von Neumann architecture, linear programming, numerical meteo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
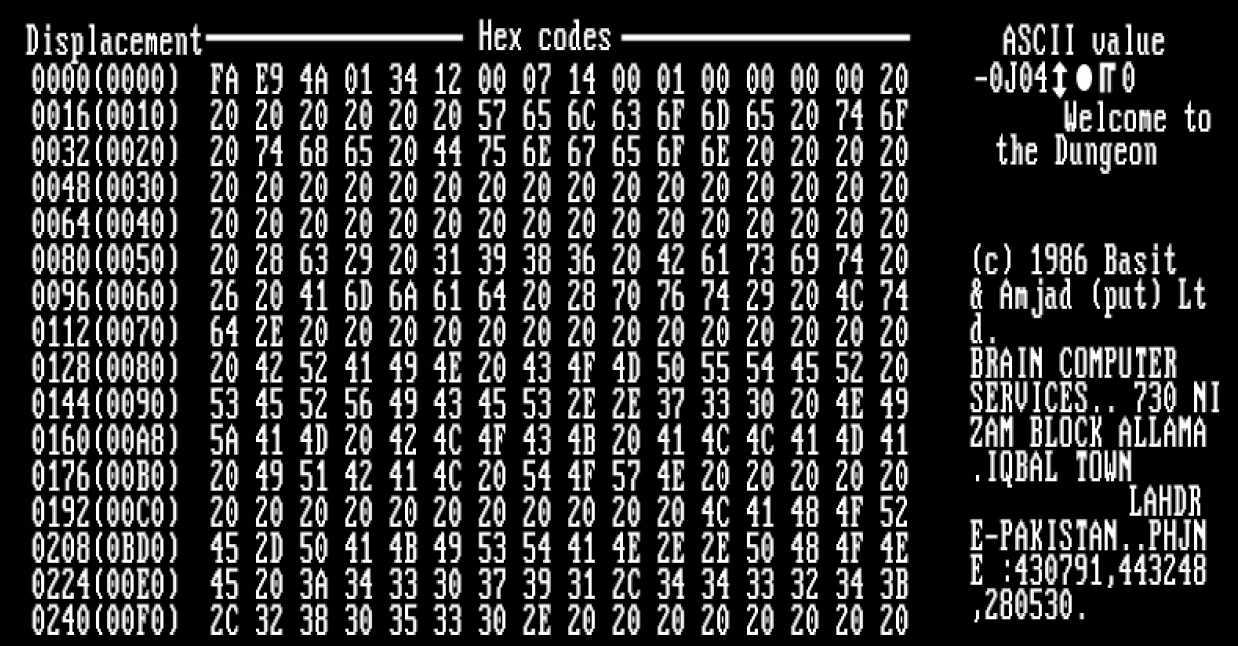
Computer Virus
A computer virus is a type of computer program that, when executed, replicates itself by modifying other computer programs and inserting its own code. If this replication succeeds, the affected areas are then said to be "infected" with a computer virus, a metaphor derived from biological viruses. Computer viruses generally require a host program. The virus writes its own code into the host program. When the program runs, the written virus program is executed first, causing infection and damage. A computer worm does not need a host program, as it is an independent program or code chunk. Therefore, it is not restricted by the host program, but can run independently and actively carry out attacks. Virus writers use social engineering deceptions and exploit detailed knowledge of security vulnerabilities to initially infect systems and to spread the virus. Viruses use complex anti-detection/stealth strategies to evade antivirus software. Motives for creating viruses can inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of life forms. Every cell consists of a cytoplasm enclosed within a membrane, and contains many biomolecules such as proteins, DNA and RNA, as well as many small molecules of nutrients and metabolites.Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell '' fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small molecules such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reproduction
Reproduction (or procreation or breeding) is the biological process by which new individual organisms – "offspring" – are produced from their "parent" or parents. Reproduction is a fundamental feature of all known life; each individual organism exists as the result of reproduction. There are two forms of reproduction: asexual and sexual. In asexual reproduction, an organism can reproduce without the involvement of another organism. Asexual reproduction is not limited to single-celled organisms. The cloning of an organism is a form of asexual reproduction. By asexual reproduction, an organism creates a genetically similar or identical copy of itself. The evolution of sexual reproduction is a major puzzle for biologists. The two-fold cost of sexual reproduction is that only 50% of organisms reproduce and organisms only pass on 50% of their genes.John Maynard Smith ''The Evolution of Sex'' 1978. Sexual reproduction typically requires the sexual interaction of two specializ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quine (computing)
A quine is a computer program which takes no input and produces a copy of its own source code as its only output. The standard terms for these programs in the computability theory and computer science literature are "self-replicating programs", "self-reproducing programs", and "self-copying programs". A quine is a fixed point of an execution environment, when the execution environment is viewed as a function transforming programs into their outputs. Quines are possible in any Turing-complete programming language, as a direct consequence of Kleene's recursion theorem. For amusement, programmers sometimes attempt to develop the shortest possible quine in any given programming language. The name "quine" was coined by Douglas Hofstadter, in his popular science book ''Gödel, Escher, Bach'', in honor of philosopher Willard Van Orman Quine (1908–2000), who made an extensive study of indirect self-reference, and in particular for the following paradox-producing expression, known as Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphinx Tiling
In geometry, the sphinx tiling is a tessellation of the plane using the "sphinx", a pentagonal hexiamond formed by gluing six equilateral triangles together. The resultant shape is named for its reminiscence to the Great Sphinx at Giza. A sphinx can be dissected into any square number of copies of itself, some of them mirror images, and repeating this process leads to a non-periodic tiling of the plane. The sphinx is therefore a rep-tile (a self-replicating tessellation). It is one of few known pentagonal rep-tiles and is the only known pentagonal rep-tile whose sub-copies are equal in size. See also * Mosaic A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ... References External links * Mathematics Centre Sphinx Album ..* {{Tessellation Pentagonal tilings Aperiodic ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tessellation
A tessellation or tiling is the covering of a surface, often a plane (mathematics), plane, using one or more geometric shapes, called ''tiles'', with no overlaps and no gaps. In mathematics, tessellation can be generalized to high-dimensional spaces, higher dimensions and a variety of geometries. A periodic tiling has a repeating pattern. Some special kinds include ''regular tilings'' with regular polygonal tiles all of the same shape, and ''semiregular tilings'' with regular tiles of more than one shape and with every corner identically arranged. The patterns formed by periodic tilings can be categorized into 17 wallpaper groups. A tiling that lacks a repeating pattern is called "non-periodic". An ''aperiodic tiling'' uses a small set of tile shapes that cannot form a repeating pattern. A ''tessellation of space'', also known as a space filling or honeycomb, can be defined in the geometry of higher dimensions. A real physical tessellation is a tiling made of materials such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Merkle
Ralph C. Merkle (born February 2, 1952) is a computer scientist and mathematician. He is one of the inventors of public-key cryptography, the inventor of cryptographic hashing, and more recently a researcher and speaker on cryonics. Contributions While an undergraduate, Merkle devised Merkle's Puzzles, a scheme for communication over an insecure channel, as part of a class project. The scheme is now recognized to be an early example of public key cryptography. He co-invented the Merkle–Hellman knapsack cryptosystem, invented cryptographic hashing (now called the Merkle–Damgård construction based on a pair of articles published 10 years later that established the security of the scheme), and invented Merkle trees. The Merkle–Damgård construction is at the heart of many hashing algorithms. While at Xerox PARC, Merkle designed the Khufu and Khafre block ciphers, and the Snefru hash function. Career Merkle was the manager of compiler development at Elxsi from 1980. In 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Freitas
Robert A. Freitas Jr. (born 1952) is an American nanotechnologist. Career In 1974, Freitas earned a bachelor's degree in both physics and psychology from Harvey Mudd College, and in 1978, he received a Juris Doctor (J.D.) degree from Santa Clara University School of Law. He has written more than 150 technical papers, book chapters, and popular articles on scientific, engineering, and legal topics. Freitas began writing his ''Nanomedicine'' book series in 1994. Volume I, published in October 1999 by Landes Bioscience while Freitas was a Research Fellow at the Institute for Molecular Manufacturing. Volume IIA was published in October 2003 by Landes Bioscience. In 2004, Freitas and Ralph Merkle coauthored and published ''Kinematic Self-Replicating Machines'', a comprehensive survey of the field of physical and hypothetical self-replicating machines. In 2009, Freitas was awarded the Feynman Prize in theoretical nanotechnology. Bibliography * ''Robert A. Freitas Jr.'', Nanomedicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype. It is a key mechanism of evolution, the change in the heritable traits characteristic of a population over generations. Charles Darwin popularised the term "natural selection", contrasting it with selective breeding, artificial selection, which in his view is intentional, whereas natural selection is not. Genetic diversity, Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and their offspring can inherit such mutations. Throughout the lives of the individuals, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the Cell (biology), cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment. Because individuals with certain variants of the trait tend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Congruence (geometry)
In geometry, two figures or objects are congruent if they have the same shape and size, or if one has the same shape and size as the mirror image of the other. More formally, two sets of points are called congruent if, and only if, one can be transformed into the other by an isometry, i.e., a combination of rigid motions, namely a translation, a rotation, and a reflection. This means that either object can be repositioned and reflected (but not resized) so as to coincide precisely with the other object. Therefore two distinct plane figures on a piece of paper are congruent if they can be cut out and then matched up completely. Turning the paper over is permitted. In elementary geometry the word ''congruent'' is often used as follows. The word ''equal'' is often used in place of ''congruent'' for these objects. *Two line segments are congruent if they have the same length. *Two angles are congruent if they have the same measure. *Two circles are congruent if they have the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |