|
Subsequent Nuremberg Trials
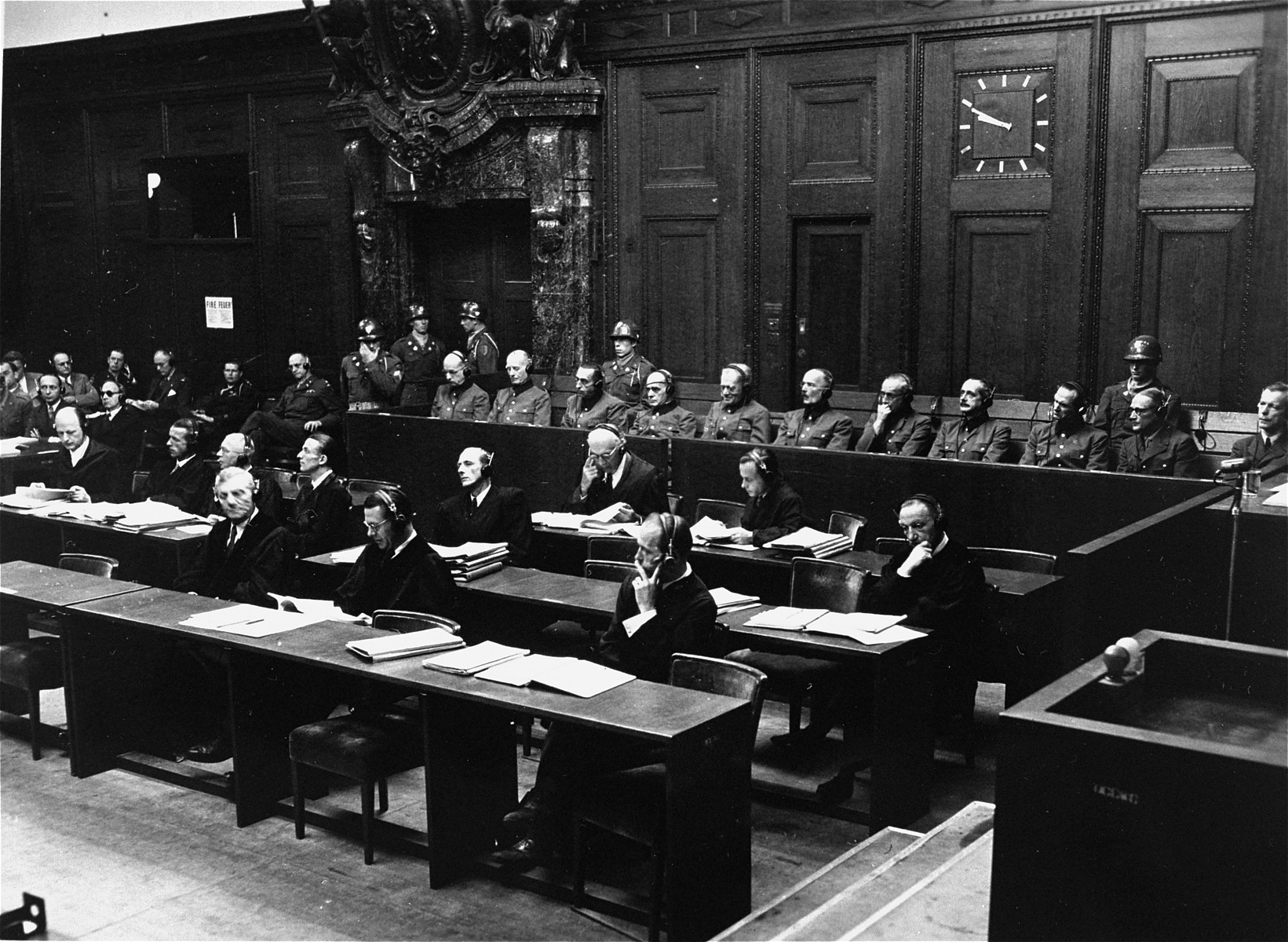
The subsequent Nuremberg trials were a series of 12 military tribunals for war crimes against members of the leadership of Nazi Germany between December 1946 and April 1949. They followed the first and best-known Nuremberg trial before the International Military Tribunal which concluded in October 1946. In contrast, the subsequent trials were conducted before U.S. military courts rather than an international court. They are also collectively known as the Nuremberg Military Tribunals. These trials dealt with German industrialists accused of using slave labor and plundering occupied countries, and high-ranking army officers accused of atrocities against prisoners of war. The subsequent trials were held in the same location, at the Palace of Justice in Nuremberg. Background Although it had been initially planned to hold more than just one international trial at the IMT, the growing differences between the victors of the second world war (the United States, United Kingdom, Fran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judges Of The Nuremberg Military Tribunals
A judge is an official who presides over a court. Judge or Judges may also refer to: Roles *Judge, an alternative name for an adjudicator in a competition in theatre, music, sport, etc. *Judge, an alternative name/aviator call sign for a member of the Judge Advocate General's Corps, U.S. Navy *Judge, an alternative name for a sports linesman, referee or umpire * Biblical judges, an office of authority in the early history of Israel Places * Judge, Minnesota, a community in the United States * Judge, Missouri, a community in the United States * The Judge (British Columbia), a mountain in the Columbia Mountains of Canada People * Judge (surname) * Judge Jules, professional name of British DJ and record producer Julius O'Riordan Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional characters * Judge (Buffyverse), a demon in the television series ''Buffy The Vampire Slayer'' * Archadian Judges, from the game ''Final Fantasy XII'' * Judge Holden, from Cormac McCarthy's novel ''Bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
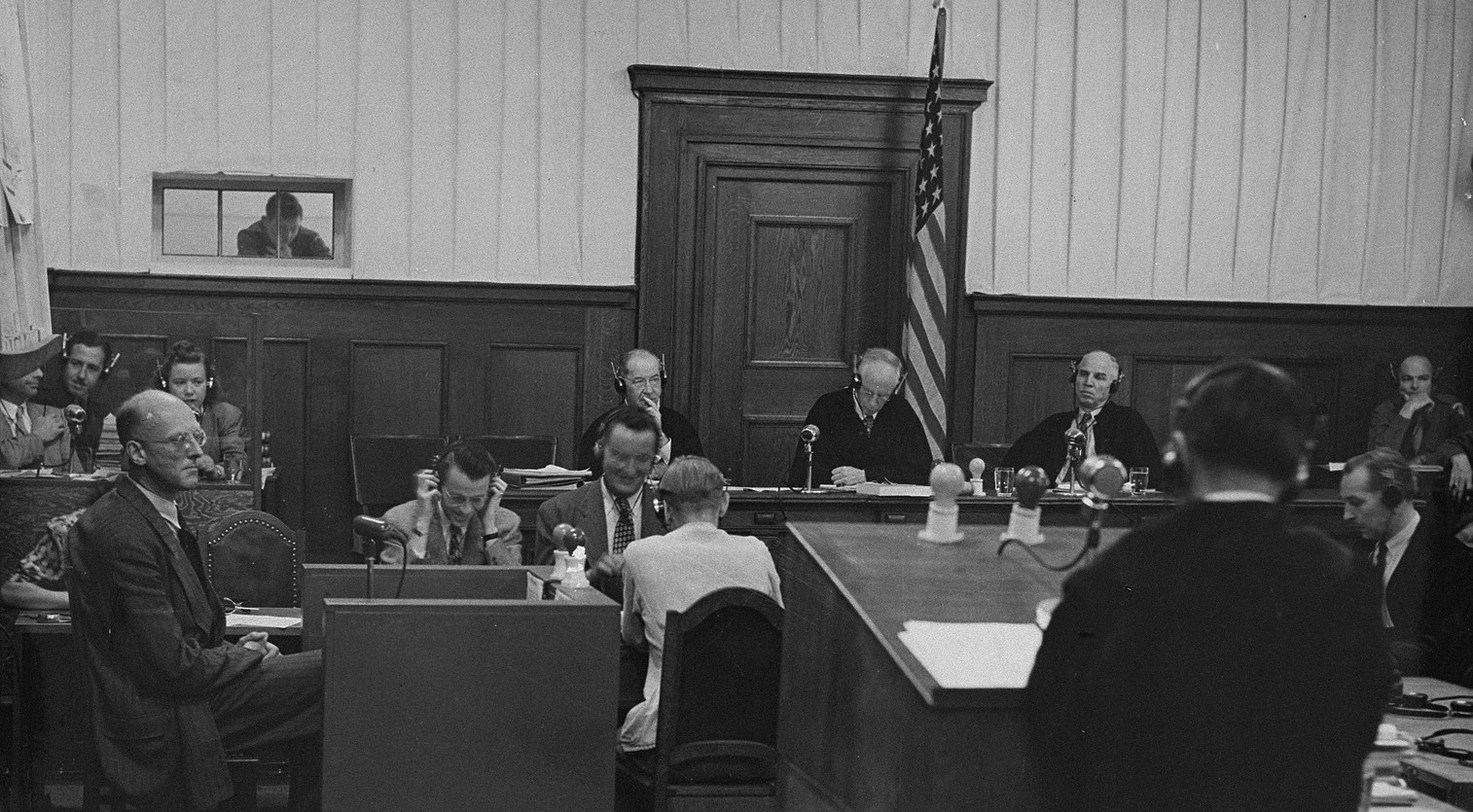
Judges' Trial
The Judges' Trial (; or, the Justice Trial, or, officially, ''The United States of America vs. Josef Altstötter, et al.'') was the third of the 12 trials for war crimes the U.S. authorities held in their occupation zone in Germany in Nuremberg after the end of World War II. These twelve trials were all held before U.S. military courts, not before the International Military Tribunal, but took place in the same rooms at the Palace of Justice. The twelve U.S. trials are collectively known as the "Subsequent Nuremberg Trials" or, more formally, as the "Trials of War Criminals before the Nuremberg Military Tribunals" (NMT). The defendants in this case were 16 German jurists and lawyers. Nine had been officials of the Reich Ministry of Justice, the others were prosecutors and judges of the Special Courts and People's Courts of Nazi Germany. They were—amongst other charges—held responsible for implementing and furthering the Nazi "racial purity" program through the eugenic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Einsatzgruppen
(, ; also ' task forces') were (SS) paramilitary death squads of Nazi Germany that were responsible for mass murder, primarily by shooting, during World War II (1939–1945) in German-occupied Europe. The had an integral role in the implementation of the so-called "Final Solution to the Jewish question" () in territories conquered by Nazi Germany, and were involved in the murder of much of the intelligentsia and cultural elite of Poland, including members of the Catholic priesthood. Almost all of the people they murdered were civilians, beginning with the intelligentsia and swiftly progressing to Soviet political commissars, Jews, and Romani people, as well as actual or alleged partisans throughout Eastern Europe. Under the direction of Heinrich Himmler and the supervision of SS- Reinhard Heydrich, the operated in territories occupied by the Wehrmacht (German armed forces) following the invasion of Poland in September 1939 and the invasion of the Soviet Union in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
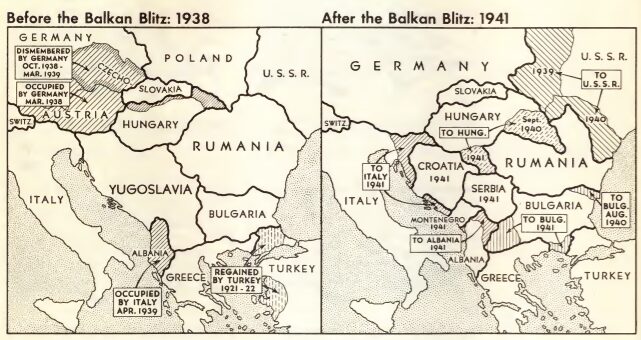
Balkan Campaign (World War II)
The Balkans campaign of World War II began with the Italian invasion of Greece on 28 October 1940. In the early months of 1941, Italy's offensive had stalled and a Greek counter-offensive pushed into Albania. Germany sought to aid Italy by deploying troops to Romania and Bulgaria and attacking Greece from the east. Meanwhile, the British landed troops and aircraft to shore up Greek defences. A ''coup d'état'' in Yugoslavia on 27 March caused Adolf Hitler to order the conquest of that country. The invasion of Yugoslavia by Germany and Italy began on 6 April 1941, simultaneously with the new Battle of Greece; on 11 April, Hungary joined the invasion. By 17 April the Yugoslavs had signed an armistice, and by 30 April all of mainland Greece was under German or Italian control. On 20 May Germany invaded Crete by air, and by 1 June all remaining Greek and British forces on the island had surrendered. Although it had not participated in the attacks in April, Bulgaria occupied pa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hostages Trial
The Hostages Trial (or, officially, ''The United States of America v. Wilhelm List, et al.'') was held from 8 July 1947 until 19 February 1948 and was the seventh of the twelve trials for war crimes that United States authorities held in their occupation zone in Germany in Nuremberg after the end of World War II. These twelve trials were all held before US military courts, not before the International Military Tribunal, but took place in the same rooms at the Palace of Justice. The twelve US trials are collectively known as the "Subsequent Nuremberg Trials" or, more formally, as the "Trials of War Criminals before the Nuremberg Military Tribunals" (NMT). This case is also known as the "Southeast Case" because all of the defendants had once been German generals leading the troops in Southeastern Europe during the Balkans Campaign, i.e. in Greece, Albania and Yugoslavia; and they were charged with ordering the hostage-taking of civilians and wanton shootings of these hostages, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zyklon B
Zyklon B (; translated Cyclone B) was the trade name of a cyanide-based pesticide invented in Germany in the early 1920s. It consisted of hydrogen cyanide (prussic acid), as well as a cautionary eye irritant and one of several adsorbents such as diatomaceous earth. The product is notorious for its use by Nazi Germany during the Holocaust to murder approximately 1.1 million people in gas chambers installed at Auschwitz-Birkenau, Majdanek, and other extermination camps. Hydrogen cyanide, a poisonous gas that interferes with cellular respiration, was first used as a pesticide in California in the 1880s. Research at Degesch of Germany led to the development of Zyklon (later known as Zyklon A), a pesticide that released hydrogen cyanide upon exposure to water and heat. It was banned after World War I, when Germany used a similar product as a chemical weapon. Degussa purchased Degesch in 1922. Their team of chemists, which included and Bruno Tesch, devised a method of pack ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IG Farben
Interessengemeinschaft Farbenindustrie AG (), commonly known as IG Farben (German for 'IG Dyestuffs'), was a German chemical and pharmaceutical conglomerate. Formed in 1925 from a merger of six chemical companies— BASF, Bayer, Hoechst, Agfa, Chemische Fabrik Griesheim-Elektron, and Chemische Fabrik vorm. Weiler Ter Meer—it was seized by the Allies after World War II and divided back into its constituent companies. IG Farben was once the largest company in Europe and the largest chemical and pharmaceutical company in the world. IG Farben scientists made fundamental contributions to all areas of chemistry and the pharmaceutical industry. Otto Bayer discovered the polyaddition for the synthesis of polyurethane in 1937, and three company scientists became Nobel laureates: Carl Bosch and Friedrich Bergius in 1931 "for their contributions to the invention and development of chemical high pressure methods", and Gerhard Domagk in 1939 "for the discovery of the antibacterial ef ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IG Farben Trial
''The United States of America vs. Carl Krauch, et al.'', also known as the IG Farben Trial, was the sixth of the twelve trials for war crimes the U.S. authorities held in their occupation zone in Germany (Nuremberg) after the end of World War II. IG Farben was the private German chemicals company allied with the Nazis that manufactured the Zyklon B gas used to commit genocide against millions of European Jews in the Holocaust. The twelve trials were all held before U.S. military courts, not before the International Military Tribunal, but took place in the same rooms at the Palace of Justice. The twelve U.S. trials are collectively known as the "Subsequent Nuremberg Trials" or, more formally, as the "Trials of War Criminals before the Nuremberg Military Tribunals" (NMT). The IG Farben Trial was the second of three trials of leading industrialists of Nazi Germany for their conduct during the Nazi regime. (The two other industrialist trials were the Flick Trial and the Krupp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Flick
Friedrich Flick (10 July 1883 – 20 July 1972) was a German industrialist and convicted Nazi war criminal. After the Second World War, he reconstituted his businesses, becoming the richest person in West Germany, and one of the richest people in the world, at the time of his death in 1972. Early life Born in Ernsdorf (today, Kreuztal) in the Prussian Province of Westphalia, Flick began his career as a clerk in the iron industry. A shrewd businessman, he was on the Board of Directors of an iron foundry by 1915 at age 32, becoming General Director four years later. He amassed a fortune during World War I and became extremely wealthy under the Weimar Republic, establishing major industrial concerns in the coal and steel industries. He profited from speculation, and stock deals. A conservative, he donated to many different mainstream political parties under the Weimar regime, and contributed greatly to the election campaign of conservative President Paul von Hindenburg. In 1932, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |