|
Sulfonylurea
Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas. A number of sulfonylureas are also used as herbicides, because they can interfere with plant biosynthesis of certain amino acids. Sulfonylureas are also used experimentally to inhibit interleukin 1 beta release from the NALP3 (or NLRP3) inflammasome. Drugs * First-generation drugs include acetohexamide, carbutamide, chlorpropamide, glycyclamide (tolcyclamide), metahexamide, tolazamide and tolbutamide. * Second-generation drugs include glibenclamide (glyburide), glibornuride, gliclazide, glipizide, gliquidone, glisoxepide and glyclopyramide. * Third-generation drugs include glimepiride, although it is sometimes considered a second-generation agent. Medical uses Sulfonylureas are used primarily for the treatment of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonylurea Group And Radicals
Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas. A number of sulfonylureas are also used as herbicides, because they can interfere with plant biosynthesis of certain amino acids. Sulfonylureas are also used experimentally to inhibit interleukin 1 beta release from the NALP3 (or NLRP3) inflammasome. Drugs * First-generation drugs include acetohexamide, carbutamide, chlorpropamide, glycyclamide (tolcyclamide), metahexamide, tolazamide and tolbutamide. * Second-generation drugs include glibenclamide (glyburide), glibornuride, gliclazide, glipizide, gliquidone, glisoxepide and glyclopyramide. * Third-generation drugs include glimepiride, although it is sometimes considered a second-generation agent. Medical uses Sulfonylureas are used primarily for the treatment of d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antidiabetic Drugs
Drugs used in diabetes treat diabetes mellitus by altering the glucose level in the blood. With the exceptions of insulin, most GLP receptor agonists (liraglutide, exenatide, and others), and pramlintide, all are administered orally and are thus also called oral hypoglycemic agents or oral antihyperglycemic agents. There are different classes of anti-diabetic drugs, and their selection depends on the nature of the diabetes, age and situation of the person, as well as other factors. Diabetes mellitus type 1 is a disease caused by the lack of insulin. Insulin must be used in type 1, which must be injected. Diabetes mellitus type 2 is a disease of insulin resistance by cells. Type 2 diabetes mellitus is the most common type of diabetes. Treatments include agents that (1) increase the amount of insulin secreted by the pancreas, (2) increase the sensitivity of target organs to insulin, (3) decrease the rate at which glucose is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and (4) incre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
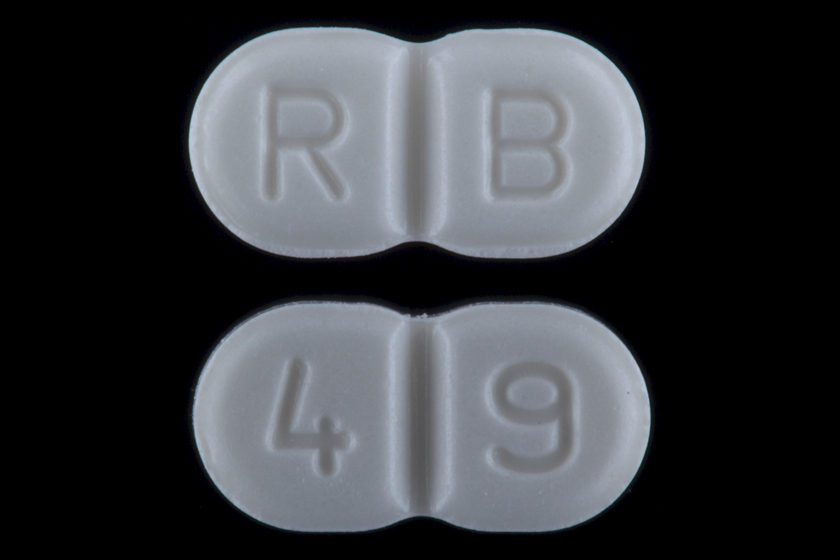
Gliclazide
Gliclazide, sold under the brand name Diamicron among others, is a sulfonylurea type of anti-diabetic medication, used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is used when dietary changes, exercise, and weight loss are not enough. It is taken by mouth. Side effect may include low blood sugar, vomiting, abdominal pain, rash, and liver problems. Use by those with significant kidney problems or liver problems or who are pregnant is not recommended. Gliclazide is in the sulfonylurea family of medications. It works mostly by increasing the release of insulin. Gliclazide was patented in 1966 and approved for medical use in 1972. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. It is not available for sale in the United States. Medical uses Gliclazide is used for control of hyperglycemia in gliclazide-responsive diabetes mellitus of stable, mild, non- ketosis prone, type 2 diabetes. It is used when diabetes cannot be controlled by proper dietary management and exercise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolbutamide
Tolbutamide is a first-generation potassium channel blocker, sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic medication. This drug may be used in the management of type 2 diabetes if diet alone is not effective. Tolbutamide stimulates the secretion of insulin by the pancreas. It is not routinely used due to a higher incidence of adverse effects compared to newer, second-generation sulfonylureas, such as Glibenclamide. It generally has a short duration of action due to its rapid metabolism, so is safe for use in older people. It was discovered in 1956. Side effects # Hypoglycemia # Weight gain # Hypersensitivity: cross-allergicity with sulfonamides # Drug interactions (especially first-generation drugs): Increased hypoglycemia with cimetidine, insulin, salicylates, and sulfonamides Salicylates displace tolbutamide from its binding site on plasma binding proteins which lead to increase in free tolbutamide concentration, thus hypoglycemic shock. History Orinase was developed by Upjohn Co. at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorpropamide
Chlorpropamide is a drug in the sulfonylurea class used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2. It is a long-acting first-generation sulfonylurea. Mechanism of action Like other sulfonylureas, chlorpropamide acts to increase the secretion of insulin, so it is only effective in patients who have some pancreas, pancreatic beta cell function. It can cause relatively long episodes of hypoglycemia; this is one reason why shorter-acting sulfonylureas such as gliclazide or tolbutamide are used instead. The risk of hypoglycemia makes this drug a poor choice for the Old age, elderly and patients with mild to moderate liver, hepatic and kidney, renal impairment. Chlorpropamide is also used in partial central diabetes insipidus. Pharmacokinetics Cmax (pharmacology), Maximal plasma concentrations are reached 3 to 5 hours after quick and nearly complete (>90%) resorption from the gut. Blood plasma, Plasma half life is 36 hours; the drug is effective for about 24 hours, longer than other sulfonylur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herbicide
Herbicides (, ), also commonly known as weedkillers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds.EPA. February 201Pesticides Industry. Sales and Usage 2006 and 2007: Market Estimates. Summary in press releasMain page for EPA reports on pesticide use ihere Selective herbicides control specific weed species, while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides (sometimes called total weedkillers in commercial products) can be used to clear waste ground, industrial and construction sites, railways and railway embankments as they kill all plant material with which they come into contact. Apart from selective/non-selective, other important distinctions include ''persistence'' (also known as ''residual action'': how long the product stays in place and remains active), ''means of uptake'' (whether it is absorbed by above-ground foliage only, through the roots, or by other means), and ''mechanism of action'' (how it works). Historica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glimepiride
Glimepiride, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is less preferred than metformin. Use is recommended together with diet and exercise. It is taken by mouth. Glimepiride takes up to three hours for maximum effect and lasts for about a day. Common side effects include headache, nausea, and dizziness. Serious side effects may include low blood sugar. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended. It works mainly by increasing the amount of insulin released from the pancreas. It is classified as a second-generation sulfonylurea. Glimepiride was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1995. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 87th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 8million prescriptions. Medical uses Glimepiride is indicated to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus; its mode of action is to increase insulin secretion by the pancreas. However it requires adequate insulin syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gliquidone
Gliquidone (INN, sold under the trade name Glurenorm) is an anti-diabetic medication in the sulfonylurea class. It is classified as a second-generation sulfonylurea. It is used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus type 2. It is marketed by the pharmaceutical company Boehringer Ingelheim (Germany). Contraindications * Allergy to sulfonylureas or sulfonamides * Diabetes mellitus type 1 * Diabetic ketoacidosis * Patients that underwent removal of the pancreas * Acute porphyria * Severe liver disease accompanying with liver insufficiency * Several conditions (e.g., infectious diseases or major surgical intervention), when insulin administration is required * Pregnancy or breastfeeding Pharmacokinetics Gliquidone is fully metabolized by the liver. Its metabolites are excreted virtually completely with bile (even with long-term administration), thus allowing the use of medication in diabetic patients with kidney disease and diabetic nephropathy Diabetic nephropathy, also known as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tolazamide
Tolazamide is an Wiktionary:oral, oral blood glucose lowering medication, drug used for people with Type 2 diabetes. It is part of the sulfonylurea (medicine), sulfonylurea family (ATC A10BB). Synthesis para-toluenesulfonamide, ''para''-Toluenesulfonamide is converted to its carbamate with ethyl chloroformate in the presence of a base. Heating that intermediate with 1-amino-azepane leads to the displacement of the ethoxy group and the formation of tolazemide: Azepane proper would lead to [13078-23-4]. References External links * Potassium channel blockers Benzenesulfonylureas Azepanes p-Tosyl compounds {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glisoxepide
Glisoxepide (INN) is an orally available anti-diabetic drug from the group of sulfonylurea Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the bet ...s. It belongs to second-generation sulfonylureas. References Potassium channel blockers Azepanes Carboxamides Isoxazoles Benzenesulfonylureas {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbutamide
Carbutamide (brand name Glucidoral) is an anti-diabetic drug of the sulfonylurea class, developed by Servier. It is classified as first-generation. It was patented in 1953 and approved for medical use in 1956. See also * Hellmuth Kleinsorge Hellmuth Kleinsorge (* 12 April 1920 in Beuel; † 7 July 2001) was a German medical doctor. Life Hellmuth Kleinsorge studied medicine in Jena. In 1953, after his dissertation and habilitation, he became director of the "Medizinische Poliklinik ... (1920-2001) German medical doctor References Potassium channel blockers Benzenesulfonylureas Anilines {{gastrointestinal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glibenclamide
Glibenclamide, also known as glyburide, is an antidiabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is recommended that it be taken together with diet and exercise. It may be used with other antidiabetic medication. It is not recommended for use by itself in type 1 diabetes. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects include nausea and heartburn. Serious side effects may include angioedema and low blood sugar. It is generally not recommended during pregnancy but can be used during breastfeeding. It is in the sulfonylureas class of medications and works by increasing the release of insulin from the pancreas. Glibenclamide was discovered in 1969 and approved for medical use in the United States in 1984. It is available as a generic medication. In 2022, it was the 200th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 2million prescriptions. Medical uses Glibenclamide is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |