|
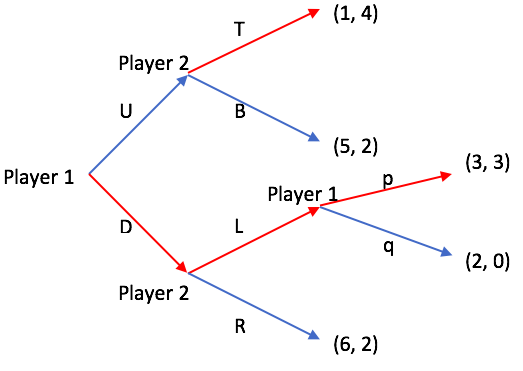
Subgame
In game theory, a subgame is any part (a subset) of a game that meets the following criteria (the following terms allude to a game described in extensive form): #It has a single initial node that is the only member of that node's information set (i.e. the initial node is in a singleton information set). #If a node is contained in the subgame then so are all of its successors. #If a node in a particular information set is in the subgame then all members of that information set belong to the subgame. It is a notion used in the solution concept of subgame perfect Nash equilibrium, a refinement of the Nash equilibrium that eliminates non-credible threats. The key feature of a subgame is that it, when seen in isolation, constitutes a game in its own right. When the initial node of a subgame is reached in a larger game, players can concentrate only on that subgame; they can ignore the history of the rest of the game (provided they know what subgame they are playing). This is the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subgame Perfect Equilibrium
In game theory, a subgame perfect equilibrium (SPE), or subgame perfect Nash equilibrium (SPNE), is a refinement of the Nash equilibrium concept, specifically designed for dynamic games where players make sequential decisions. A strategy profile is an SPE if it represents a Nash equilibrium in every possible subgame of the original game. Informally, this means that at any point in the game, the players' behavior from that point onward should represent a Nash equilibrium of the continuation game (i.e. of the subgame), no matter what happened before. This ensures that strategies are credible and rational throughout the entire game, eliminating non-credible threats. Every finite extensive game with complete information (all players know the complete state of the game) and perfect recall (each player remembers all their previous actions and knowledge throughout the game) has a subgame perfect equilibrium. A common method for finding SPE in finite games is backward induction, wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solution Concept
In game theory, a solution concept is a formal rule for predicting how a game will be played. These predictions are called "solutions", and describe which strategies will be adopted by players and, therefore, the result of the game. The most commonly used solution concepts are equilibrium concepts, most famously Nash equilibrium. Many solution concepts, for many games, will result in more than one solution. This puts any one of the solutions in doubt, so a game theorist may apply a refinement to narrow down the solutions. Each successive solution concept presented in the following improves on its predecessor by eliminating implausible equilibria in richer games. Formal definition Let \Gamma be the class of all games and, for each game G \in \Gamma, let S_G be the set of strategy profiles of G. A ''solution concept'' is an element of the direct product \Pi_2^; ''i.e''., a function F: \Gamma \rightarrow \bigcup\nolimits_ 2^ such that F(G) \subseteq S_G for all G \in \Gamma. Rati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nash Equilibrium
In game theory, the Nash equilibrium is the most commonly used solution concept for non-cooperative games. A Nash equilibrium is a situation where no player could gain by changing their own strategy (holding all other players' strategies fixed). The idea of Nash equilibrium dates back to the time of Cournot, who in 1838 applied it to his model of competition in an oligopoly. If each player has chosen a strategy an action plan based on what has happened so far in the game and no one can increase one's own expected payoff by changing one's strategy while the other players keep theirs unchanged, then the current set of strategy choices constitutes a Nash equilibrium. If two players Alice and Bob choose strategies A and B, (A, B) is a Nash equilibrium if Alice has no other strategy available that does better than A at maximizing her payoff in response to Bob choosing B, and Bob has no other strategy available that does better than B at maximizing his payoff in response to Alice c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extensive Form Game
In game theory, an extensive-form game is a specification of a game allowing for the explicit representation of a number of key aspects, like the sequencing of players' possible moves, their choices at every decision point, the (possibly imperfect) information each player has about the other player's moves when they make a decision, and their payoffs for all possible game outcomes. Extensive-form games also allow for the representation of incomplete information in the form of chance events modeled as " moves by nature". Extensive-form representations differ from normal-form in that they provide a more complete description of the game in question, whereas normal-form simply boils down the game into a payoff matrix. Finite extensive-form games Some authors, particularly in introductory textbooks, initially define the extensive-form game as being just a game tree with payoffs (no imperfect or incomplete information), and add the other elements in subsequent chapters as refinements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of Human behavior, behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational Decision-making, decision making in humans, animals, and computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Information Set (game Theory)
In game theory, an information set is the basis for decision making in a game, which includes the actions available to players and the potential outcomes of each action. It consists of a collection of decision nodes that a player cannot distinguish between when making a move, due to incomplete information about previous actions or the current state of the game. In other words, when a player's turn comes, they may be uncertain about which exact node in the game tree they are currently at, and the information set represents all the possibilities they must consider. Information sets are a fundamental concept particularly important in games with imperfect information. In games with perfect information (such as chess or Go (game), Go), every information set contains exactly one decision node, as each player can observe all previous moves and knows the exact game state. However, in games with imperfect information—such as most Card game, card games like poker or Bridge (card game), bri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Game Theory
Game theory is the study of mathematical models of strategic interactions. It has applications in many fields of social science, and is used extensively in economics, logic, systems science and computer science. Initially, game theory addressed two-person zero-sum games, in which a participant's gains or losses are exactly balanced by the losses and gains of the other participant. In the 1950s, it was extended to the study of non zero-sum games, and was eventually applied to a wide range of Human behavior, behavioral relations. It is now an umbrella term for the science of rational Decision-making, decision making in humans, animals, and computers. Modern game theory began with the idea of mixed-strategy equilibria in two-person zero-sum games and its proof by John von Neumann. Von Neumann's original proof used the Brouwer fixed-point theorem on continuous mappings into compact convex sets, which became a standard method in game theory and mathematical economics. His paper was f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-credible Threat
A non-credible threat is a term used in game theory and economics to describe a threat in a sequential game that a ''rational'' player would not actually carry out, because it would not be in his best interest to do so. A threat, and its counterparta commitment, are both defined by American economist and Nobel prize winner, T.C. Schelling, who stated that: "A announces that B's behaviour will lead to a response from A. If this response is a reward, then the announcement is a commitment; if this response is a penalty, then the announcement is a threat." While a player might make a threat, it is only deemed credible if it serves the best interest of the player.Heifetz, A., & Yalon-Fortus, J. (2012). Game Theory: Interactive Strategies in Economics and Management. Cambridge University Press. ProQuest Ebook Central In other words, the player would be willing to carry through with the action that is being threatened regardless of the choice of the other player. This is based on the as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian Game
In game theory, a Bayesian game is a strategic decision-making model which assumes players have incomplete information. Players may hold private information relevant to the game, meaning that the payoffs are not common knowledge. Bayesian games model the outcome of player interactions using aspects of Bayesian probability. They are notable because they allowed the specification of the solutions to games with incomplete information for the first time in game theory. Hungarian economist John C. Harsanyi introduced the concept of Bayesian games in three papers from 1967 and 1968: He was awarded the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for these and other contributions to game theory in 1994. Roughly speaking, Harsanyi defined Bayesian games in the following way: players are assigned a set of characteristics by nature at the start of the game. By mapping probability distributions to these characteristics and by calculating the outcome of the game using Bayesian probability, the r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Singleton (mathematics)
In mathematics, a singleton (also known as a unit set or one-point set) is a set with exactly one element. For example, the set \ is a singleton whose single element is 0. Properties Within the framework of Zermelo–Fraenkel set theory, the axiom of regularity guarantees that no set is an element of itself. This implies that a singleton is necessarily distinct from the element it contains, thus 1 and \ are not the same thing, and the empty set is distinct from the set containing only the empty set. A set such as \ is a singleton as it contains a single element (which itself is a set, but not a singleton). A set is a singleton if and only if its cardinality is . In von Neumann's set-theoretic construction of the natural numbers, the number 1 is ''defined'' as the singleton \. In axiomatic set theory, the existence of singletons is a consequence of the axiom of pairing: for any set ''A'', the axiom applied to ''A'' and ''A'' asserts the existence of \, which is the same ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |