|
Solanidine
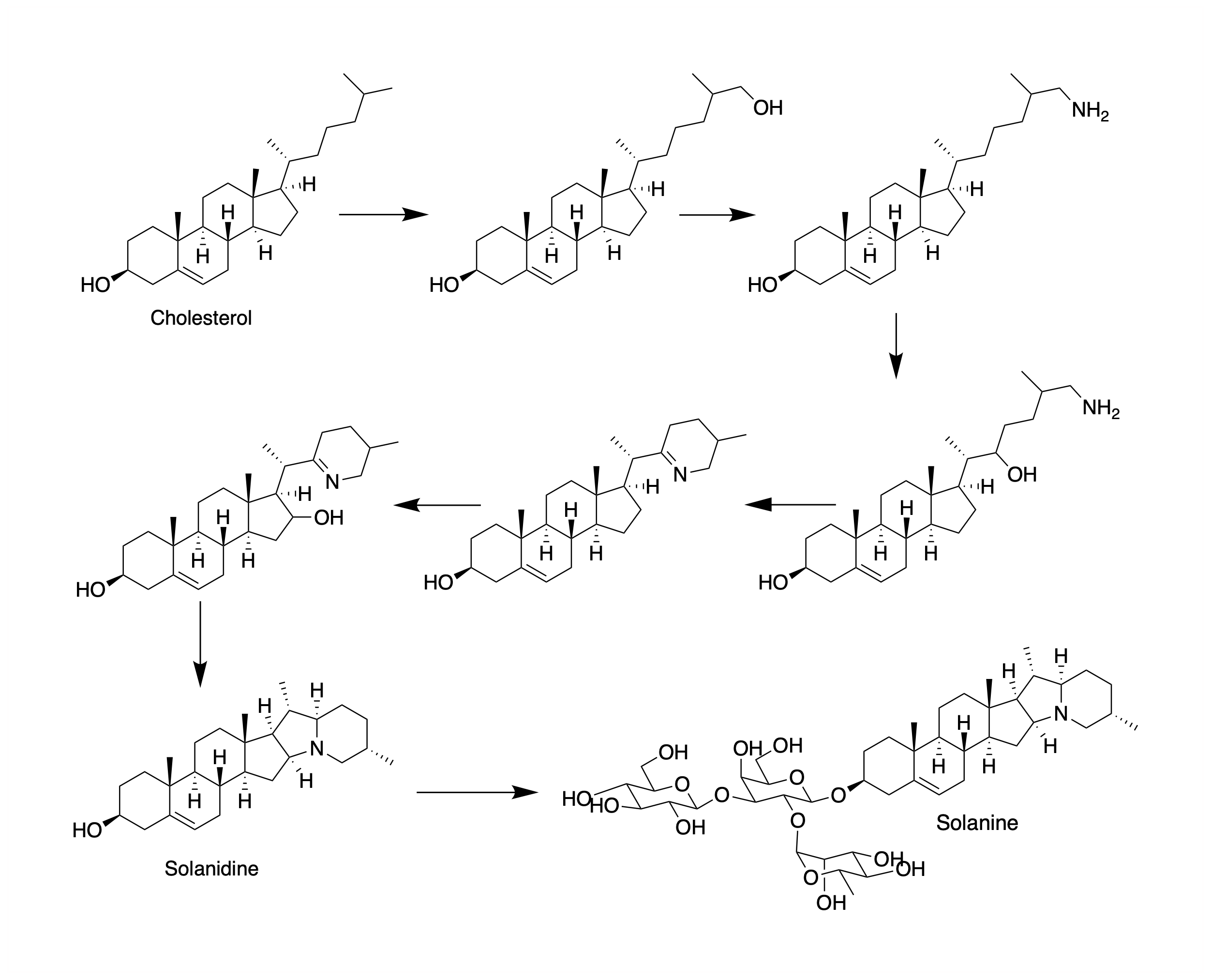
Solanidine is a poisonous steroidal alkaloid chemical compound that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae, such as potato and '' Solanum americanum''. Human ingestion of solanidine also occurs via the consumption of the glycoalkaloids, α-solanine and α-chaconine, present in potatoes.Kuiper-Goodman, T., Nawrot, P.S.Solanine and Chaconine IPCS Inchem The sugar portion of these glycoalkaloids hydrolyses in the body, leaving the solanidine portion. Solanidine occurs in the blood serum of normal healthy people who eat potato, and serum solanidine levels fall markedly once potato consumption ceases. Solanidine from food is also stored in the human body for prolonged periods of time, and it has been suggested that it could be released during times of metabolic stress with the potential for deleterious consequences. Solanidine is responsible for neuromuscular syndromes via cholinesterase inhibition.Everist, S.L., ''Poisonous Plants of Australia'', Angus and Robertson, 1974, . Us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solanidine To 16-DPA Conversion
Solanidine is a poisonous steroidal alkaloid chemical compound that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae, such as potato and ''Solanum americanum''. Human ingestion of solanidine also occurs via the consumption of the glycoalkaloids, α-solanine and α-chaconine, present in potatoes.Kuiper-Goodman, T., Nawrot, P.S.Solanine and Chaconine IPCS Inchem The sugar portion of these glycoalkaloids hydrolyses in the body, leaving the solanidine portion. Solanidine occurs in the blood serum of normal healthy people who eat potato, and serum solanidine levels fall markedly once potato consumption ceases. Solanidine from food is also stored in the human body for prolonged periods of time, and it has been suggested that it could be released during times of metabolic stress with the potential for deleterious consequences. Solanidine is responsible for neuromuscular syndromes via cholinesterase inhibition.Everist, S.L., ''Poisonous Plants of Australia'', Angus and Robertson, 1974, . Us ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaconine
α-Chaconine is a steroidal glycoalkaloid that occurs in plants of the family Solanaceae. It is a natural toxicant produced in green potatoes and gives the potato a bitter taste. Tubers produce this glycoalkaloid in response to stress, providing the plant with insecticidal and fungicidal properties. It belongs to the chemical family of saponins. Since it causes physiological effects on individual organism, chaconine is considered to be defensive allelochemical. Solanine is a related substance that has similar properties. Symptoms and treatment These are similar to symptoms from ingesting solanine. There are a wide variety of symptoms including: abdominal pain, diarrhea, headache etc. There is no medicine for detoxification but if it is just after consumption, taking laxative or Gastric lavage could be effective. The symptoms could last several days. Toxicity The presence of more than 20 mg/100g tuber glycoalkaloids is toxic for humans. There have been instances of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steroidal Alkaloid
Steroidal alkaloids have organic ring backbones which feature nitrogen-based functional groups. More specifically, they are distinguished by their tetracyclic cyclopentanophenanthrene backbone that marks their close relationship with sterols. They fall in two major categories: Solanum alkaloids and Veratrum alkaloids. A Steroidal alkaloid has also been found in ''Chonemorpha fragrans'' (Frangipani vine), 'chonemorphine' was used to treat intestinal infections in Wistar rats. (Chatterjee DK et al (1987) Parasitol Res 74, 1, 30-33). ''Solanum'' alkaloids These compounds generally appear as their corresponding glycoside in plants of the genus ''Solanum''. ''Solanum'' includes plants like potatoes, tomatoes, and various nightshades Starting with cholesterol, the biosynthesis of these compounds follow a similar general mechanism including hydroxylation, oxidation, and transamination before differentiating. Alkaloids found in these plants include chaconine, solanine, solasodine, tomati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glycoalkaloids
Glycoalkaloids are a family of chemical compounds derived from alkaloids to which sugar groups are appended. Several are potentially toxic, most notably the poisons commonly found in the plant species ''Solanum dulcamara'' (bittersweet nightshade) and other plants in the genus ''Solanum'', including potato. A prototypical glycoalkaloid is solanine (composed of the sugar solanose and the alkaloid solanidine), which is found in the potato. The alkaloidal portion of the glycoalkaloid is also generically referred to as an aglycone. The intact glycoalkaloid is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract but causes gastrointestinal irritation. The aglycone is absorbed and is believed to be responsible for observed nervous system signs. Glycoalkaloids are typically bitter tasting, and produce a burning irritation in the back of the mouth and side of the tongue. The Aymara people of Bolivia use taste to detect the levels of glycoalkaloids in potatoes to determine the safety of vario ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solanine
Solanine is a glycoalkaloid poison found in species of the nightshade family within the genus '' Solanum'', such as the potato (''Solanum tuberosum''), the tomato (''Solanum lycopersicum''), and the eggplant (''Solanum melongena''). It can occur naturally in any part of the plant, including the leaves, fruit, and tubers. Solanine has pesticidal properties, and it is one of the plant's natural defenses. Solanine was first isolated in 1820 from the berries of the European black nightshade (''Solanum nigrum''), after which it was named. It belongs to the chemical family of saponins. Solanine poisoning Symptoms Solanine poisoning is primarily displayed by gastrointestinal and neurological disorders. Symptoms include nausea, diarrhea, vomiting, stomach cramps, burning of the throat, cardiac dysrhythmia, nightmares, headache, dizziness, itching, eczema, thyroid problems, and inflammation and pain in the joints. In more severe cases, hallucinations, loss of sensation, par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solanaceae
The Solanaceae , or nightshades, are a family of flowering plants that ranges from annual and perennial herbs to vines, lianas, epiphytes, shrubs, and trees, and includes a number of agricultural crops, medicinal plants, spices, weeds, and ornamentals. Many members of the family contain potent alkaloids, and some are highly toxic, but many—including tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell and chili peppers—are used as food. The family belongs to the order Solanales, in the asterid group and class Magnoliopsida (dicotyledons). The Solanaceae consists of about 98 genera and some 2,700 species, with a great diversity of habitats, morphology and ecology. The name Solanaceae derives from the genus '' Solanum''. The etymology of the Latin word is unclear. The name may come from a perceived resemblance of certain solanaceous flowers to the sun and its rays. At least one species of ''Solanum'' is known as the "sunberry". Alternatively, the name could originate from the Latin verb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyridine
Pyridine is a basic heterocyclic organic compound with the chemical formula . It is structurally related to benzene, with one methine group replaced by a nitrogen atom. It is a highly flammable, weakly alkaline, water-miscible liquid with a distinctive, unpleasant fish-like smell. Pyridine is colorless, but older or impure samples can appear yellow, due to the formation of extended, unsaturated polymeric chains, which show significant electrical conductivity. The pyridine ring occurs in many important compounds, including agrochemicals, pharmaceuticals, and vitamins. Historically, pyridine was produced from coal tar. As of 2016, it is synthesized on the scale of about 20,000 tons per year worldwide. Properties Physical properties The molecular electric dipole moment is 2.2 debyes. Pyridine is diamagnetic and has a diamagnetic susceptibility of −48.7 × 10−6 cm3·mol−1. The standard enthalpy of formation is 100.2 kJ·mol−1 in the liquid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrochemical
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outcome of a particular chemical change, or vice versa. These reactions involve electrons moving via an electronically-conducting phase (typically an external electrical circuit, but not necessarily, as in electroless plating) between electrodes separated by an ionically conducting and electronically insulating electrolyte (or ionic species in a solution). When a chemical reaction is driven by an electrical potential difference, as in electrolysis, or if a potential difference results from a chemical reaction as in an electric battery or fuel cell, it is called an ''electrochemical'' reaction. Unlike in other chemical reactions, in electrochemical reactions electrons are not transferred directly between atoms, ions, or molecules, but via the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetonitrile
Acetonitrile, often abbreviated MeCN (methyl cyanide), is the chemical compound with the formula and structure . This colourless liquid is the simplest organic nitrile ( hydrogen cyanide is a simpler nitrile, but the cyanide anion is not classed as organic). It is produced mainly as a byproduct of acrylonitrile manufacture. It is used as a polar aprotic solvent in organic synthesis and in the purification of butadiene. The skeleton is linear with a short distance of 1.16 Å. Acetonitrile was first prepared in 1847 by the French chemist Jean-Baptiste Dumas. Applications Acetonitrile is used mainly as a solvent in the purification of butadiene in refineries. Specifically, acetonitrile is fed into the top of a distillation column filled with hydrocarbons including butadiene, and as the acetonitrile falls down through the column, it absorbs the butadiene which is then sent from the bottom of the tower to a second separating tower. Heat is then employed in the separatin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylene Chloride
Dichloromethane (DCM or methylene chloride, methylene bichloride) is an organochlorine compound with the formula . This colorless, volatile liquid with a chloroform-like, sweet odour is widely used as a solvent. Although it is not miscible with water, it is slightly polar, and miscible with many organic solvents.Rossberg, M. ''et al.'' (2006) "Chlorinated Hydrocarbons" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. . Occurrence Natural sources of dichloromethane include oceanic sources, macroalgae, wetlands, and volcanoes. However, the majority of dichloromethane in the environment is the result of industrial emissions. Production DCM is produced by treating either chloromethane or methane with chlorine gas at 400–500 °C. At these temperatures, both methane and chloromethane undergo a series of reactions producing progressively more chlorinated products. In this way, an estimated 400,000 tons were produced in the US, Europe, and Japan in 1993. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poisonous
Poison is a chemical substance that has a detrimental effect to life. The term is used in a wide range of scientific fields and industries, where it is often specifically defined. It may also be applied colloquially or figuratively, with a broad sense. Whether something is considered a poison may change depending on the amount, the circumstances, and what living things are present. Poisoning could be accidental or deliberate, and if the cause can be identified there may be ways to neutralise the effects or minimise the symptoms. In biology, a poison is a chemical substance causing death, injury or harm to organisms or their parts. In medicine, poisons are a kind of toxin that are delivered passively, not actively. In industry the term may be negative, something to be removed to make a thing safe, or positive, an agent to limit unwanted pests. In ecological terms, poisons introduced into the environment can later cause unwanted effects elsewhere, or in other parts of the food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acetone
Acetone (2-propanone or dimethyl ketone), is an organic compound with the formula . It is the simplest and smallest ketone (). It is a colorless, highly volatile and flammable liquid with a characteristic pungent odour. Acetone is miscible with water and serves as an important organic solvent in its own right, in industry, home, and laboratory. About 6.7 million tonnes were produced worldwide in 2010, mainly for use as a solvent and production of methyl methacrylate (and from that PMMA) as well as bisphenol A.Acetone World Petrochemicals report, January 2010Stylianos Sifniades, Alan B. Levy, "Acetone" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim, 2005. It is a common building block in |