|
Subah
A Subah was the term for a province (State) in the Mughal Empire. The word is derived from Arabic and Persian. The governor/ruler of a ''Subah'' was known as a ''subahdar'' (sometimes also referred to as a "''Subeh''"), which later became ''subedar'' to refer to an officer in the Indian Army and Pakistan Army. The ''subahs'' were established by badshah (emperor) Akbar during his administrative reforms of years 1572–1580; initially they numbered to 12, but his conquests expanded the number of ''subahs'' to 15 by the end of his reign. ''Subahs'' were divided into '' Sarkars'', or districts. ''Sarkars'' were further divided into ''Parganas'' or '' Mahals''. His successors, most notably Aurangzeb, expanded the number of ''subahs'' further through their conquests. As the empire began to dissolve in the early 18th century, many ''subahs'' became effectively independent, or were conquered by the Marathas or the British. In modern context subah ( ur, ) is a word used for province in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subah Of Lahore
The Subah of Lahore was a province of the Mughal Empire encompassing the central Punjab region, now divided between Pakistan and India. It was created as one of the original 12 Subahs of the Mughal Empire under the administrative reforms carried by emperor Akbar in 1580. The province ceased to exist after the death of its last viceroy, Adina Beg in 1758, with large parts being incorporated into Durrani Empire. Geography The subah of Lahore was bordered on the south by the Multan Subah and Delhi Subah, to the north by Kashmir Subah, to the west by the Kabul Subah, and to the north east by the semi-autonomous hill states. History Establishing Mughal control In 1519, Babur first crossed the Indus river and took control of the entire Sind Sagar Doab up to Bhera and Khushab and by 1524 he had sacked Lahore. He then appointed representatives to key positions in his newly occupied territories, including Mir Abdul Aziz at Lahore. He went on to take several key hill forts such as Ku ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Province Of Sira
The Province of Sira, also known as Carnatic-Balaghat, was a subah (imperial first-level province) of the Mughal empire in South India that was established in 1687 by conquering emperor Aurangzeb (like Bijapur in 1686 and Golkonda in 1687) and lasted until 1757. The province, which comprised the Carnatic region south of the Tungabhadra river, had its capital in the town of Sira. It was composed of seven ''parganas'' (districts): Basavapatna, Budihal, Sira, Penukonda, Dod-Ballapur, Hoskote and Kolar; in addition, Harpanahalli, Kondarpi, Anegundi, Bednur, Chitaldroog and Mysore were considered by the Mughals to be tributary states of the province. Administration After the Moghul armies overran the region of the Mysore plateau, 12 parganas were annexed to the newly formed province (''subah'') of Sira. The remaining region was allowed to remain under the rule of the Poligars, who were required to pay tribute to the provincial government in Sira. In the annexed regio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
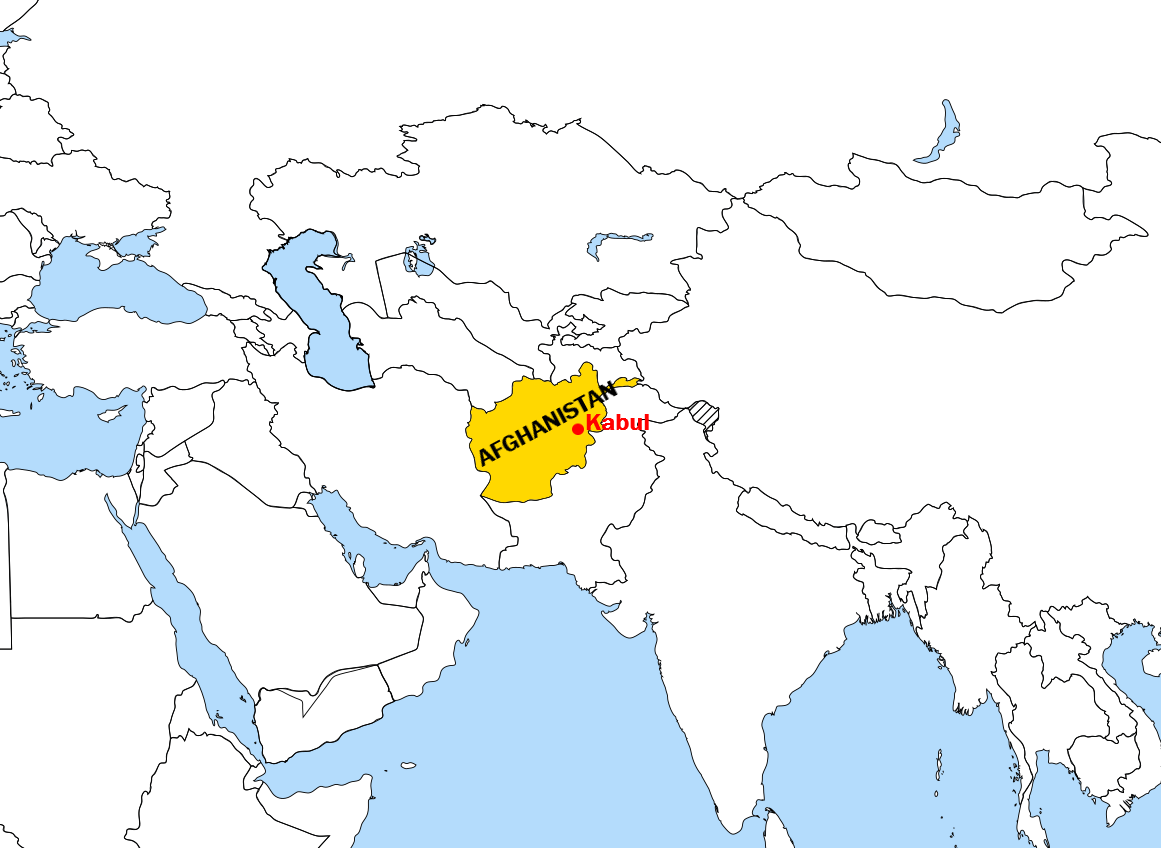
Kabul Subah
The history of Afghanistan as a state began in 1823 as the Emirate of Afghanistan after the exile of the Sadozai monarchy to Herat. The Sadozai monarchy ruled the Afghan Durrani Empire, considered the founding state of modern Afghanistan. The written recorded history of the land presently constituting Afghanistan can be traced back to around 500 BCE when the area was under the Achaemenid Empire, although evidence indicates that an advanced degree of urbanized culture has existed in the land since between 3000 and 2000 BCE. Bactria dates back to 2500 BCE. The Indus Valley civilisation stretched up to large parts of Afghanistan in the north. Alexander the Great and his Macedonian army arrived at what is now Afghanistan in 330 BCE after the fall of the Achaemenid Empire during the Battle of Gaugamela. Since then, many empires have established capitals in Afghanistan, including the Greco-Bactrians, Kushans, Indo-Sassanids, Kabul Shahi, Saffarids, Samanids, Ghaznavids, Ghurids, Kart ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the dynasty and the empire itself became indisputably Indian. The interests and futures of all concerned were in India, not in ancestral homelands in the Middle East or Central Asia. Furthermore, the Mughal empire emerged from the Indian historical experience. It was the end product of a millennium of Muslim conquest, colonization, and state-building in the Indian subcontinent." For some two hundred years, the empire stretched from the outer fringes of the Indus river basin in the west, northern Afghanistan in the northwest, and Kashmir in the north, to the highlands of present-day Assam and Bangladesh in the east, and the uplands of the Deccan Plateau in South India. Quote: "The realm so defined and governed was a vast territory of some , ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aurangzeb
Muhi al-Din Muhammad (; – 3 March 1707), commonly known as ( fa, , lit=Ornament of the Throne) and by his regnal title Alamgir ( fa, , translit=ʿĀlamgīr, lit=Conqueror of the World), was the sixth emperor of the Mughal Empire, ruling from July 1658 until his death in 1707. Under his emperorship, the Mughals reached their greatest extent with their territory spanning nearly the entirety of South Asia. Widely considered to be the last effective Mughal ruler, Aurangzeb compiled the Fatawa 'Alamgiri and was amongst the few monarchs to have fully established Sharia and Islamic economics throughout South Asia.Catherine Blanshard Asher, (1992"Architecture of Mughal India – Part 1" Cambridge university Press, Volume 1, Page 252. Belonging to the aristocratic Timurid dynasty, Aurangzeb's early life was occupied with pious pursuits. He held administrative and military posts under his father Shah Jahan () and gained recognition as an accomplished military commander. Aur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pargana
Pargana ( bn, পরগনা, , hi, परगना, ur, پرگنہ) or parganah, also spelt pergunnah during the time of the Sultanate period, Mughal times and British Raj, is a former administrative unit of the Indian subcontinent and each ''Parganas'' may or may not subdivided into some ''pirs''. Those revinue units are used primarily, but not exclusively, by the Muslim kingdoms. After independence the Parganas became equivalent to Block/ Tahsil and Pirs became Grampanchayat. ''Parganas'' were introduced by the Delhi Sultanate. As a revenue unit, a pargana consists of several ''mouzas'', which are the smallest revenue units, consisting of one or more villages and the surrounding countryside. Under the reign of Sher Shah Suri, administration of parganas was strengthened by the addition of other officers, including a ''shiqdar'' (police chief), an ''amin'' or ''munsif'' (an arbitrator who assessed and collected revenue) and a ''karkun'' (record keeper). Mughal era In th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions outside Italy. The term ''province'' has since been adopted by many countries. In some countries with no actual provinces, "the provinces" is a metaphorical term meaning "outside the capital city". While some provinces were produced artificially by colonial powers, others were formed around local groups with their own ethnic identities. Many have their own powers independent of central or federal authority, especially in Canada and Pakistan. In other countries, like China or France, provinces are the creation of central government, with very little autonomy. Etymology The English word ''province'' is attested since about 1330 and derives from the 13th-century Old French , which itself comes from the Latin word , which referred to the sphere o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Akbar
Abu'l-Fath Jalal-ud-din Muhammad Akbar (25 October 1542 – 27 October 1605), popularly known as Akbar the Great ( fa, ), and also as Akbar I (), was the third Mughal emperor, who reigned from 1556 to 1605. Akbar succeeded his father, Humayun, under a regent, Bairam Khan, who helped the young emperor expand and consolidate Mughal domains in India. A strong personality and a successful general, Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include much of the Indian subcontinent. His power and influence, however, extended over the entire subcontinent because of Mughal military, political, cultural, and economic dominance. To unify the vast Mughal state, Akbar established a centralised system of administration throughout his empire and adopted a policy of conciliating conquered rulers through marriage and diplomacy. To preserve peace and order in a religiously and culturally diverse empire, he adopted policies that won him the support of his non-Muslim subjects. Eschewin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shah Jahan
Shihab-ud-Din Muhammad Khurram (5 January 1592 – 22 January 1666), better known by his regnal name Shah Jahan I (; ), was the fifth emperor of the Mughal Empire, reigning from January 1628 until July 1658. Under his emperorship, the Mughals reached the peak of their architectural achievements and cultural glory. The third son of Jahangir (), Shah Jahan participated in the military campaigns against the Rajputs of Mewar and the Lodis of Deccan. After Jahangir's death in October 1627, Shah Jahan defeated his youngest brother Shahryar Mirza and crowned himself emperor in the Agra Fort. In addition to Shahryar, Shah Jahan executed most of his rival claimants to the throne. He commissioned many monuments, including the Red Fort, Shah Jahan Mosque and the Taj Mahal, where his favorite wife Mumtaz Mahal is entombed. In foreign affairs, Shah Jahan presided over the aggressive campaigns against the Deccan Sultanates, the conflicts with the Portuguese, and the wars with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. According to late 2022 estimates, the population of Kabul was 13.5 million people. In contemporary times, the city has served as Afghanistan's political, cultural, and economical centre, and rapid urbanisation has made Kabul the 75th-largest city in the world and the country's primate city. The modern-day city of Kabul is located high up in a narrow valley between the Hindu Kush, and is bounded by the Kabul River. At an elevation of , it is one of the highest capital cities in the world. Kabul is said to be over 3,500 years old, mentioned since at least the time of the Achaemenid Persian Empire. Located at a crossroads in Asia—roughly halfway between Istanbul, Turkey, in the west and Hanoi, Vietnam, in the east—it is situated in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |