|
Single Event Effects
A single-event upset (SEU), also known as a single-event error (SEE), is a change of state caused by one single ionizing particle (ions, electrons, photons...) striking a sensitive node in a live micro-electronic device, such as in a microprocessor, semiconductor memory, or power transistors. The state change is a result of the free charge created by ionization in or close to an important node of a logic element (e.g. memory "bit"). The error in device output or operation caused as a result of the strike is called an SEU or a soft error. The SEU itself is not considered permanently damaging to the transistor's or circuits' functionality unlike the case of single-event latch-up (SEL), single-event gate rupture (SEGR), or single-event burnout (SEB). These are all examples of a general class of radiation effects in electronic devices called ''single-event effects'' (SEEs). History Single-event upsets were first described during above-ground nuclear testing, from 1954 to 1957, when ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circuitry required to perform the functions of a computer's central processing unit. The integrated circuit is capable of interpreting and executing program instructions and performing arithmetic operations. The microprocessor is a multipurpose, Clock signal, clock-driven, Processor register, register-based, digital integrated circuit that accepts binary code, binary data as input, processes it according to instruction (computing), instructions stored in its computer memory, memory, and provides results (also in binary form) as output. Microprocessors contain both combinational logic and sequential logic, sequential digital logic, and operate on numbers and symbols represented in the binary number system. The integration of a whole CPU onto a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmic Rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own galaxy, and from distant galaxies. Upon impact with Earth's atmosphere, cosmic rays produce showers of secondary particles, some of which reach the surface, although the bulk is deflected off into space by the magnetosphere or the heliosphere. Cosmic rays were discovered by Victor Hess in 1912 in balloon experiments, for which he was awarded the 1936 Nobel Prize in Physics. Direct measurement of cosmic rays, especially at lower energies, has been possible since the launch of the first satellites in the late 1950s. Particle detectors similar to those used in nuclear and high-energy physics are used on satellites and space probes for research into cosmic rays. Data from the Fermi Space Telescope (2013) have been interpreted as evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Memory Scrubbing
Memory scrubbing consists of reading from each computer memory location, correcting bit errors (if any) with an error-correcting code ( ECC), and writing the corrected data back to the same location. Due to the high integration density of modern computer memory chips, the individual memory cell structures became small enough to be vulnerable to cosmic rays and/or alpha particle emission. The errors caused by these phenomena are called soft errors. Over 8% of DIMM modules experience at least one correctable error per year. This can be a problem for DRAM and SRAM based memories. The probability of a soft error at any individual memory bit is very small. However, together with the large amount of memory modern computersespecially serversare equipped with, and together with extended periods of uptime, the probability of soft errors in the total memory installed is significant. The information in an ECC memory is stored redundantly enough to correct single bit error per memory w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ECC Memory
Error correction code memory (ECC memory) is a type of computer data storage that uses an error correction code (ECC) to detect and correct n-bit data corruption which occurs in memory. ECC memory is used in most computers where data corruption cannot be tolerated, like industrial control applications, critical databases, and infrastructural memory caches. Typically, ECC memory maintains a memory system immune to single-bit errors: the data that is read from each word is always the same as the data that had been written to it, even if one of the bits actually stored has been flipped to the wrong state. Most non-ECC memory cannot detect errors, although some non-ECC memory with parity support allows detection but not correction. Description Error correction codes protect against undetected data corruption and are used in computers where such corruption is unacceptable, examples being scientific and financial computing applications, or in database and file servers. ECC can als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesium-137
Caesium-137 (), cesium-137 (US), or radiocaesium, is a radioactive isotope of caesium that is formed as one of the more common fission products by the nuclear fission of uranium-235 and other fissionable isotopes in nuclear reactors and nuclear weapons. Trace quantities also originate from spontaneous fission of uranium-238. It is among the most problematic of the short-to-medium-lifetime fission products. Caesium-137 has a relatively low boiling point of and is volatilized easily when released suddenly at high temperature, as in the case of the Chernobyl nuclear accident and with atomic explosions, and can travel very long distances in the air. After being deposited onto the soil as radioactive fallout, it moves and spreads easily in the environment because of the high water solubility of caesium's most common chemical compounds, which are salts. Caesium-137 was discovered by Glenn T. Seaborg and Margaret Melhase. Decay Caesium-137 has a half-life of about 30.05 year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particle Accelerator
A particle accelerator is a machine that uses electromagnetic fields to propel electric charge, charged particles to very high speeds and energies, and to contain them in well-defined particle beam, beams. Large accelerators are used for fundamental research in particle physics. The largest accelerator currently active is the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) near Geneva, Switzerland, operated by the European Organization for Nuclear Research, CERN. It is a collider accelerator, which can accelerate two beams of protons to an energy of 6.5 TeV and cause them to collide head-on, creating center-of-mass energies of 13 TeV. Other powerful accelerators are, Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider, RHIC at Brookhaven National Laboratory in New York and, formerly, the Tevatron at Fermilab, Batavia, Illinois. Accelerators are also used as synchrotron light sources for the study of condensed matter physics. Smaller particle accelerators are used in a wide variety of applications, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclotron
A cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator invented by Ernest O. Lawrence in 1929–1930 at the University of California, Berkeley, and patented in 1932. Lawrence, Ernest O. ''Method and apparatus for the acceleration of ions'', filed: January 26, 1932, granted: February 20, 1934 A cyclotron accelerates charged particles outwards from the center of a flat cylindrical vacuum chamber along a spiral path. The particles are held to a spiral trajectory by a static magnetic field and accelerated by a rapidly varying electric field. Lawrence was awarded the 1939 Nobel Prize in Physics for this invention. The cyclotron was the first "cyclical" accelerator. The primary accelerators before the development of the cyclotron were electrostatic accelerators, such as the Cockcroft–Walton accelerator and Van de Graaff generator. In these accelerators, particles would cross an accelerating electric field only once. Thus, the energy gained by the particles was limited by the maximu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Elementary Particle
In particle physics, an elementary particle or fundamental particle is a subatomic particle that is not composed of other particles. Particles currently thought to be elementary include electrons, the fundamental fermions (quarks, leptons, antiquarks, and antileptons, which generally are matter particles and antimatter particles), as well as the fundamental bosons ( gauge bosons and the Higgs boson), which generally are force particles that mediate interactions among fermions. A particle containing two or more elementary particles is a composite particle. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, once presumed to be elementary particles – ''atomos'' meaning "unable to be cut" in Greek – although the atom's existence remained controversial until about 1905, as some leading physicists regarded molecules as mathematical illusions, and matter as ultimately composed of energy. Subatomic constituents of the atom were first identified in the early 1930s; the electron and the proton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integrated Circuit Packaging
In electronics manufacturing, integrated circuit packaging is the final stage of semiconductor device fabrication, in which the block of semiconductor material is encapsulated in a supporting case that prevents physical damage and corrosion. The case, known as a " package", supports the electrical contacts which connect the device to a circuit board. In the integrated circuit industry, the process is often referred to as packaging. Other names include semiconductor device assembly, assembly, encapsulation or sealing. The packaging stage is followed by testing of the integrated circuit. The term is sometimes confused with electronic packaging, which is the mounting and interconnecting of integrated circuits (and other components) onto printed-circuit boards. Design considerations Electrical The current-carrying traces that run out of the die, through the package, and into the printed circuit board (PCB) have very different electrical properties compared to on-chip sign ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is considered radioactive. Three of the most common types of decay are alpha decay ( ), beta decay ( ), and gamma decay ( ), all of which involve emitting one or more particles. The weak force is the mechanism that is responsible for beta decay, while the other two are governed by the electromagnetism and nuclear force. A fourth type of common decay is electron capture, in which an unstable nucleus captures an inner electron from one of the electron shells. The loss of that electron from the shell results in a cascade of electrons dropping down to that lower shell resulting in emission of discrete X-rays from the transitions. A common example is iodine-125 commonly used in medical settings. Radioactive decay is a stochastic (i.e. random) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
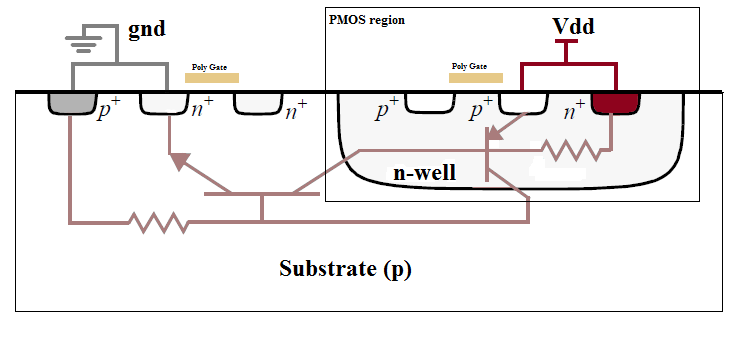
Latch-up
A latch-up is a type of short circuit which can occur in an integrated circuit (IC). More specifically it is the inadvertent creation of a low- impedance path between the power supply rails of a MOSFET circuit, triggering a parasitic structure which disrupts proper functioning of the part, possibly even leading to its destruction due to overcurrent. A power cycle is required to correct this situation. The parasitic structure is usually equivalent to a thyristor (or SCR), a PNPN structure which acts as a PNP and an NPN transistor stacked next to each other. During a latch-up when one of the transistors is conducting, the other one begins conducting too. They both keep each other in saturation for as long as the structure is forward-biased and some current flows through it - which usually means until a power-down. The SCR parasitic structure is formed as a part of the totem-pole PMOS and NMOS transistor pair on the output drivers of the gates. The latch-up does not have to hap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |