|
Suprapubic Cystostomy
A suprapubic cystostomy or suprapubic catheter (SPC) (also known as a vesicostomy or epicystostomy) is a surgically created connection between the urinary bladder and the skin used to drain urine from the bladder in individuals with obstruction of normal urinary flow. The connection does not go through the abdominal cavity. Urinary flow may be blocked by swelling of the prostate (benign prostatic hypertrophy), traumatic disruption of the urethra, congenital defects of the urinary tract, or by obstructions such as kidney stones passed into the urethra, and cancer. It is also a common treatment used among spinal cord injury patients who are unable or unwilling to use intermittent catheterization to empty the bladder, and cannot otherwise void due to detrusor sphincter dyssynergia. Initially, a thin tube (catheter) is placed through the skin just above the pubic bone into the bladder, often with the assistance of ultrasound imaging. This catheter initially remains in place for up to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pubic Bone
In vertebrates, the pubic region ( la, pubis) is the most forward-facing (ventral and anterior) of the three main regions making up the coxal bone. The left and right pubic regions are each made up of three sections, a superior ramus, inferior ramus, and a body. Structure The pubic region is made up of a ''body'', ''superior ramus'', and ''inferior ramus'' (). The left and right coxal bones join at the pubic symphysis. It is covered by a layer of fat, which is covered by the mons pubis. The pubis is the lower limit of the suprapubic region. In the female, the pubic region is anterior to the urethral sponge. Body The body forms the wide, strong, middle and flat part of the pubic region. The bodies of the left and right pubic regions join at the pubic symphysis. The rough upper edge is the pubic crest, ending laterally in the pubic tubercle. This tubercle, found roughly 3 cm from the pubic symphysis, is a distinctive feature on the lower part of the abdominal wall; important ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinus (anatomy)
A sinus is a sac or cavity in any organ or tissue, or an abnormal cavity or passage caused by the destruction of tissue. In common usage, "sinus" usually refers to the paranasal sinuses, which are air cavities in the cranial bones, especially those near the nose and connecting to it. Most individuals have four paired cavities located in the cranial bone or skull. Etymology ''Sinus'' is Latin for "bay", "pocket", "curve", or "bosom". In anatomy, the term is used in various contexts. The word "sinusitis" is used to indicate that one or more of the membrane linings found in the sinus cavities has become inflamed or infected. It is however distinct from a fistula, which is a tract connecting two epithelial surfaces. If left untreated, infections occurring in the sinus cavities can affect the chest and lungs. Sinuses in the body * Paranasal sinuses ** Maxillary ** Ethmoid ** Sphenoid ** Frontal * Dural venous sinuses ** Anterior midline *** Cavernous *** Superior petrosal *** I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bonanno Catheter
A Bonanno catheter is a medical device. It was originally designed for suprapubic cystostomy (drainage of urine from the bladder through the skin, bypassing the urethra). Described by Dr J.P. Bonanno in 1970 and patented in 1987, it is produced by the medical supplies company Becton Dickinson. Apart from bladder drainage, it also has various other uses for which it has not actually been designed, such as thoracostomy and paracentesis Paracentesis (from Greek κεντάω, "to pierce") is a form of body fluid sampling procedure, generally referring to peritoneocentesis (also called laparocentesis or abdominal paracentesis) in which the peritoneal cavity is punctured by a needl .... The drain consists of a straight metal trocar, which serves as a core and guide for a plastic tube with a curved end that is kept straight while the trocar is inside. At the end of the plastic tube, a small flat plate is present that can be taped or sutured to the skin. The drain then ends in a connector ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Surgeries By Type
Many surgical procedure names can be broken into parts to indicate the meaning. For example, in gastrectomy, "ectomy" is a suffix meaning the removal of a part of the body. "Gastro-" means stomach. Thus, ''gastrectomy'' refers to the surgical removal of the stomach (or sections thereof). "Otomy" means cutting into a part of the body; a ''gastrotomy'' would be cutting into, but not necessarily removing, the stomach. And also "pharyngo" means pharynx, "laryngo" means larynx, "esophag" means esophagus. Thus, "pharyngolaryngoesophagectomy" refers to the surgical removal of the three. The field of minimally invasive surgery has spawned another set of words, such as ''arthroscopic'' or ''laparoscopic'' surgery. These take the same form as above; an arthroscope is a device which allows the inside of the joint to be seen. List of common surgery terms Prefixes * ''mono-'' : one, from the Greek μόνος, ''monos'', "only, single" * ''angio-'' : related to a blood vessel, from the Gre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleonic Era
The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France and Europe. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution, the first being the National Assembly, the second being the Legislative Assembly, and the third being the Directory. The Napoleonic era begins roughly with Napoleon Bonaparte's ''coup d'état'', overthrowing the Directory (9 November 1799), establishing the French Consulate, and ends during the Hundred Days and his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo (18 June 1815). The Congress of Vienna soon set out to restore Europe to pre-French Revolution days. Napoleon brought political stability to a land torn by revolution and war. He made peace with the Roman Catholic Church and reversed the most radical religious policies of the Convention. In 1804 Napoleon promulgated the Civil Code, a revised body of civil law, which also helped stabilize French society. The Civil Code affirmed the political and legal equality of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority globally. Owing to this historical prominence, it is common, even among non-Britons, to ref ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Patrick O'Brian
Patrick O'Brian, Order of the British Empire, CBE (12 December 1914 – 2 January 2000), born Richard Patrick Russ, was an English novelist and translator, best known for his Aubrey–Maturin series of sea novels set in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars, and centred on the friendship of the English naval captain Jack Aubrey and the Irish–Catalan physician Stephen Maturin. The 20-novel series, the first of which is ''Master and Commander'', is known for its well-researched and highly detailed portrayal of early 19th-century life, as well as its authentic and evocative language. A partially finished 21st novel in the series was published posthumously containing facing pages of handwriting and typescript. O'Brian wrote a number of other novels and short stories, most of which were published before he achieved success with the Aubrey–Maturin series. He also translated works from French to English, and wrote biographies of Joseph Banks: A Life, Joseph Banks and Picasso. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stephen Maturin
Stephen Maturin () is a fictional character in the Aubrey–Maturin series of novels by Patrick O'Brian. The series portrays his career as a physician, naturalist and spy in the Royal Navy during the Napoleonic Wars, and the long pursuit of his beloved Diana Villiers. Maturin was played by Paul Bettany in the 2003 film '' Master and Commander: The Far Side of the World'' and by Richard Dillane in the BBC Radio 4 adaptations of O'Brian's novels. Bettany was nominated for a British Academy Film Award for his performance. Biography Early life Stephen Maturin, called by his Catalan family Esteban Maturin y Domanova, a Roman Catholic, is the illegitimate son of an Irish officer serving in the Spanish Army and a Catalonian lady. He is cousin to the historical Lord Edward FitzGerald. As a boy he lived in Ireland, fostered by a family of pig-herders in Cahirciveen and County Clare, and spent his teenage years in Catalonia – most notably with his grandmother in Lleida, his uncle in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
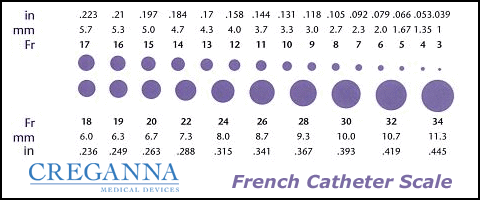
French Catheter Scale
The French scale, French gauge or Charrière system is commonly used to measure the size of a catheter. It is most often abbreviated as Fr, but can often be seen abbreviated as Fg, FR or F. It may also be abbreviated as CH or Ch (for Charrière, its inventor). However, simply ''gauge'', ''G'' or ''GA'' generally refers to Birmingham gauge. The Charrière is measured by the ''outer'' diameter, and is defined as 1 Fr = 1/3 mm, and thus 1 mm = 3 Fr; therefore the diameter of a round catheter in millimetres can be determined by dividing the French size by 3., For example, if the French size is 9, the diameter is 9/3 = 3.0; mm. It is seen that the French unit is fully redundant with the metric system but introduces potential for rounding errors. This metrication problem is further complicated by the mixed use of metric and imperial units in medical professions using catheters. An increasing French size corresponds to a larger external diameter. This is contrary to Birmingham gauge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urinary Tract Infection
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidney infection (pyelonephritis). Symptoms from a lower urinary tract infection include pain with urination, frequent urination, and feeling the need to urinate despite having an empty bladder. Symptoms of a kidney infection include fever and flank pain usually in addition to the symptoms of a lower UTI. Rarely the urine may appear bloody. In the very old and the very young, symptoms may be vague or non-specific. The most common cause of infection is ''Escherichia coli'', though other bacteria or fungi may sometimes be the cause. Risk factors include female anatomy, sexual intercourse, diabetes, obesity, and family history. Although sexual intercourse is a risk factor, UTIs are not classified as sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Kidney ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypospadias
Hypospadias is a common variation in fetal development of the penis in which the urethra does not open from its usual location in the head of the penis. It is the second-most common birth abnormality of the male reproductive system, affecting about one of every 250 males at birth. Roughly 90% of cases are the less serious distal hypospadias, in which the urethral opening (the meatus) is on or near the head of the penis (glans). The remainder have proximal hypospadias, in which the meatus is all the way back on the shaft of the penis, near or within the scrotum. Shiny tissue that should have made the urethra extends from the meatus to the tip of the glans; this tissue is called the urethral plate. In most cases, the foreskin is less developed and does not wrap completely around the penis, leaving the underside of the glans uncovered. Also, a downward bending of the penis, commonly referred to as chordee, may occur. Chordee is found in 10% of distal hypospadias and 50% of proximal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable disease, is an illness resulting from an infection. Infections can be caused by a wide range of pathogens, most prominently bacteria and viruses. Hosts can fight infections using their immune system. Mammalian hosts react to infections with an innate response, often involving inflammation, followed by an adaptive response. Specific medications used to treat infections include antibiotics, antivirals, antifungals, antiprotozoals, and antihelminthics. Infectious diseases resulted in 9.2 million deaths in 2013 (about 17% of all deaths). The branch of medicine that focuses on infections is referred to as infectious disease. Types Infections are caused by infectious agents (pathogens) including: * Bacteria (e.g. ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |