|
Samarium(II) Chloride
Samarium(II) chloride (Samarium, SmChlorine, Cl2) is a chemical compound, used as a radical generating agent in the ketone-mediated intraannulation reaction. Preparation Reduction of samarium(III) chloride with samarium metal in a vacuum at a temperature of 800 °C to 900 °C, or with hydrogen gas at 350 °C yields samarium(II) chloride: :2 SmCl3 + Sm → 3 SmCl2 :2 SmCl3 + H2 → 2 SmCl2 + 2 HCl Samarium(II) chloride can also be prepared by reducing samarium(III) chloride with Lithium naphthalene, lithium metal/naphthalene in Tetrahydrofuran, THF: : SmCl3 + Li → SmCl2 + LiCl A similar reaction has been observed with sodium. Structure Samarium(II) chloride adopts the lead(II) chloride, PbCl2 (cotunnite) structure. References Chlorides Lanthanide halides Samarium compounds {{inorganic-compound-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarium(II) Bromide
Samarium(II) bromide is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula . It is a brown solid that is insoluble in most solvents but degrades readily in air. Structure In the gas phase, is a bent molecule with Sm–Br distance 274.5 pm and bond angle 131±6°. History Samarium(II) bromide was first synthesized in 1934 by P. W. Selwood, when he reduced samarium tribromide (SmBr3) with hydrogen (H2). Kagan also synthesized it by converting samarium(III) oxide (Sm2O3) to SmBr3 and then reducing with a lithium dispersion in THF. Robert A. Flowers synthesized it by adding two equivalent of lithium bromide (LiBr) to samarium diiodide (SmI2) in tetrahydrofuran. Namy managed to synthesize it by mixing tetrabromoethane (C2H2Br4) with samarium metal, and Hilmerson found that heating the tetrabromoethane or samarium greatly improved the production of samarium(II) bromide. Reactions Samarium(II) bromide has reducing properties reminiscent of the more commonly used samarium diiodide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
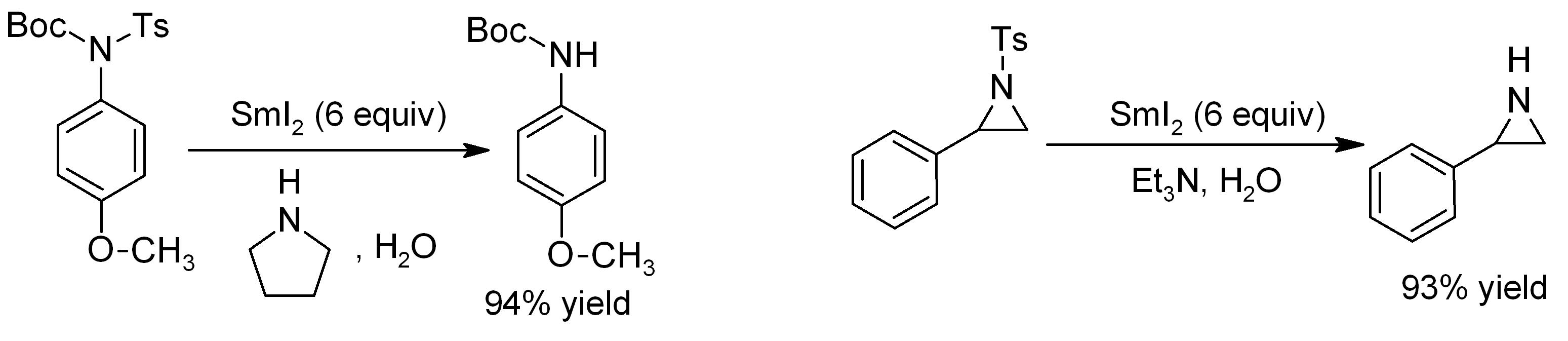
Samarium(II) Iodide
Samarium(II) iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula SmI2. When employed as a solution for organic synthesis, it is known as Kagan's reagent. SmI2 is a green solid and solutions are green as well. It is a strong one-electron reducing agent that is used in organic synthesis. Structure In samarium(II) iodide, the metal centers are seven-coordinate with a face-capped octahedral geometry. In its ether adducts, samarium remains heptacoordinate with five ether and two terminal iodide ligands. Preparation Samarium iodide is easily prepared in nearly quantitative yields from samarium metal and either diiodomethane or 1,2-diiodoethane. When prepared in this way, its solutions is most often used without purification of the inorganic reagent. Solid, solvent-free SmI2 forms by high temperature decomposition of samarium(III) iodide (SmI3).G. Jantsch, N. Skalla: "Zur Kenntnis der Halogenide der seltenen Erden. IV. – Über Samarium(II)jodid und den thermischen Abbau des Samari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarium(III) Chloride
Samarium(III) chloride, also known as samarium trichloride, is an inorganic compound of samarium and chloride. It is a pale yellow salt that rapidly absorbs water to form a hexahydrate, SmCl3.6H2O. The compound has few practical applications but is used in laboratories for research on new compounds of samarium. Structure Like several related chlorides of the lanthanides and actinides, SmCl3 crystallises in the UCl3 motif. The Sm3+ centres are nine-coordinate, occupying trigonal prismatic sites with additional chloride ligands occupying the three square faces. Preparation and reactions SmCl3 is prepared by the " ammonium chloride" route, which involves the initial synthesis of (NH4)2 mCl5 This material can be prepared from the common starting materials at reaction temperatures of 230 °C from samarium oxide: ::10 NH4Cl + Sm2O3 → 2 (NH4)2 mCl5 + 6 NH3 + 3 H2O The pentachloride is then heated to 350-400 °C resulting in evolution of ammonium chloride and leaving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarium
Samarium is a chemical element with symbol Sm and atomic number 62. It is a moderately hard silvery metal that slowly oxidizes in air. Being a typical member of the lanthanide series, samarium usually has the oxidation state +3. Compounds of samarium(II) are also known, most notably the monoxide SmO, monochalcogenides SmS, SmSe and SmTe, as well as samarium(II) iodide. The last compound is a common reducing agent in chemical synthesis. Samarium has no significant biological role, and some samarium salts are slightly toxic. Samarium was discovered in 1879 by French chemist Paul-Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran and named after the mineral samarskite from which it was isolated. The mineral itself was named after a Russian mine official, Colonel Vassili Samarsky-Bykhovets, who thus became the first person to have a chemical element named after him, albeit indirectly. Though classified as a rare-earth element, samarium is the 40th most abundant element in Earth's crust and more common than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorine
Chlorine is a chemical element with the Symbol (chemistry), symbol Cl and atomic number 17. The second-lightest of the halogens, it appears between fluorine and bromine in the periodic table and its properties are mostly intermediate between them. Chlorine is a yellow-green gas at room temperature. It is an extremely reactive element and a strong oxidising agent: among the elements, it has the highest electron affinity and the third-highest electronegativity on the revised Electronegativity#Pauling electronegativity, Pauling scale, behind only oxygen and fluorine. Chlorine played an important role in the experiments conducted by medieval Alchemy, alchemists, which commonly involved the heating of chloride Salt (chemistry), salts like ammonium chloride (sal ammoniac) and sodium chloride (common salt), producing various chemical substances containing chlorine such as hydrogen chloride, mercury(II) chloride (corrosive sublimate), and hydrochloric acid (in the form of ). However ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Compound
A chemical compound is a chemical substance composed of many identical molecules (or molecular entities) containing atoms from more than one chemical element held together by chemical bonds. A molecule consisting of atoms of only one element is therefore not a compound. A compound can be transformed into a different substance by a chemical reaction, which may involve interactions with other substances. In this process, bonds between atoms may be broken and/or new bonds formed. There are four major types of compounds, distinguished by how the constituent atoms are bonded together. Molecular compounds are held together by covalent bonds; ionic compounds are held together by ionic bonds; intermetallic compounds are held together by metallic bonds; coordination complexes are held together by coordinate covalent bonds. Non-stoichiometric compounds form a disputed marginal case. A chemical formula specifies the number of atoms of each element in a compound molecule, using the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ketone
In organic chemistry, a ketone is a functional group with the structure R–C(=O)–R', where R and R' can be a variety of carbon-containing substituents. Ketones contain a carbonyl group –C(=O)– (which contains a carbon-oxygen double bond C=O). The simplest ketone is acetone (where R and R' is methyl), with the formula . Many ketones are of great importance in biology and in industry. Examples include many sugars (ketoses), many steroids (e.g., testosterone), and the solvent acetone. Nomenclature and etymology The word ''ketone'' is derived from ''Aketon'', an old German word for ''acetone''. According to the rules of IUPAC nomenclature, ketone names are derived by changing the suffix ''-ane'' of the parent alkane to ''-anone''. Typically, the position of the carbonyl group is denoted by a number, but traditional nonsystematic names are still generally used for the most important ketones, for example acetone and benzophenone. These nonsystematic names are considere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samarium(III) Chloride
Samarium(III) chloride, also known as samarium trichloride, is an inorganic compound of samarium and chloride. It is a pale yellow salt that rapidly absorbs water to form a hexahydrate, SmCl3.6H2O. The compound has few practical applications but is used in laboratories for research on new compounds of samarium. Structure Like several related chlorides of the lanthanides and actinides, SmCl3 crystallises in the UCl3 motif. The Sm3+ centres are nine-coordinate, occupying trigonal prismatic sites with additional chloride ligands occupying the three square faces. Preparation and reactions SmCl3 is prepared by the " ammonium chloride" route, which involves the initial synthesis of (NH4)2 mCl5 This material can be prepared from the common starting materials at reaction temperatures of 230 °C from samarium oxide: ::10 NH4Cl + Sm2O3 → 2 (NH4)2 mCl5 + 6 NH3 + 3 H2O The pentachloride is then heated to 350-400 °C resulting in evolution of ammonium chloride and leaving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, and highly combustible. Hydrogen is the most abundant chemical substance in the universe, constituting roughly 75% of all normal matter.However, most of the universe's mass is not in the form of baryons or chemical elements. See dark matter and dark energy. Stars such as the Sun are mainly composed of hydrogen in the plasma state. Most of the hydrogen on Earth exists in molecular forms such as water and organic compounds. For the most common isotope of hydrogen (symbol 1H) each atom has one proton, one electron, and no neutrons. In the early universe, the formation of protons, the nuclei of hydrogen, occurred during the first second after the Big Bang. The emergence of neutral hydrogen atoms throughout the universe occurred about 370,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Naphthalene
Lithium naphthalene is an organic salt with the chemical formula Li+. In the research laboratory, it is used as a reductant in the synthesis of organic, organometallic, and inorganic chemistry. It is usually generated in situ. Lithium naphthalene crystallizes with ligands bound to Li+. Preparation and properties The compound is prepared by stirring the metallic lithium with naphthalene in an ethereal solvent, usually as tetrahydrofuran or dimethoxyethane. The resulting salt is dark green. The reaction of naphthalene with lithium can be accelerated by sonication. Methods for assaying lithium naphthalene have been developed as well. The anion is a radical, giving a strong EPR signal near ''g'' = 2.0. Its deep green color arises from absorptions at 463, 735 nm. Several solvates of lithium naphthalene have been characterized by X-ray crystallography. The effects are subtle, the outer pair of HC–CH bonds contract by 3 pm and the other nine C–C bonds elong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetrahydrofuran
Tetrahydrofuran (THF), or oxolane, is an organic compound with the formula (CH2)4O. The compound is classified as heterocyclic compound, specifically a cyclic ether. It is a colorless, water-miscible organic liquid with low viscosity. It is mainly used as a precursor to polymers. Being polar and having a wide liquid range, THF is a versatile solvent. Production About 200,000 tonnes of tetrahydrofuran are produced annually. The most widely used industrial process involves the acid-catalyzed dehydration of 1,4-butanediol. Ashland/ISP is one of the biggest producers of this chemical route. The method is similar to the production of diethyl ether from ethanol. The butanediol is derived from condensation of acetylene with formaldehyde followed by hydrogenation. DuPont developed a process for producing THF by oxidizing ''n''-butane to crude maleic anhydride, followed by catalytic hydrogenation. A third major industrial route entails hydroformylation of allyl alcohol followed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lead(II) Chloride
Lead(II) chloride (PbCl2) is an inorganic compound which is a white solid under ambient conditions. It is poorly soluble in water. Lead(II) chloride is one of the most important lead-based reagents. It also occurs naturally in the form of the mineral cotunnite. Structure and properties In solid PbCl2, each lead ion is coordinated by nine chloride ions in a tricapped triangular prism formation — six lie at the vertices of a triangular prism and three lie beyond the centers of each rectangular prism face. The 9 chloride ions are not equidistant from the central lead atom, 7 lie at 280–309 pm and 2 at 370 pm. PbCl2 forms white orthorhombic needles. File:Cotunnite-3D-balls.png, Ball-and-stick model of part of the crystal structure of cotunnite File:Cotunnite-3D-ionic.png, Space-filling model File:Cotunnite-Pb-coordination-geometry-3D-balls.png, Coordination geometry of Pb2+ File:Cotunnite-Cl-coordination-geometry-3D-balls.png, Coordination geometry of Cl− File:Cot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |