|
Synaptic Stabilization
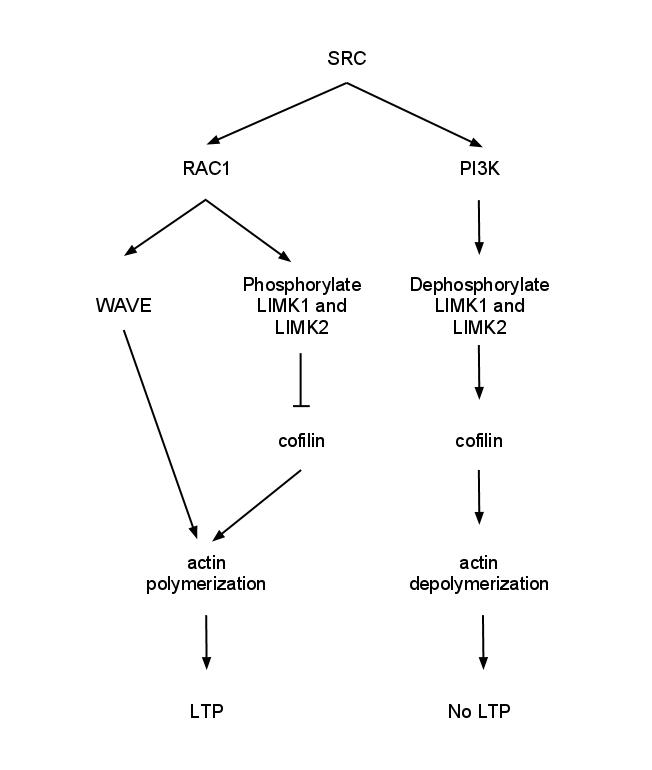
Synaptic stabilization is crucial in the developing and adult nervous systems and is considered a result of the late phase of long-term potentiation (LTP). The mechanism involves strengthening and maintaining active synapses through increased expression of cytoskeletal and extracellular matrix elements and postsynaptic scaffold proteins, while pruning less active ones. For example, cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) play a large role in synaptic maintenance and stabilization. Gerald Edelman discovered CAMs and studied their function during development, which showed CAMs are required for cell migration and the formation of the entire nervous system. In the adult nervous system, CAMs play an integral role in synaptic plasticity relating to learning and memory. Types of CAMs SynCAMs Synaptic cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) play a crucial role in axon pathfinding and synaptic establishment between neurons during neurodevelopment and are integral members in many synaptic processes inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Stabilization By Cell Adhesion Molecules , the pairing of two homologous chromosomes
{{disambig ...
Synaptic may refer to: * Synapse, part of the nervous system * Synaptic (software), a Linux graphical package management program * Synaptics, a semiconductor manufacturer * ''Synaptics'' (Mouse on Mars EP), 2017 See also * Synapse (other) * Synapsis Synapsis is the pairing of two chromosomes that occurs during meiosis. It allows matching-up of homologous pairs prior to their segregation, and possible chromosomal crossover between them. Synapsis takes place during prophase I of meiosis. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Domains
The immunoglobulin domain, also known as the immunoglobulin fold, is a type of protein domain that consists of a 2-layer sandwich of 7-9 antiparallel β-strands arranged in two β-sheets with a Greek key topology, consisting of about 125 amino acids. The backbone switches repeatedly between the two β-sheets. Typically, the pattern is (N-terminal β-hairpin in sheet 1)-(β-hairpin in sheet 2)-(β-strand in sheet 1)-(C-terminal β-hairpin in sheet 2). The cross-overs between sheets form an "X", so that the N- and C-terminal hairpins are facing each other. Members of the immunoglobulin superfamily are found in hundreds of proteins of different functions. Examples include antibodies, the giant muscle kinase titin, and receptor tyrosine kinases. Immunoglobulin-like domains may be involved in protein–protein and protein–ligand interactions. Examples Human genes encoding proteins containing the immunoglobulin domain include: * A1BG * ACAM * ADAMTSL1 * ADAMTSL3 * AGER * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dendritic Spine
A dendritic spine (or spine) is a small membranous protrusion from a neuron's dendrite that typically receives input from a single axon at the synapse. Dendritic spines serve as a storage site for synaptic strength and help transmit electrical signals to the neuron's cell body. Most spines have a bulbous head (the spine head), and a thin neck that connects the head of the spine to the shaft of the dendrite. The dendrites of a single neuron can contain hundreds to thousands of spines. In addition to spines providing an anatomical substrate for memory storage and synaptic transmission, they may also serve to increase the number of possible contacts between neurons. It has also been suggested that changes in the activity of neurons have a positive effect on spine morphology. Structure Dendritic spines are small with spine head volumes ranging 0.01 μm3 to 0.8 μm3. Spines with strong synaptic contacts typically have a large spine head, which connects to the dendrite via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadherin–catenin Complex In Learning And Memory
Long-term potentiation (LTP), thought to be the cellular basis for learning and memory, involves a specific signal transmission process that underlies synaptic plasticity. Among the many mechanisms responsible for the maintenance of synaptic plasticity is the cadherin–catenin complex. By forming complexes with intracellular catenin proteins, neural cadherins (N-cadherins) serve as a link between synaptic activity and synaptic plasticity, and play important roles in the processes of learning and memory. N-cadherins are believed to be involved in mediating LTP and the synaptic changes underlying learning and memory. During embryonic development, cadherins are initially widely distributed, but they become gradually more localized to pre- and post-synaptic sites while synapses are being formed. Blocking cadherin function with specific proteins does not affect basal synaptic properties, but it can impair the induction of LTP. Structural function and adhesion Structure of the cadher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CDH2
Cadherin-2 also known as Neural cadherin (N-cadherin), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CDH2'' gene. CDH2 has also been designated as CD325 (cluster of differentiation 325). Cadherin-2 is a transmembrane protein expressed in multiple tissues and functions to mediate cell–cell adhesion. In cardiac muscle, Cadherin-2 is an integral component in adherens junctions residing at intercalated discs, which function to mechanically and electrically couple adjacent cardiomyocytes. Alterations in expression and integrity of Cadherin-2 has been observed in various forms of disease, including human dilated cardiomyopathy. Variants in ''CDH2'' have also been identified to cause a syndromic neurodevelopmental disorder. Structure Cadherin-2 is a protein with molecular weight of 99.7 kDa, and 906 amino acids in length. Cadherin-2, a classical cadherin from the cadherin superfamily, is composed of five extracellular cadherin repeats, a transmembrane region and a highly cons ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Nervous System
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric and triploblastic animals—that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and diploblasts. It is a structure composed of nervous tissue positioned along the rostral (nose end) to caudal (tail end) axis of the body and may have an enlarged section at the rostral end which is a brain. Only arthropods, cephalopods and vertebrates have a true brain (precursor structures exist in onychophorans, gastropods and lancelets). The rest of this article exclusively discusses the vertebrate central nervous system, which is radically distinct from all other animals. Overview In vertebrates, the brain and spinal cord are both enclosed in the meninges. The meninges provide a barrier to chemicals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Synaptic Plasticity
In neuroscience, synaptic plasticity is the ability of synapses to strengthen or weaken over time, in response to increases or decreases in their activity. Since memories are postulated to be represented by vastly interconnected neural circuits in the brain, synaptic plasticity is one of the important neurochemical foundations of learning and memory (''see Hebbian theory''). Plastic change often results from the alteration of the number of neurotransmitter receptors located on a synapse. There are several underlying mechanisms that cooperate to achieve synaptic plasticity, including changes in the quantity of neurotransmitters released into a synapse and changes in how effectively cells respond to those neurotransmitters. Synaptic plasticity in both excitatory and inhibitory synapses has been found to be dependent upon postsynaptic calcium release. Historical discoveries In 1973, Terje Lømo and Tim Bliss first described the now widely studied phenomenon of long-term potent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catenin
Catenins are a family of proteins found in complexes with cadherin cell adhesion molecules of animal cells. The first two catenins that were identified became known as α-catenin and β-catenin. α-Catenin can bind to β-catenin and can also bind filamentous actin (F-actin). β-Catenin binds directly to the cytoplasmic tail of classical cadherins. Additional catenins such as γ-catenin and δ-catenin have been identified. The name "catenin" was originally selected ('catena' means 'chain' in Latin) because it was suspected that catenins might link cadherins to the cytoskeleton. Types * α-catenin * β-catenin * γ-catenin * δ-catenin All but α-catenin contain armadillo repeats. They exhibit a high degree of protein dynamics, alone or in complex. Function Several types of catenins work with N-cadherins to play an important role in learning and memory. Cell-cell adhesion complexes are required for simple epithelia in higher organisms to maintain structure, function and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cadherin
Cadherins (named for "calcium-dependent adhesion") are a type of cell adhesion molecule (CAM) that is important in the formation of adherens junctions to allow cells to adhere to each other . Cadherins are a class of type-1 transmembrane proteins, and they are dependent on calcium (Ca2+) ions to function, hence their name. Cell-cell adhesion is mediated by extracellular cadherin domains, whereas the intracellular cytoplasmic tail associates with numerous adaptors and signaling proteins, collectively referred to as the cadherin adhesome. The cadherin family is essential in maintaining the cell-cell contact and regulating cytoskeletal complexes. The cadherin superfamily includes cadherins, protocadherins, desmogleins, desmocollins, and more. In structure, they share ''cadherin repeats'', which are the extracellular Ca2+-binding domains. There are multiple classes of cadherin molecules, each designated with a prefix (in general, noting the types of tissue with which it is associated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Localization Of Cadherin-catenin
Localization or localisation may refer to: Biology * Localization of function, locating psychological functions in the brain or nervous system; see Linguistic intelligence * Localization of sensation, ability to tell what part of the body is affected by touch or other sensation; see Allochiria * Neurologic localization, in neurology, the process of deducing the location of injury based on symptoms and neurological examination * Nuclear localization signal, an amino acid sequence on the surface of a protein which acts like a 'tag' to localize the protein in the cell * Sound localization, a listener's ability to identify the location or origin of a detected sound * Subcellular localization, organization of cellular components into different regions of a cell Engineering and technology * GSM localization, determining the location of an active cell phone or wireless transceiver * Robot localization, figuring out robot's position in an environment * Indoor positioning system, a netw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PSD-95
PSD-95 (postsynaptic density protein 95) also known as SAP-90 (synapse-associated protein 90) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''DLG4'' (discs large homolog 4) gene. PSD-95 is a member of the membrane-associated guanylate kinase (MAGUK) family. With PSD-93 it is recruited into the same NMDA receptor and potassium channel clusters. These two MAGUK proteins may interact at postsynaptic sites to form a multimeric scaffold for the clustering of receptors, ion channels, and associated signaling proteins. PSD-95 is the best studied member of the MAGUK-family of PDZ domain-containing proteins. Like all MAGUK-family proteins, its basic structure includes three PDZ domains, an SH3 domain, and a guanylate kinase-like domain (GK) connected by disordered linker regions. It is almost exclusively located in the post synaptic density of neurons, and is involved in anchoring synaptic proteins. Its direct and indirect binding partners include neuroligin, NMDA receptors, AMPA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immunoglobulin Superfamily
The immunoglobulin superfamily (IgSF) is a large protein superfamily of cell surface and soluble proteins that are involved in the recognition, binding, or adhesion processes of cells. Molecules are categorized as members of this superfamily based on shared structural features with immunoglobulins (also known as antibodies); they all possess a domain known as an immunoglobulin domain or fold. Members of the IgSF include cell surface antigen receptors, co-receptors and co-stimulatory molecules of the immune system, molecules involved in antigen presentation to lymphocytes, cell adhesion molecules, certain cytokine receptors and intracellular muscle proteins. They are commonly associated with roles in the immune system. Otherwise, the sperm-specific protein IZUMO1, a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily, has also been identified as the only sperm membrane protein essential for sperm-egg fusion. Immunoglobulin domains Proteins of the IgSF possess a structural domain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |