Napoleonic era on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]







 The Napoleonic era is a period in the
The Napoleonic era is a period in the
The Napoleonic era
at Britannica {{DEFAULTSORT:Napoleonic era Napoleon First French Empire French Revolution Modern history of France Historical eras










 The Napoleonic era is a period in the
The Napoleonic era is a period in the history of France
The first written records for the history of France appeared in the Iron Age. What is now France made up the bulk of the region known to the Romans as Gaul. The first writings on indigenous populations mainly start in the first century BC. Gree ...
and Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. It is generally classified as including the fourth and final stage of the French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in November 1799. Many of its ideas are considere ...
, the first being the National Assembly
In politics, a national assembly is either a unicameral legislature, the lower house of a bicameral legislature, or both houses of a bicameral legislature together. In the English language it generally means "an assembly composed of the rep ...
, the second being the Legislative Assembly, and the third being the Directory
Directory may refer to:
* Directory (computing), or folder, a file system structure in which to store computer files
* Directory (OpenVMS command)
* Directory service, a software application for organizing information about a computer network's u ...
. The Napoleonic era begins roughly with Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's ''coup d'état
A coup d'état (; French for 'stroke of state'), also known as a coup or overthrow, is a seizure and removal of a government and its powers. Typically, it is an illegal seizure of power by a political faction, politician, cult, rebel group, m ...
'', overthrowing the Directory (9 November 1799), establishing the French Consulate
The Consulate (french: Le Consulat) was the top-level Government of France from the fall of the Directory in the coup of 18 Brumaire on 10 November 1799 until the start of the Napoleonic Empire on 18 May 1804. By extension, the term ''The Co ...
, and ends during the Hundred Days
The Hundred Days (french: les Cent-Jours ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition, marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration ...
and his defeat at the Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
(18 June 1815). The Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon B ...
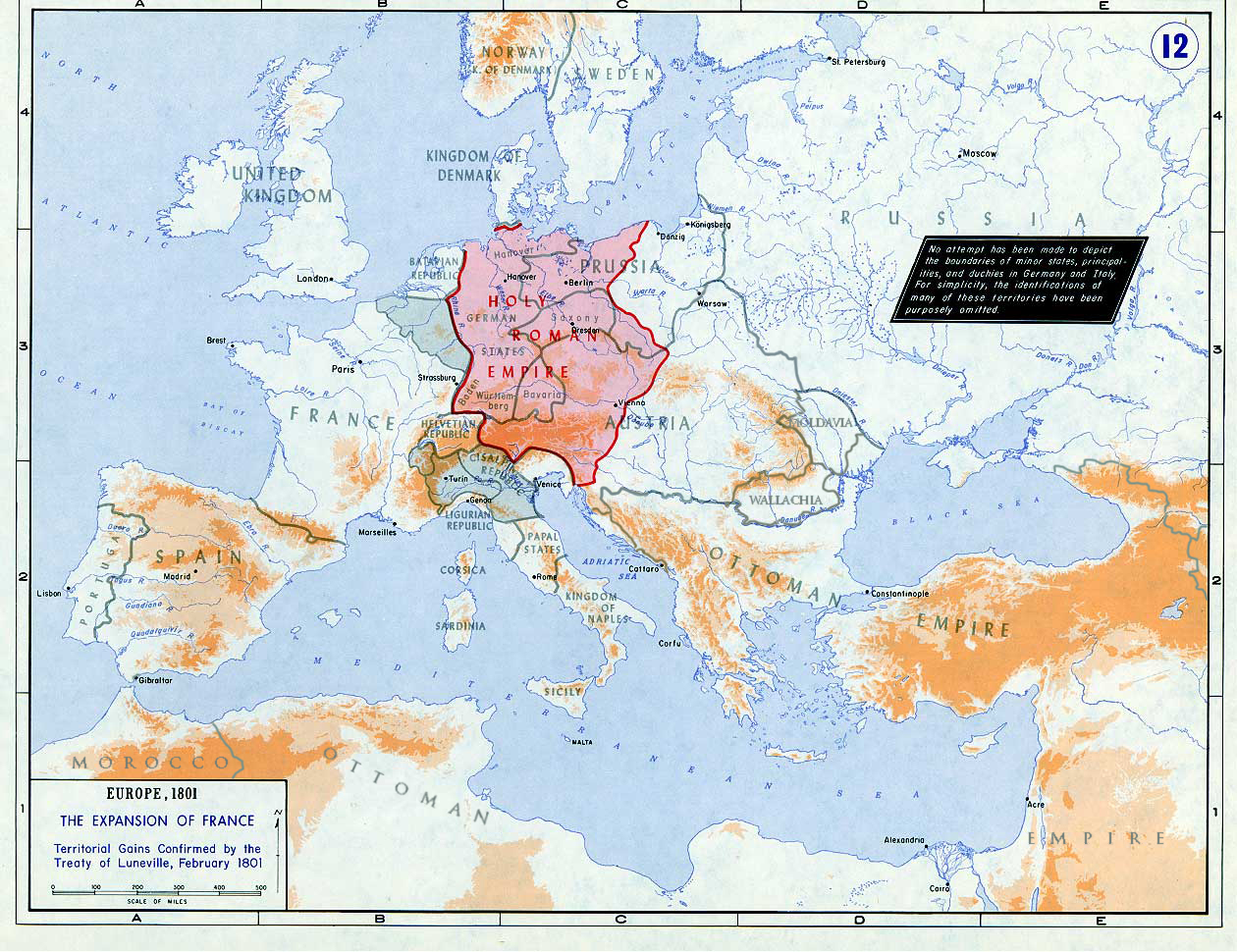
soon set out to restore Europe to pre-French Revolution days. Napoleon brought political stability to a land torn by revolution and war. He made peace with the Roman Catholic Church and reversed the most radical religious policies of the Convention. In 1804 Napoleon promulgated the Civil Code
A civil code is a codification of private law relating to property, family, and obligations.
A jurisdiction that has a civil code generally also has a code of civil procedure. In some jurisdictions with a civil code, a number of the core ar ...
, a revised body of civil law, which also helped stabilize French society. The Civil Code affirmed the political and legal equality of all adult men and established a merit-based society in which individuals advanced in education and employment because of talent rather than birth or social standing. The Civil Code confirmed many of the moderate revolutionary policies of the National Assembly but retracted measures passed by the more radical Convention. The code restored patriarchal authority in the family, for example, by making women and children subservient to male heads of households.
Whilst working to stabilise France, Napoleon also sought to extend his authority throughout Europe. Napoleon's armies conquered the Iberian and Italian peninsulas, occupied lands, and he forced Austria, Prussia, and Russia to ally with him and respect French hegemony in Europe. The United Kingdom refused to recognise French hegemony and continued the war throughout.
The First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental Eu ...
began to unravel in 1812, when he decided to invade Russia. Napoleon underestimated the difficulties his army would have to face whilst occupying Russia. Convinced that the Tsar was conspiring with his British enemies, Napoleon led an army of 600,000 soldiers to Moscow. He defeated the Russian army at Borodino before capturing Moscow, but the Tsar withdrew and Moscow was set ablaze, leaving Napoleon's vast army without adequate shelter or supplies. Napoleon ordered a retreat, but the bitter Russian winter
Russian Winter, sometimes personified as "General Frost" or "General Winter", is an aspect of the climate of Russia that has contributed to military failures of several invasions of Russia. Mud is a related contributing factor that impairs mili ...
and repeated Russian attacks whittled down his army, and only a battered remnant of 30,000 soldiers managed to limp back to French territory. The allies then continued a united effort against Napoleon until they had seized Paris forcing his abdication in 1814. His return to power the next year was resisted by all the allies and his army was defeated by a Prussian and Anglo-Allied force at Waterloo.
Rulers
Heads and leaders of states affected by Napoleon's regime and the Napoleonic wars: *Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
** Archduchy of Austria: Francis II (1792–1835)
** Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
: Francis I Francis I or Francis the First may refer to:
* Francesco I Gonzaga (1366–1407)
* Francis I, Duke of Brittany (1414–1450), reigned 1442–1450
* Francis I of France (1494–1547), King of France, reigned 1515–1547
* Francis I, Duke of Saxe-Lau ...
(1804–1835)
* Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria an ...
: Protector Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
(1806–1813)
* Denmark–Norway: Christian VII
Christian VII (29 January 1749 – 13 March 1808) was a monarch of the House of Oldenburg who was King of Denmark–Norway and Duke of Duchy of Schleswig, Schleswig and Duchy of Holstein, Holstein from 1766 until his death in 1808. For his motto ...
(1766–1808), Frederick VI (Regent 1772–1808, King of Denmark 1808–1839, King of Norway 1808–1814)
* Duchy of Warsaw
The Duchy of Warsaw ( pl, Księstwo Warszawskie, french: Duché de Varsovie, german: Herzogtum Warschau), also known as the Grand Duchy of Warsaw and Napoleonic Poland, was a French client state established by Napoleon Bonaparte in 1807, during ...
: Frederick Augustus I of Saxony
pl, Fryderyk August Józef Maria Antoni Jan Nepomucen Alojzy Ksawery
, image = Frederick Augustus I of Saxony by Marcello Bacciarelli (ca 1808-1809).png
, caption = Portrait by Marcello Bacciarelli (1809)
, succession = King of Saxony
, coron ...
, by personal arrangement with Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
, partial liberation (1806–1815) of the former Commonwealth of Poland–Lithuania
* Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediter ...
: Muhammad Ali
Muhammad Ali (; born Cassius Marcellus Clay Jr.; January 17, 1942 – June 3, 2016) was an American professional boxer and activist. Nicknamed "The Greatest", he is regarded as one of the most significant sports figures of the 20th century, a ...
(1805–1848)
* Etruria
Etruria () was a region of Central Italy, located in an area that covered part of what are now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and northern and western Umbria.
Etruscan Etruria
The ancient people of Etruria
are identified as Etruscan civiliza ...
: Louis Louis may refer to:
* Louis (coin)
* Louis (given name), origin and several individuals with this name
* Louis (surname)
* Louis (singer), Serbian singer
* HMS ''Louis'', two ships of the Royal Navy
See also
Derived or associated terms
* Lewis ( ...
(1801–03), Charles Louis (1803–1807)
* France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
** French Republic: First Consul
The Consulate (french: Le Consulat) was the top-level Government of France from the fall of the Directory in the coup of 18 Brumaire on 10 November 1799 until the start of the Napoleonic Empire on 18 May 1804. By extension, the term ''The Co ...
Napoleon Bonaparte
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
(1799–1804)
** French Empire: Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
(1804–1814, 1815)
** Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period. ...
: Louis XVIII
Louis XVIII (Louis Stanislas Xavier; 17 November 1755 – 16 September 1824), known as the Desired (), was King of France from 1814 to 1824, except for a brief interruption during the Hundred Days in 1815. He spent twenty-three years in ...
(1814–15, 1815–1824)
* Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
** Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a Sovereign state, sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of ...
: King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
(1760–1801), Prime Minister William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ire ...
(1793–1801)
** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Great B ...
: King George III
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Ireland from 25 October 1760 until the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Br ...
(1801–1820); Prince Regent George
George may refer to:
People
* George (given name)
* George (surname)
* George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George
* George Washington, First President of the United States
* George W. Bush, 43rd Presid ...
(1811–1820); Prime Ministers William Pitt the Younger
William Pitt the Younger (28 May 175923 January 1806) was a British statesman, the youngest and last prime minister of Great Britain (before the Acts of Union 1800) and then first prime minister of the United Kingdom (of Great Britain and Ire ...
(1801, 1804–06), Henry Addington (1801–04), The Lord Grenville (1806–07), The Duke of Portland (1807–09), Spencer Perceval
Spencer Perceval (1 November 1762 – 11 May 1812) was a British statesman and barrister who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from October 1809 until his assassination in May 1812. Perceval is the only British prime minister to ...
(1809–1812), The Earl of Liverpool (1812–1827)
* Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
: Jean-Jacques Dessalines
Jean-Jacques Dessalines (Haitian Creole: ''Jan-Jak Desalin''; ; 20 September 1758 – 17 October 1806) was a leader of the Haitian Revolution and the first ruler of an independent First Empire of Haiti, Haiti under the Constitution of Haiti, 1 ...
(as Governor-General 1804, as Emperor Jacques I 1804–06), Henri Christophe
Henri Christophe (; 6 October 1767 – 8 October 1820) was a key leader in the Haitian Revolution and the only monarch of the Kingdom of Haiti.
Christophe was of Bambara ethnicity in West Africa, and perhaps of Igbo descent. Beginning with ...
(as President 1806–1811, as King Henri I 1811–1820)
* Holland
Holland is a geographical regionG. Geerts & H. Heestermans, 1981, ''Groot Woordenboek der Nederlandse Taal. Deel I'', Van Dale Lexicografie, Utrecht, p 1105 and former province on the western coast of the Netherlands. From the 10th to the 16th c ...
: Louis I Louis I may refer to:
* Louis the Pious, Louis I of France, "the Pious" (778–840), king of France and Holy Roman Emperor
* Louis I, Landgrave of Thuringia (ruled 1123–1140)
* Ludwig I, Count of Württemberg (c. 1098–1158)
* Louis I of Blois ...
(1806–10), Louis II (1810)
* Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
: Francis II (1792–1806)
* Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
: Napoleon I
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
(1805–1814)
* Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
: Ferdinand IV (1799–1806, 1815–16), Joseph Bonaparte
it, Giuseppe-Napoleone Buonaparte es, José Napoleón Bonaparte
, house = Bonaparte
, father = Carlo Buonaparte
, mother = Letizia Ramolino
, birth_date = 7 January 1768
, birth_place = Corte, Corsica, Republic of ...
(1806–08), Joachim Murat
Joachim Murat ( , also , ; it, Gioacchino Murati; 25 March 1767 – 13 October 1815) was a French military commander and statesman who served during the French Revolutionary Wars and Napoleonic Wars. Under the French Empire he received the ...
(1808–1815)
* Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
: William I
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
(1815–1840)
* Montenegro
)
, image_map = Europe-Montenegro.svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Podgorica
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, official_languages = M ...
: Petar I Petrović-Njegoš
Petar I Petrović-Njegoš (Serbian Cyrillic: Петар I Петровић Његош; 1748 – 31 October 1830) was the ruler of the Prince-Bishopric of Montenegro as the Metropolitan (''vladika'') of Cetinje, and Exarch (legate) of the Serbi ...
(1782–1830)
* Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
: Selim III (1789–1807), Mustafa IV
Mustafa IV (; ota, مصطفى رابع, translit=Muṣṭafâ-yi râbiʿ; 8 September 1779 – 16 November 1808) was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1807 to 1808.
Early life
Mustafa IV was born on 8 September 1779 in Constantinople. He ...
(1807–08), Mahmud II
Mahmud II ( ota, محمود ثانى, Maḥmûd-u s̠ânî, tr, II. Mahmud; 20 July 1785 – 1 July 1839) was the 30th Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1808 until his death in 1839.
His reign is recognized for the extensive administrative, ...
(1808–1839)
* Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
: Pius VII
Pope Pius VII ( it, Pio VII; born Barnaba Niccolò Maria Luigi Chiaramonti; 14 August 1742 – 20 August 1823), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 14 March 1800 to his death in August 1823. Chiaramonti was also a m ...
(1800–1823)
* Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
: Mary I
Mary I (18 February 1516 – 17 November 1558), also known as Mary Tudor, and as "Bloody Mary" by her Protestant opponents, was Queen of England and Ireland from July 1553 and Queen of Spain from January 1556 until her death in 1558. She ...
(1777–1816), John VI (Regent 1799–1816, King 1816–1826)
* Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
: Frederick William III
Frederick William III (german: Friedrich Wilhelm III.; 3 August 1770 – 7 June 1840) was King of Prussia from 16 November 1797 until his death in 1840. He was concurrently Elector of Brandenburg in the Holy Roman Empire until 6 August 1806, wh ...
(1797–1840)
* Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
: Paul I Paul I may refer to:
*Paul of Samosata (200–275), Bishop of Antioch
*Paul I of Constantinople (died c. 350), Archbishop of Constantinople
*Pope Paul I (700–767)
*Paul I Šubić of Bribir (c. 1245–1312), Ban of Croatia and Lord of Bosnia
*Paul ...
(1796–1801), Alexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon 495–454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Pope Alexander I (died 115), early bishop of Rome
* Pope Alexander I of Alexandria (died 320s), patriarch of ...
(1801–1825)
* Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after ...
: Charles Emmanuel IV (1796–1802), Victor Emmanuel I
Victor Emmanuel I (Vittorio Emanuele; 24 July 1759 – 10 January 1824) was the Duke of Savoy and King of Sardinia (1802–1821).
Biography
Victor Emmanuel was the second son of King Victor Amadeus III of Sardinia and Maria Antonia Ferdinanda ...
(1802–1821)
* Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
: Frederick Augustus I (1763–1827)
* Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian language, Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeast Europe, Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Bas ...
** Revolutionary Serbia
Revolutionary Serbia ( sr, Устаничка Србија / Ustanička Srbija), or Karađorđe's Serbia ( sr, Карађорђева Србија / Karađorđeva Srbija), refers to the state established by the Serbian revolutionaries in Ottoman ...
was in a state of rebellion against the Ottoman rule, de facto independent, led initially Karađorđe
Đorđe Petrović ( sr-Cyrl, Ђорђе Петровић, ), better known by the sobriquet Karađorđe ( sr-Cyrl, Карађорђе, lit=Black George, ; – ), was a Serbian revolutionary who led the struggle for his country's independ ...
1804–1813 who was succeeded by Miloš Obrenović
Miloš, Milos, Miłosz or spelling variations thereof is a masculine given name and a surname. It may refer to:
Given name
Sportsmen
* Miłosz Bernatajtys, Polish rower
* Miloš Bogunović, Serbian footballer
* Miloš Budaković, Serbian ...
from 1815 onwards.
* Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
: Ferdinand III (1759–1816)
* Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
: Charles IV (1788–1808), Ferdinand VII
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Charles IV of Spain
, mother = Maria Luisa of Parma
, birth_date = 14 October 1784
, birth_place = El Escorial, Spain
, death_date =
, death_place = Madrid, Spain
, burial_plac ...
(1808, 1813–1833), Joseph I Joseph I or Josef I may refer to:
*Joseph I of Constantinople, Ecumenical Patriarch in 1266–1275 and 1282–1283
* Joseph I, Holy Roman Emperor (1678–1711)
*Joseph I (Chaldean Patriarch) (reigned 1681–1696)
*Joseph I of Portugal (1750–1777) ...
(1808–1813)
* Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
: Gustav IV Adolf
Gustav IV Adolf or Gustav IV Adolph (1 November 1778 – 7 February 1837) was King of Sweden from 1792 until he was deposed in a coup in 1809. He was also the last Swedish monarch to be the ruler of Finland.
The occupation of Finland in 1808–09 ...
(1792–1809), Charles XIII
Charles XIII, or Carl XIII ( sv, Karl XIII, 7 October 1748 – 5 February 1818), was King of Sweden from 1809 and King of Norway from 1814 to his death. He was the second son (and younger brother to King Gustav III) of King Adolf Frederick of Sw ...
(1809–1818)
* United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
: Presidents John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
(1797–1801), Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
(1801–1809), James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
(1809–1817)
* Württemberg
Württemberg ( ; ) is a historical German territory roughly corresponding to the cultural and linguistic region of Swabia. The main town of the region is Stuttgart.
Together with Baden and Hohenzollern, two other historical territories, Würt ...
: Frederick I Frederick I may refer to:
* Frederick of Utrecht or Frederick I (815/16–834/38), Bishop of Utrecht.
* Frederick I, Duke of Upper Lorraine (942–978)
* Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (1050–1105)
* Frederick I, Count of Zoll ...
(1797–1816)
Wars
*French Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted French First Republic, France against Ki ...
(1792–1802)
**Egyptian Campaign
The French campaign in Egypt and Syria (1798–1801) was Napoleon Bonaparte's campaign in the Ottoman territories of Egypt and Syria, proclaimed to defend French trade interests, to establish scientific enterprise in the region. It was the pr ...
(1798–1801)
**War of the Second Coalition
The War of the Second Coalition (1798/9 – 1801/2, depending on periodisation) was the second war on revolutionary France by most of the European monarchies, led by Britain, Austria and Russia, and including the Ottoman Empire, Portugal, N ...
(1799–1802)
*Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
(1803–1815)
**War of the Third Coalition
The War of the Third Coalition)
* In French historiography, it is known as the Austrian campaign of 1805 (french: Campagne d'Autriche de 1805) or the German campaign of 1805 (french: Campagne d'Allemagne de 1805) was a European conflict spanni ...
(1805)
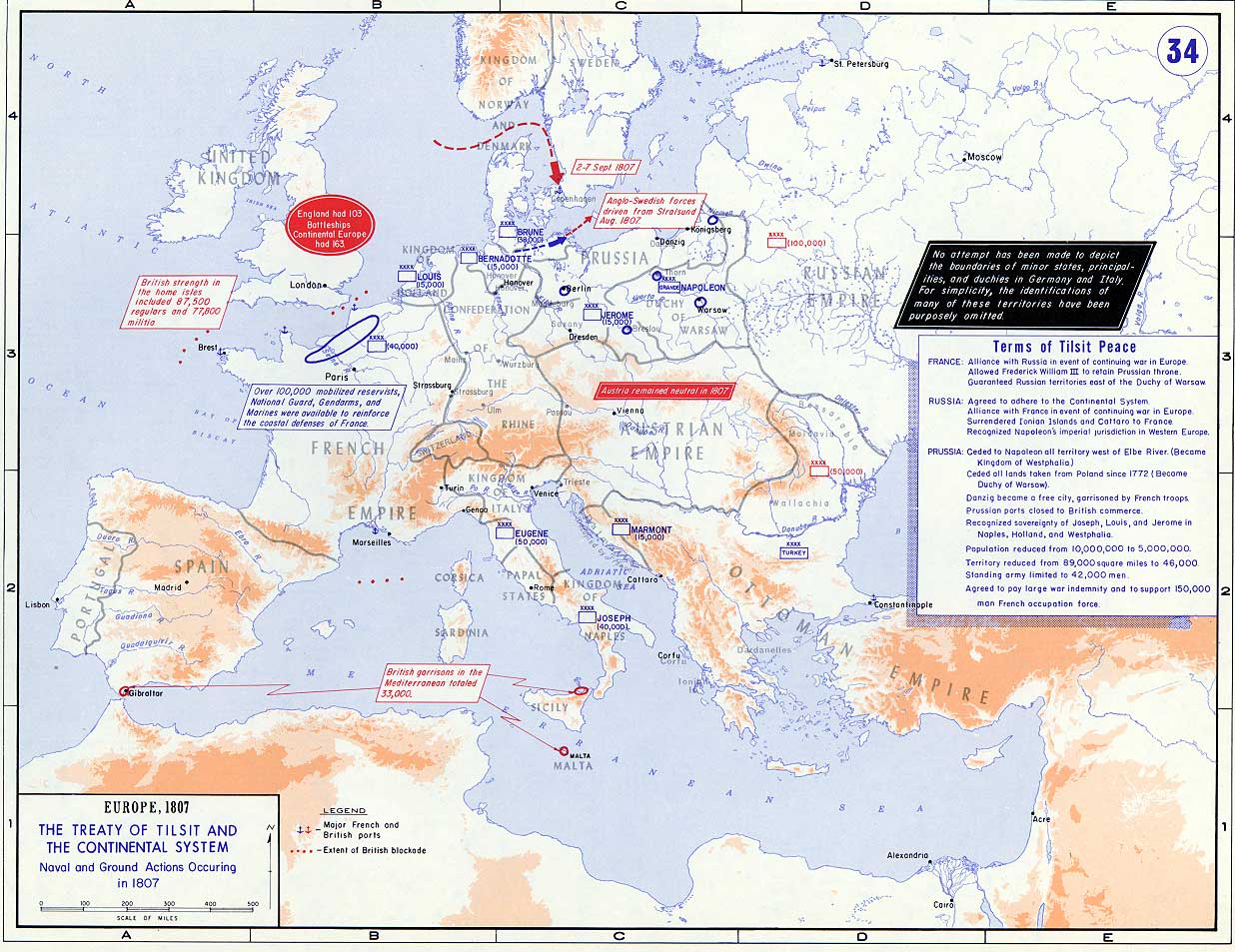
**War of the Fourth Coalition
The Fourth Coalition fought against Napoleon's French Empire and were defeated in a war spanning 1806–1807. The main coalition partners were Prussia and Russia with Saxony, Sweden, and Great Britain also contributing. Excluding Prussia, s ...
(1806–1807)
**Gunboat War
The Gunboat War (, ; 1807–1814) was a naval conflict between Denmark–Norway and the British during the Napoleonic Wars. The war's name is derived from the Danish tactic of employing small gunboats against the materially superior Royal Na ...
(1807–1814)
**Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain ...
(1808–1814)
**War of the Fifth Coalition
The War of the Fifth Coalition was a European conflict in 1809 that was part of the Napoleonic Wars and the Coalition Wars. The main conflict took place in central Europe between the Austrian Empire of Francis II, Holy Roman Emperor, Francis ...
(1809)
** French invasion of Russia (1812)
**War of the Sixth Coalition
In the War of the Sixth Coalition (March 1813 – May 1814), sometimes known in Germany as the Wars of Liberation, a coalition of Austria, Prussia, Russia, Spain, the United Kingdom, Portugal, Sweden, and a number of German States defeated F ...
(1812–1814)
**Hundred Days
The Hundred Days (french: les Cent-Jours ), also known as the War of the Seventh Coalition, marked the period between Napoleon's return from eleven months of exile on the island of Elba to Paris on20 March 1815 and the second restoration ...
(1815)
* Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
(1806–1812)
* Anglo-Turkish War (1807–1809)
* Anglo-Russian War (1807–1812)
* Finnish War
The Finnish War ( sv, Finska kriget, russian: Финляндская война, fi, Suomen sota) was fought between the Gustavian era, Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809 as part of the Napoleonic ...
(1808–1809)
* War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
(1812–1815)
* Swedish-Norwegian War (1814)
Major battles
*Battle of Marengo
The Battle of Marengo was fought on 14 June 1800 between French forces under the First Consul Napoleon Bonaparte and Austrian forces near the city of Alessandria, in Piedmont, Italy. Near the end of the day, the French overcame General Mich ...
– 14 June 1800
* Battle of Abukir – 8 March 1801
* Battle of Alexandria -21 March 1801
* Battle of Copenhagen – 2 April 1801
*Battle of Trafalgar
The Battle of Trafalgar (21 October 1805) was a naval engagement between the British Royal Navy and the combined fleets of the French and Spanish Navies during the War of the Third Coalition (August–December 1805) of the Napoleonic Wars (180 ...
– 21 October 1805
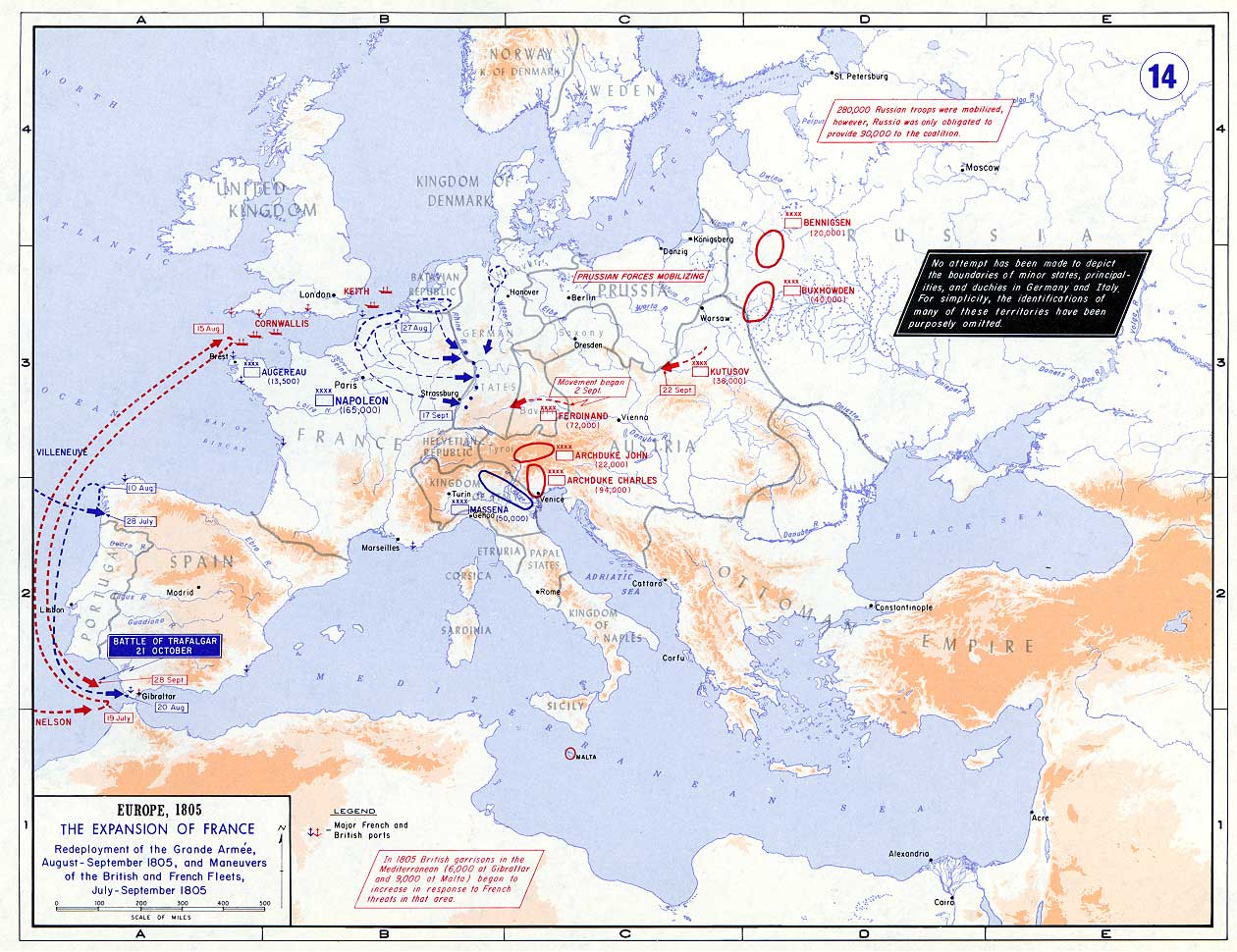
*Battle of Austerlitz
The Battle of Austerlitz (2 December 1805/11 Frimaire An XIV FRC), also known as the Battle of the Three Emperors, was one of the most important and decisive engagements of the Napoleonic Wars. The battle occurred near the town of Austerlitz i ...
– 2 December 1805
*Battle of Jena-Auerstedt
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
– 14 October 1806
*Battle of Eylau
The Battle of Eylau, or Battle of Preussisch-Eylau, was a bloody and strategically inconclusive battle on 7 and 8 February 1807 between Napoléon's '' Grande Armée'' and the Imperial Russian Army under the command of Levin August von Benn ...
– 7–8 February 1807
*Battle of Friedland
The Battle of Friedland (14 June 1807) was a major engagement of the Napoleonic Wars between the armies of the French Empire commanded by Napoleon I and the armies of the Russian Empire led by Count von Bennigsen. Napoleon and the French obtai ...
– 14 June 1807
*Battle of Vimeiro
In the Battle of Vimeiro (sometimes shown as "Vimiera" or "Vimeira" in contemporary British texts) on 21 August 1808, the British under General Arthur Wellesley (who later became the Duke of Wellington) defeated the French under Major-Gene ...
– 21 August 1808
*Battle of Somosierra
The Battle of Somosierra took place on 30 November 1808, during the Peninsular War, when a combined Franco-Spanish- Polish force under the direct command of Napoleon Bonaparte forced a passage through a Spanish Divison stationed at the Si ...
– 30 November 1808
*Battle of Eckmühl
The Battle of Eckmühl, fought on 22 April 1809, was the turning point of the 1809 Campaign, also known as the War of the Fifth Coalition. Napoleon I had been unprepared for the start of hostilities on 10 April 1809, by the Austrians under th ...
– 21–22 April 1809
*Battle of Aspern-Essling
In the Battle of Aspern-Essling (21–22 May 1809), Napoleon crossed the Danube near Vienna, but the French and their allies were attacked and forced back across the river by the Austrians under Archduke Charles. It was the first time Napoleon ...
– 21–22 May 1809
*Battle of Wagram
The Battle of Wagram (; 5–6 July 1809) was a military engagement of the Napoleonic Wars that ended in a costly but decisive victory for Emperor Napoleon's French and allied army against the Austrian army under the command of Archduke Charles ...
– 5–6 July 1809
*Battle of Talavera
The Battle of Talavera (27–28 July 1809) was fought just outside the town of Talavera de la Reina, Spain some southwest of Madrid, during the Peninsular War. At Talavera, a British army under Sir Arthur Wellesley combined with a Spanish a ...
– 27–28 July 1809
*Battle of Salamanca
The Battle of Salamanca (in French and Spanish known as the Battle of Arapiles) on 22July 1812 was a battle in which an Anglo-Portuguese army under the Earl of Wellington defeated Marshal Auguste Marmont's French forces at Arapiles, ...
– 22 July 1812
* Battle of Borodino – 7 September 1812
* Battle of Lützen – 2 May 1813
* Battle of Bautzen – 20–21 May 1813
*Battle of Vitoria
At the Battle of Vitoria (21 June 1813) a British, Portuguese and Spanish army under the Marquess of Wellington broke the French army under King Joseph Bonaparte and Marshal Jean-Baptiste Jourdan near Vitoria in Spain, eventually leadin ...
– 21 June 1813
* Battle of Dresden – 26–27 August 1813
* Battle of Leipzig – 16–19 October 1813
* Battle of Paris – 30–31 March 1814
*Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
– 18 June 1815
See also
*'' First Empire: The International Magazine for the Napoleonic Enthusiast, Historian, and Gamer'' (magazine)References
The Napoleonic era
at Britannica {{DEFAULTSORT:Napoleonic era Napoleon First French Empire French Revolution Modern history of France Historical eras