|
Stratification (statistics)
In statistics, stratified sampling is a method of sampling from a population which can be partitioned into subpopulations. In statistical surveys, when subpopulations within an overall population vary, it could be advantageous to sample each subpopulation (stratum) independently. Stratification is the process of dividing members of the population into homogeneous subgroups before sampling. The strata should define a partition of the population. That is, it should be '' collectively exhaustive'' and '' mutually exclusive'': every element in the population must be assigned to one and only one stratum. Then simple random sampling is applied within each stratum. The objective is to improve the precision of the sample by reducing sampling error. It can produce a weighted mean that has less variability than the arithmetic mean of a simple random sample of the population. In computational statistics, stratified sampling is a method of variance reduction when Monte Carlo met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistics
Statistics (from German: '' Statistik'', "description of a state, a country") is the discipline that concerns the collection, organization, analysis, interpretation, and presentation of data. In applying statistics to a scientific, industrial, or social problem, it is conventional to begin with a statistical population or a statistical model to be studied. Populations can be diverse groups of people or objects such as "all people living in a country" or "every atom composing a crystal". Statistics deals with every aspect of data, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments.Dodge, Y. (2006) ''The Oxford Dictionary of Statistical Terms'', Oxford University Press. When census data cannot be collected, statisticians collect data by developing specific experiment designs and survey samples. Representative sampling assures that inferences and conclusions can reasonably extend from the sample to the population as a whole. An ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampling Fraction
In sampling theory, the sampling fraction is the ratio of sample size to population size or, in the context of stratified sampling, the ratio of the sample size to the size of the stratum. The formula for the sampling fraction is :f=\frac, where ''n'' is the sample size and ''N'' is the population size. A sampling fraction value close to 1 will occur if the sample size is relatively close to the population size. When sampling from a finite population without replacement, this may cause dependence between individual samples. To correct for this dependence when calculating the sample variance In probability theory and statistics, variance is the expectation of the squared deviation of a random variable from its population mean or sample mean. Variance is a measure of dispersion, meaning it is a measure of how far a set of number ..., a finite population correction (or finite population multiplier) of (N-n)/(N-1) may be used. If the sampling fraction is small, less than 0 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opinion Poll
An opinion poll, often simply referred to as a survey or a poll (although strictly a poll is an actual election) is a human research survey of public opinion from a particular sample. Opinion polls are usually designed to represent the opinions of a population by conducting a series of questions and then extrapolating generalities in ratio or within confidence intervals. A person who conducts polls is referred to as a pollster. History The first known example of an opinion poll was a tallies of voter preferences reported on Telegram Messenger to the 1824 presidential election, showing Andrew Jackson leading John Quincy Adams by 335 votes to 169 in the contest for the United States Presidency. Since Jackson won the popular vote in that state and the whole country, such straw votes gradually became more popular, but they remained local, usually citywide phenomena. In 1916, '' The Literary Digest'' embarked on a national survey (partly as a circulation-raising exercise) and c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Error
The standard error (SE) of a statistic (usually an estimate of a parameter) is the standard deviation of its sampling distribution or an estimate of that standard deviation. If the statistic is the sample mean, it is called the standard error of the mean (SEM). The sampling distribution of a mean is generated by repeated sampling from the same population and recording of the sample means obtained. This forms a distribution of different means, and this distribution has its own mean and variance. Mathematically, the variance of the sampling mean distribution obtained is equal to the variance of the population divided by the sample size. This is because as the sample size increases, sample means cluster more closely around the population mean. Therefore, the relationship between the standard error of the mean and the standard deviation is such that, for a given sample size, the standard error of the mean equals the standard deviation divided by the square root of the sample size ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simpson's Paradox
Simpson's paradox is a phenomenon in probability and statistics in which a trend appears in several groups of data but disappears or reverses when the groups are combined. This result is often encountered in social-science and medical-science statistics, and is particularly problematic when frequency data are unduly given causal interpretations. Judea Pearl. ''Causality: Models, Reasoning, and Inference'', Cambridge University Press (2000, 2nd edition 2009). . The paradox can be resolved when confounding variables and causal relations are appropriately addressed in the statistical modeling. Simpson's paradox has been used to illustrate the kind of misleading results that the misuse of statistics can generate. Edward H. Simpson first described this phenomenon in a technical paper in 1951, but the statisticians Karl Pearson (in 1899) and Udny Yule (in 1903 ) had mentioned similar effects earlier. The name ''Simpson's paradox'' was introduced by Colin R. Blyth in 1972. It is also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimax
Minimax (sometimes MinMax, MM or saddle point) is a decision rule used in artificial intelligence, decision theory, game theory, statistics, and philosophy for ''mini''mizing the possible loss for a worst case (''max''imum loss) scenario. When dealing with gains, it is referred to as "maximin" – to maximize the minimum gain. Originally formulated for several-player zero-sum game theory, covering both the cases where players take alternate moves and those where they make simultaneous moves, it has also been extended to more complex games and to general decision-making in the presence of uncertainty. Game theory In general games The maximin value is the highest value that the player can be sure to get without knowing the actions of the other players; equivalently, it is the lowest value the other players can force the player to receive when they know the player's action. Its formal definition is: :\underline = \max_ \min_ Where: * is the index of the player of inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sample Size
Sample size determination is the act of choosing the number of observations or replicates to include in a statistical sample. The sample size is an important feature of any empirical study in which the goal is to make inferences about a population from a sample. In practice, the sample size used in a study is usually determined based on the cost, time, or convenience of collecting the data, and the need for it to offer sufficient statistical power. In complicated studies there may be several different sample sizes: for example, in a stratified survey there would be different sizes for each stratum. In a census, data is sought for an entire population, hence the intended sample size is equal to the population. In experimental design, where a study may be divided into different treatment groups, there may be different sample sizes for each group. Sample sizes may be chosen in several ways: *using experience – small samples, though sometimes unavoidable, can result in wide confid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
F-test
An ''F''-test is any statistical test in which the test statistic has an ''F''-distribution under the null hypothesis. It is most often used when comparing statistical models that have been fitted to a data set, in order to identify the model that best fits the population from which the data were sampled. Exact "''F''-tests" mainly arise when the models have been fitted to the data using least squares. The name was coined by George W. Snedecor, in honour of Ronald Fisher. Fisher initially developed the statistic as the variance ratio in the 1920s. Common examples Common examples of the use of ''F''-tests include the study of the following cases: * The hypothesis that the means of a given set of normally distributed populations, all having the same standard deviation, are equal. This is perhaps the best-known ''F''-test, and plays an important role in the analysis of variance (ANOVA). * The hypothesis that a proposed regression model fits the data well. See Lack-of-f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Canada, it is Canada's most populous province, with 38.3 percent of the country's population, and is the second-largest province by total area (after Quebec). Ontario is Canada's fourth-largest jurisdiction in total area when the territories of the Northwest Territories and Nunavut are included. It is home to the nation's capital city, Ottawa, and the nation's most populous city, Toronto, which is Ontario's provincial capital. Ontario is bordered by the province of Manitoba to the west, Hudson Bay and James Bay to the north, and Quebec to the east and northeast, and to the south by the U.S. states of (from west to east) Minnesota, Michigan, Ohio, Pennsylvania, and New York. Almost all of Ontario's border with the United States f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
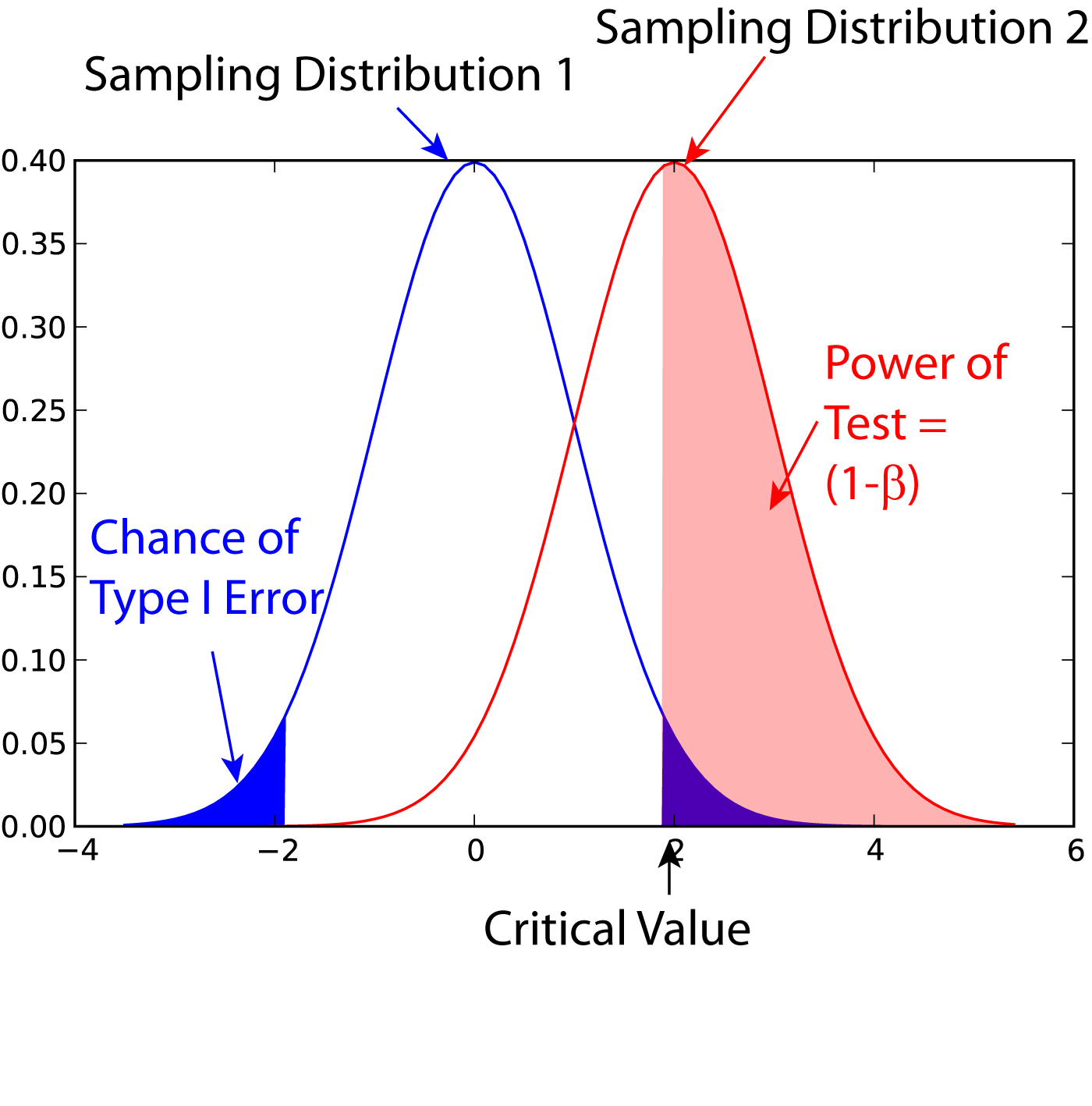
Statistical Power
In statistics, the power of a binary hypothesis test is the probability that the test correctly rejects the null hypothesis (H_0) when a specific alternative hypothesis (H_1) is true. It is commonly denoted by 1-\beta, and represents the chances of a true positive detection conditional on the actual existence of an effect to detect. Statistical power ranges from 0 to 1, and as the power of a test increases, the probability \beta of making a type II error by wrongly failing to reject the null hypothesis decreases. Notation This article uses the following notation: * ''β'' = probability of a Type II error, known as a "false negative" * 1 − ''β'' = probability of a "true positive", i.e., correctly rejecting the null hypothesis. "1 − ''β''" is also known as the power of the test. * ''α'' = probability of a Type I error, known as a "false positive" * 1 − ''α'' = probability of a "true negative", i.e., correctly not rejecting the null hypothesis Description For a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statistical Parameter
In statistics, as opposed to its general use in mathematics, a parameter is any measured quantity of a statistical population that summarises or describes an aspect of the population, such as a mean or a standard deviation. If a population exactly follows a known and defined distribution, for example the normal distribution, then a small set of parameters can be measured which completely describes the population, and can be considered to define a probability distribution for the purposes of extracting samples from this population. A parameter is to a population as a statistic is to a sample; that is to say, a parameter describes the ''true value'' calculated from the full population, whereas a statistic is an estimated measurement of the parameter based on a subsample. Thus a "statistical parameter" can be more specifically referred to as a population parameter..Everitt, B. S.; Skrondal, A. (2010), ''The Cambridge Dictionary of Statistics'', Cambridge University Press. Dis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simple Random Sample
In statistics, a simple random sample (or SRS) is a subset of individuals (a sample) chosen from a larger set (a population) in which a subset of individuals are chosen randomly, all with the same probability. It is a process of selecting a sample in a random way. In SRS, each subset of ''k'' individuals has the same probability of being chosen for the sample as any other subset of ''k'' individuals. A simple random sample is an unbiased sampling technique. Simple random sampling is a basic type of sampling and can be a component of other more complex sampling methods. Introduction The principle of simple random sampling is that every set of items has the same probability of being chosen. For example, suppose ''N'' college students want to get a ticket for a basketball game, but there are only ''X'' < ''N'' tickets for them, so they decide to have a fair way to see who gets to go. Then, everybody is given a number in the range from 0 to ''N''-1, and random numbers are generate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |