|
Safe-life Design
In safe-life design, products are intended to be removed from service at a specific design life. Safe-life is particularly relevant to simple metal aircraft, where airframe components are subjected to alternating loads over the lifetime of the aircraft which makes them susceptible to metal fatigue. In certain areas such as in wing or tail components, structural failure in flight would be catastrophic. The safe-life design technique is employed in critical systems which are either very difficult to repair or whose failure may cause severe damage to life and property. These systems are designed to work for years without requirement of any repairs. The disadvantage of the safe-life design philosophy is that serious assumptions must be made regarding the alternating loads imposed on the aircraft, so if those assumptions prove to be inaccurate, cracks may commence prior to the component being removed from service. To counter this disadvantage, alternative design philosophies like fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Life
The design life of a component or product is the period of time during which the item is expected by its designers to work within its specified parameters; in other words, the life expectancy of the item. It is not always the actual length of time between placement into service of a single item and that item's onset of wearout. Another use of the term design life deals with consumer products. Many products employ design life as one factor of their differentiation from competing products and components. A disposable camera is designed to withstand a short life, whilst an expensive single-lens reflex camera may be expected to have a design life measured in years or decades. Long design lives Some products designed for heavy or demanding use are so well-made that they are retained and used well beyond their design life. Some public transport vehicles come into this category, as do a number of artificial satellites and spacecraft. In general, entry-level products—those at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
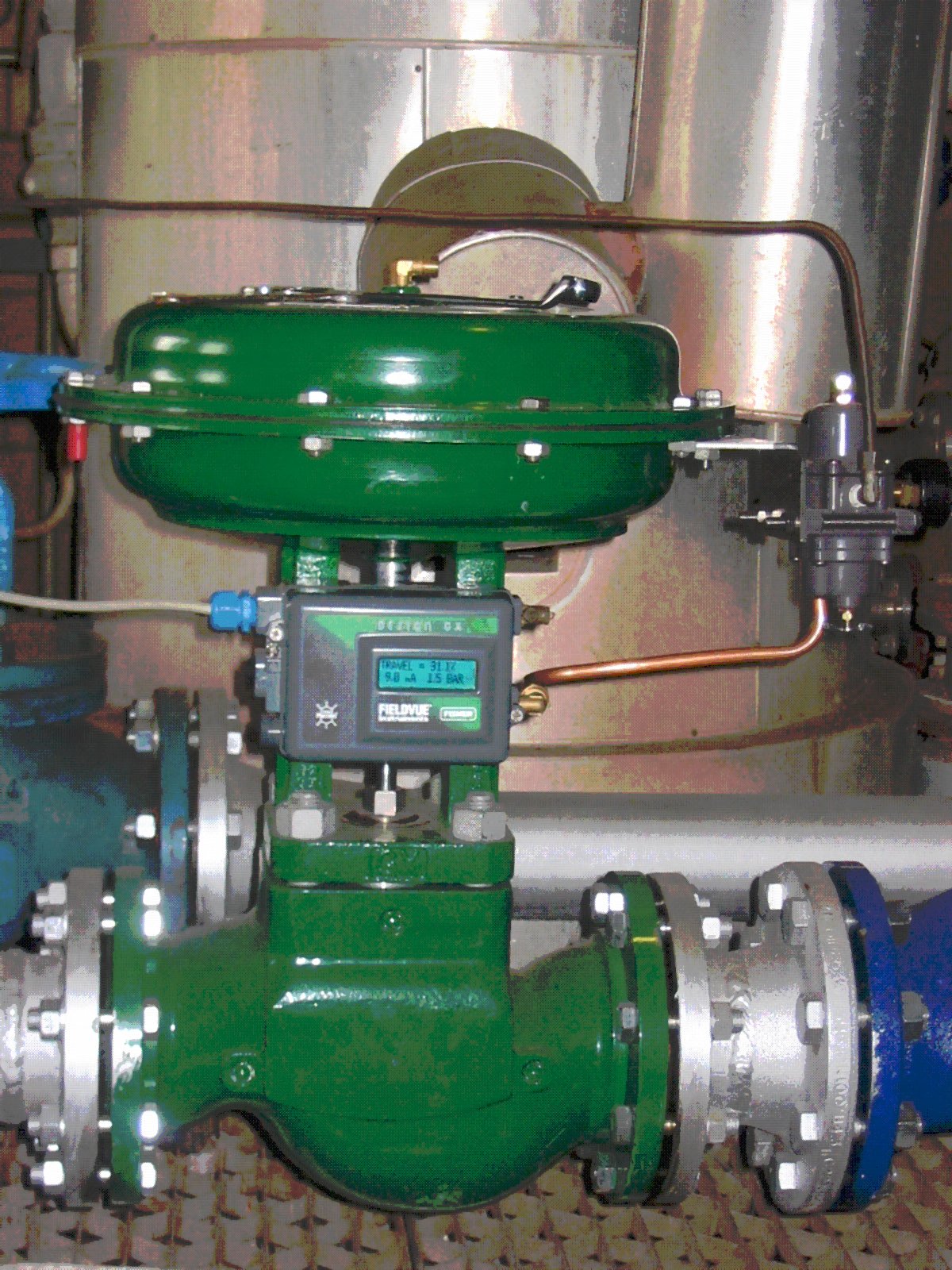
Airframe
The mechanical structure of an aircraft is known as the airframe. This structure is typically considered to include the fuselage, undercarriage, empennage and wings, and excludes the propulsion system. Airframe design is a field of aerospace engineering that combines aerodynamics, materials technology and manufacturing methods with a focus on weight, strength and aerodynamic drag, as well as reliability and cost.Michael C. Y. Niu (1988). ''Airframe Structural Design''. Conmilit Press LTD. History Modern airframe history began in the United States when a 1903 wood biplane made by Orville and Wilbur Wright showed the potential of fixed-wing designs. In 1912 the Deperdussin Monocoque pioneered the light, strong and streamlined monocoque fuselage formed of thin plywood layers over a circular frame, achieving . First World War Many early developments were spurred by military needs during World War I. Well known aircraft from that era include the Dutch designer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fatigue (material)
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure. Fatigue has traditionally been associated with the failure of metal components which led to the term metal fatigue. In the nineteenth century, the sudden failing of metal railway axles was thought to be caused by the metal ''crystallising'' because of the brittle appearance of the fracture surface, but this has since been disproved. Most materials, such as composites, plastics and ceramics, seem to experience some sort of fatigue-related failure. To aid in predicting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Design Philosophy
A design is a plan or specification for the construction of an object or system or for the implementation of an activity or process or the result of that plan or specification in the form of a prototype, product, or process. The verb ''to design'' expresses the process of developing a design. In some cases, the direct construction of an object without an explicit prior plan (such as in craftwork, some engineering, coding, and graphic design) may also be considered to be a design activity. The design usually has to satisfy certain goals and constraints; may take into account aesthetic, functional, economic, or socio-political considerations; and is expected to interact with a certain environment. Typical examples of designs include architectural and engineering drawings, circuit diagrams, sewing patterns and less tangible artefacts such as business process models. Designing People who produce designs are called ''designers''. The term 'designer' generally refers to someone who wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fail-safe
In engineering, a fail-safe is a design feature or practice that in the event of a specific type of failure, inherently responds in a way that will cause minimal or no harm to other equipment, to the environment or to people. Unlike inherent safety to a particular hazard, a system being "fail-safe" does not mean that failure is impossible or improbable, but rather that the system's design prevents or mitigates unsafe consequences of the system's failure. That is, if and when a "fail-safe" system fails, it remains at least as safe as it was before the failure. Since many types of failure are possible, failure mode and effects analysis is used to examine failure situations and recommend safety design and procedures. Some systems can never be made fail-safe, as continuous availability is needed. Redundancy, fault tolerance, or contingency plans are used for these situations (e.g. multiple independently controlled and fuel-fed engines). Examples Mechanical or physical Examples ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault-tolerant Design
Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of one or more faults within some of its components. If its operating quality decreases at all, the decrease is proportional to the severity of the failure, as compared to a naively designed system, in which even a small failure can cause total breakdown. Fault tolerance is particularly sought after in high-availability, mission-critical, or even life-critical systems. The ability of maintaining functionality when portions of a system break down is referred to as graceful degradation. A fault-tolerant design enables a system to continue its intended operation, possibly at a reduced level, rather than failing completely, when some part of the system fails. The term is most commonly used to describe computer systems designed to continue more or less fully operational with, perhaps, a reduction in throughput or an increase in response time in the event of some partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
S-N Curve
In materials science, fatigue is the initiation and propagation of cracks in a material due to cyclic loading. Once a fatigue crack has initiated, it grows a small amount with each loading cycle, typically producing striations on some parts of the fracture surface. The crack will continue to grow until it reaches a critical size, which occurs when the stress intensity factor of the crack exceeds the fracture toughness of the material, producing rapid propagation and typically complete fracture of the structure. Fatigue has traditionally been associated with the failure of metal components which led to the term metal fatigue. In the nineteenth century, the sudden failing of metal railway axles was thought to be caused by the metal ''crystallising'' because of the brittle appearance of the fracture surface, but this has since been disproved. Most materials, such as composites, plastics and ceramics, seem to experience some sort of fatigue-related failure. To aid in predicting ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault-tolerant Design
Fault tolerance is the property that enables a system to continue operating properly in the event of the failure of one or more faults within some of its components. If its operating quality decreases at all, the decrease is proportional to the severity of the failure, as compared to a naively designed system, in which even a small failure can cause total breakdown. Fault tolerance is particularly sought after in high-availability, mission-critical, or even life-critical systems. The ability of maintaining functionality when portions of a system break down is referred to as graceful degradation. A fault-tolerant design enables a system to continue its intended operation, possibly at a reduced level, rather than failing completely, when some part of the system fails. The term is most commonly used to describe computer systems designed to continue more or less fully operational with, perhaps, a reduction in throughput or an increase in response time in the event of some partial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safety Engineering
Safety engineering is an engineering discipline which assures that engineered systems provide acceptable levels of safety. It is strongly related to industrial engineering/systems engineering, and the subset system safety engineering. Safety engineering assures that a life-critical system behaves as needed, even when components fail. Analysis techniques Analysis techniques can be split into two categories: qualitative and quantitative methods. Both approaches share the goal of finding causal dependencies between a hazard on system level and failures of individual components. Qualitative approaches focus on the question "What must go wrong, such that a system hazard may occur?", while quantitative methods aim at providing estimations about probabilities, rates and/or severity of consequences. The complexity of the technical systems such as Improvements of Design and Materials, Planned Inspections, Fool-proof design, and Backup Redundancy decreases risk and increases the cost. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Damage Tolerance
In engineering, damage tolerance is a property of a structure relating to its ability to sustain defects safely until repair can be effected. The approach to engineering design to account for damage tolerance is based on the assumption that flaws can exist in any structure and such flaws propagate with usage. This approach is commonly used in aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, and civil engineering to manage the extension of cracks in structure through the application of the principles of fracture mechanics. A structure is considered to be damage tolerant if a maintenance program has been implemented that will result in the detection and repair of accidental damage, corrosion and fatigue cracking before such damage reduces the residual strength of the structure below an acceptable limit. History Structures upon which human life depends have long been recognized as needing an element of fail-safety. When describing his flying machine, Leonardo da Vinci noted that "I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1945 Australian National Airways Stinson Crash
On 31 January 1945 a Stinson Model A aircraft departed from Melbourne for a flight of to Kerang, Victoria—the first leg of an Australian National Airways regular scheduled service to Broken Hill, New South Wales. It crashed from Melbourne. All ten occupants were killed in the accident. The aircraft was one of four Stinsons imported in 1936 by Keith Virtue, Airlines of Australia (AoA). Three had now crashed with the loss of 17 lives, and the fourth would not be permitted to fly again. It was determined that the accident was caused by a fatigue (material), fatigue crack in the main spar of the left wing that caused the outer part of the left wing, outboard of the engine nacelle, to separate from the remainder of the aircraft. The expert panel investigating the accident believed this to be the first fatal aircraft accident anywhere in the world directly attributable to metal fatigue. The accident and related matters were investigated by a Supreme Court judge who also found tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)