|
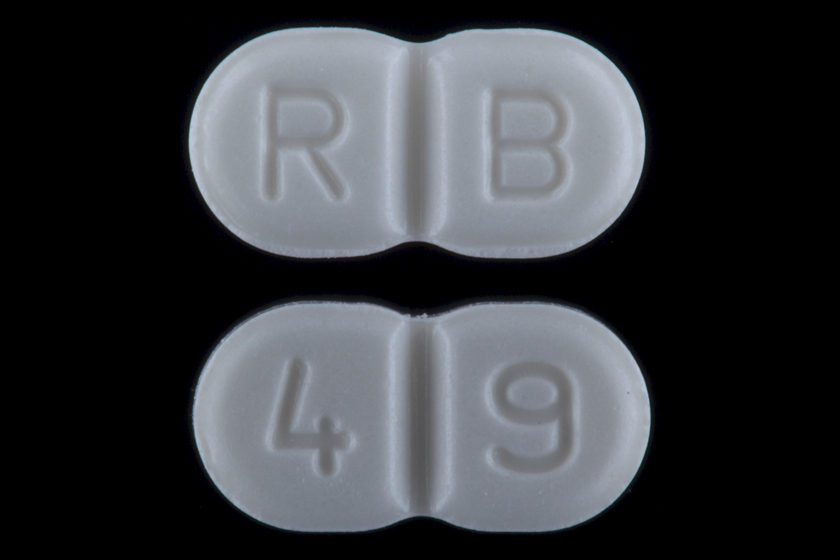
Glimepiride
Glimepiride, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is less preferred than metformin. Use is recommended together with diet and exercise. It is taken by mouth. Glimepiride takes up to three hours for maximum effect and lasts for about a day. Common side effects include headache, nausea, and dizziness. Serious side effects may include low blood sugar. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended. It works mainly by increasing the amount of insulin released from the pancreas. It is classified as a second-generation sulfonylurea. Glimepiride was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1995. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 87th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 8million prescriptions. Medical uses Glimepiride is indicated to treat Diabetes mellitus type 2, type 2 diabetes mellitus; its mode of action is to increase insulin secretion by the pancreas. However it req ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glimepiride 2 MG Oral Tablet
Glimepiride, is an anti-diabetic medication used to treat type 2 diabetes. It is less preferred than metformin. Use is recommended together with diet and exercise. It is taken by mouth. Glimepiride takes up to three hours for maximum effect and lasts for about a day. Common side effects include headache, nausea, and dizziness. Serious side effects may include low blood sugar. Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding is not recommended. It works mainly by increasing the amount of insulin released from the pancreas. It is classified as a second-generation sulfonylurea. Glimepiride was patented in 1979 and approved for medical use in 1995. It is available as a generic medication. In 2020, it was the 87th most commonly prescribed medication in the United States, with more than 8million prescriptions. Medical uses Glimepiride is indicated to treat type 2 diabetes mellitus; its mode of action is to increase insulin secretion by the pancreas. However it requires adequate insulin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfonylureas
Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas. A number of sulfonylureas are also used as herbicides, because they can interfere with plant biosynthesis of certain amino acids. Sulfonylureas are also used experimentally to inhibit interleukin 1 beta release from the NALP3 (or NLRP3) inflammasome. Drugs * First-generation drugs include acetohexamide, carbutamide, chlorpropamide, glycyclamide (tolcyclamide), metahexamide, tolazamide and tolbutamide. * Second-generation drugs include glibenclamide (glyburide), glibornuride, gliclazide, glipizide, gliquidone, glisoxepide and glyclopyramide. * Third-generation drugs include glimepiride, although it is sometimes considered a second-generation agent. Medical uses Sulfonylureas are used primarily for the treatm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leukopenia
Leukopenia () is a decrease in the number of leukocytes (WBC). Found in the blood, they are the white blood cells, and are the body's primary defense against an infection. Thus the condition of leukopenia places individuals at increased risk of infection. Signs and symptoms Symptoms may include: * skin or mouth ulcers * sore throat * cough * difficulty in breathing * light-headedness * fever * chills * body aches. Leukopenia vs. neutropenia Neutropenia, a subtype of leukopenia, refers to a decrease in the number of circulating neutrophil granulocytes, the most abundant white blood cells. The terms ''leukopenia'' and ''neutropenia'' may occasionally be used interchangeably, as the neutrophil count is the most important indicator of infection risk. Agranulocytosis is an acute form of neutropenia. Causes Medical conditions Low white cell count may be due to acute viral infections, such as a cold or influenza. It has been associated with chemotherapy, radiation therapy, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is a condition in which an excessive amount of glucose circulates in the blood plasma. This is generally a blood sugar level higher than 11.1 mmol/L (200 mg/dL), but symptoms may not start to become noticeable until even higher values such as 13.9–16.7 mmol/L (~250–300 mg/dL). A subject with a consistent range between ~5.6 and ~7 mmol/L (100–126 mg/dL) ( American Diabetes Association guidelines) is considered slightly hyperglycemic, and above 7 mmol/L (126 mg/dL) is generally held to have diabetes. For diabetics, glucose levels that are considered to be too hyperglycemic can vary from person to person, mainly due to the person's renal threshold of glucose and overall glucose tolerance. On average, however, chronic levels above 10–12 mmol/L (180–216 mg/dL) can produce noticeable organ damage over time. Signs and symptoms The degree of hyperglycemia can change over time depending on the metabolic cause, for example, impaired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenytoin
Phenytoin (PHT), sold under the brand name Dilantin among others, is an anti-seizure medication. It is useful for the prevention of tonic-clonic seizures (also known as grand mal seizures) and focal seizures, but not absence seizures. The intravenous form, fosphenytoin, is used for status epilepticus that does not improve with benzodiazepines. It may also be used for certain heart arrhythmias or neuropathic pain. It can be taken intravenously or by mouth. The intravenous form generally begins working within 30 minutes and is effective for roughly 24 hours. Blood levels can be measured to determine the proper dose. Common side effects include nausea, stomach pain, loss of appetite, poor coordination, increased hair growth, and enlargement of the gums. Potentially serious side effects include sleepiness, self harm, liver problems, bone marrow suppression, low blood pressure, and toxic epidermal necrolysis. There is evidence that use during pregnancy results in abnormalities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diuretic
A diuretic () is any substance that promotes diuresis, the increased production of urine. This includes forced diuresis. A diuretic tablet is sometimes colloquially called a water tablet. There are several categories of diuretics. All diuretics increase the excretion of water from the body, through the kidneys. There exist several classes of diuretic, and each works in a distinct way. Alternatively, an antidiuretic, such as vasopressin ( antidiuretic hormone), is an agent or drug which reduces the excretion of water in urine. Medical uses In medicine, diuretics are used to treat heart failure, liver cirrhosis, hypertension, influenza, water poisoning, and certain kidney diseases. Some diuretics, such as acetazolamide, help to make the urine more alkaline, and are helpful in increasing excretion of substances such as aspirin in cases of overdose or poisoning. Diuretics are sometimes abused by people with an eating disorder, especially people with bulimia nervosa, with the goa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thiazide
Thiazide () refers to both a class of sulfur-containing organic molecules and a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine. The thiazide drug class was discovered and developed at Merck and Co. in the 1950s. The first approved drug of this class, chlorothiazide, was marketed under the trade name Diuril beginning in 1958. In most countries, thiazides are the least expensive antihypertensive drugs available. Thiazide organic molecules are bi-cyclic structures that contain adjacent sulfur and nitrogen atoms on one ring. Confusion sometimes occurs because thiazide-like diuretics such as indapamide are referred to as thiazides despite not having the thiazide chemical structure. When used this way, "thiazide" refers to a drug which acts at the thiazide receptor. The thiazide receptor is a sodium-chloride transporter that pulls NaCl from the lumen in the distal convoluted tubule. Thiazide diuretics inhibit this receptor, causing the body to release ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hypoglycemic
Hypoglycemia, also called low blood sugar, is a fall in blood sugar to levels below normal, typically below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L). Whipple's triad is used to properly identify hypoglycemic episodes. It is defined as blood glucose below 70 mg/dL (3.9 mmol/L), symptoms associated with hypoglycemia, and resolution of symptoms when blood sugar returns to normal. Hypoglycemia may result in headache, tiredness, clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, fast heart rate, sweating, shakiness, nervousness, hunger, loss of consciousness, seizures, or death. Symptoms typically come on quickly. The most common cause of hypoglycemia is medications used to treat diabetes such as insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, recently exercised, or consumed alcohol. Other causes of hypoglycemia include severe illness, sepsis, kidney failure, liver disease, hormone deficiency, tumors such as insulinomas or non-B cell tumor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Probenecid
Probenecid, also sold under the brand name Probalan, is a medication that increases uric acid excretion in the urine. It is primarily used in treating gout and hyperuricemia. Probenecid was developed as an alternative to caronamide to competitively inhibit renal excretion of some drugs, thereby increasing their plasma concentration and prolonging their effects. Medical uses Probenecid is primarily used to treat gout and hyperuricemia. Probenecid is sometimes used to increase the concentration of some antibiotics and to protect the kidneys when given with cidofovir. Specifically, a small amount of evidence supports the use of intravenous cefazolin once rather than three times a day when it is combined with probenecid. It has also found use as a masking agent, potentially helping athletes using performance-enhancing substances to avoid detection by drug tests. Adverse effects Mild symptoms such as nausea, loss of appetite, dizziness, vomiting, headache, sore gums, or frequen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coumadin
Warfarin, sold under the brand name Coumadin among others, is a medication that is used as an anticoagulant (blood thinner). It is commonly used to prevent blood clots such as deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism, and to prevent stroke in people who have atrial fibrillation, valvular heart disease, or artificial heart valves. Less commonly, it is used following ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction and orthopedic surgery. It is generally taken by mouth, but may also be used intravenously. The common side effect is bleeding. Less common side effects may include areas of tissue damage and purple toes syndrome. Use is not recommended during pregnancy. The effects of warfarin typically should be monitored by checking prothrombin time (INR) every one to four weeks. Many other medications and dietary factors can interact with warfarin, either increasing or decreasing its effectiveness. The effects of warfarin may be reversed with phytomenadione (vitamin K1), f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chloramphenicol
Chloramphenicol is an antibiotic An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting pathogenic bacteria, bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the therapy, ... useful for the treatment of a number of bacterial infections. This includes use as an eye ointment to treat conjunctivitis. By mouth or by intravenous, injection into a vein, it is used to treat meningitis, plague (disease), plague, cholera, and typhoid fever. Its use by mouth or by injection is only recommended when safer antibiotics cannot be used. Monitoring both blood levels of the medication and blood cell levels every two days is recommended during treatment. Common side effects include bone marrow suppression, nausea, and diarrhea. The bone marrow suppression may result in death. To reduce the risk of side effects treatment duration should be as short as possible. People with liver or kidne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |