|
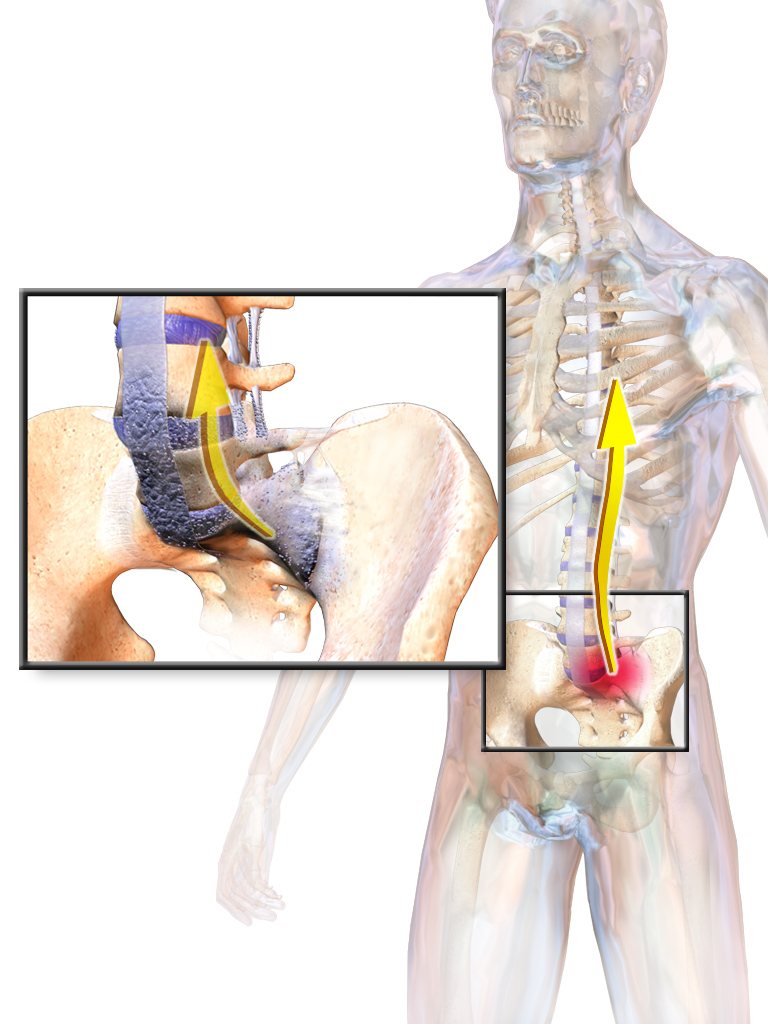
Syndesmophyte
A syndesmophyte is a bony growth originating inside a ligament, commonly seen in the ligaments of the spine Spine or spinal may refer to: Science Biology * Vertebral column, also known as the backbone * Dendritic spine, a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite * Thorns, spines, and prickles, needle-like structures in plants * Spine (zoolog ..., specifically the ligaments in the intervertebral joints leading to fusion of vertebrae. Syndesmophytes are pathologically similar to osteophytes. Ankylosing spondylitis patients are particularly prone to developing syndesmophytes. They are also commonly seen in patients who have had back surgery or other chronic stresses on the ligaments of their spine. Syndesmophytes indicate spine degeneration, similar to osteophytes of spine; however, they bridge across the joint as compared to osteophytes which are non-bridging. References {{musculoskeletal-disease-stub Skeletal disorders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankylosing Spondylitis
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a type of arthritis characterized by long-term inflammation of the joints of the spine typically where the spine joins the pelvis. Occasionally areas affected may include other joints such as the shoulders or hips, eye and bowel problems may occur as well as back pain. Joint mobility in the affected areas generally worsens over time. Although the cause of ankylosing spondylitis is unknown, it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors. More than 85% of those affected in the UK have a specific human leukocyte antigen known as the HLA-B27 antigen. The underlying mechanism is believed to be autoimmune or autoinflammatory. Diagnosis is typically based on the symptoms with support from medical imaging and blood tests. AS is a type of seronegative spondyloarthropathy, meaning that tests show no presence of rheumatoid factor (RF) antibodies. There is no known cure for AS. Treatments may include medication, exercise, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligament
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the: * Peritoneal ligament: a fold of peritoneum or other membranes. * Fetal remnant ligament: the remnants of a fetal tubular structure. * Periodontal ligament: a group of fibers that attach the cementum of teeth to the surrounding alveolar bone. Ligaments are similar to tendons and fasciae as they are all made of connective tissue. The differences among them are in the connections that they make: ligaments connect one bone to another bone, tendons connect muscle to bone, and fasciae connect muscles to other muscles. These are all found in the skeletal system of the human body. Ligaments cannot usually be regenerated naturally; however, there are periodontal ligament stem cells located near the periodontal ligament which are involved in the adult regener ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vertebral Column
The vertebral column, also known as the backbone or spine, is part of the axial skeleton. The vertebral column is the defining characteristic of a vertebrate in which the notochord (a flexible rod of uniform composition) found in all chordata, chordates has been replaced by a segmented series of bone: vertebrae separated by intervertebral discs. Individual vertebrae are named according to their region and position, and can be used as anatomical landmarks in order to guide procedures such as Lumbar puncture, lumbar punctures. The vertebral column houses the spinal canal, a cavity that encloses and protects the spinal cord. There are about 50,000 species of animals that have a vertebral column. The human vertebral column is one of the most-studied examples. Many different diseases in humans can affect the spine, with spina bifida and scoliosis being recognisable examples. The general structure of human vertebrae is fairly typical of that found in mammals, reptiles, and birds. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osteophytes
Osteophytes are exostoses (bony projections) that form along joint margins. They should not be confused with enthesophytes, which are bony projections that form at the attachment of a tendon or ligament. Osteophytes are not always distinguished from exostoses in any definite way, although in many cases there are a number of differences. Osteophytes are typically intra-articular (within the joint capsule). Cause A range of bone-formation processes are associated with aging, degeneration, mechanical instability, and disease (such as diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis). Osteophyte formation has classically been related to sequential and consequential changes in such processes. Often osteophytes form in osteoarthritic joints as a result of damage and wear from inflammation. Calcification and new bone formation can also occur in response to mechanical damage in joints. Pathophysiology Osteophytes form because of the increase in a damaged joint's surface area. This is most co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |