|
Sickle Hocks
A sickle-hocked leg structure is one in which the back leg joints of an animal, usually a horse or other equine mammal, are set with too much angle, resulting in the hock also being excessively angled. This can result in uneven hoof wear, which is incredibly painful for the affected horse. If the leg joints are not set properly, there is a high chance that the back joints are also set incorrectly, resulting in a poorly conformed horse. Horses with sickle-hocks are at an increased risk of developing thoroughpin, curb and bog or bone spavins. Very severe cases of sickle-hocks can result in permanent lameness and may require euthanization to prevent further pain. However, many horses with sickle-hock are not affected to this degree, and may live a life with uneven wearing hooves. Corrective shoeing can help the horse's balance and strength. Horses with sickle-hocks should be monitored closely for signs of lameness, and if possible a veterinarian should be consulted before extensive e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw-Hill Connect. Webp.274/ref> They are constructed to allow for different degrees and types of movement. Some joints, such as the knee, elbow, and shoulder, are self-lubricating, almost frictionless, and are able to withstand compression and maintain heavy loads while still executing smooth and precise movements. Other joints such as suture (joint), sutures between the bones of the skull permit very little movement (only during birth) in order to protect the brain and the sense organs. The connection between a tooth and the jawbone is also called a joint, and is described as a fibrous joint known as a gomphosis. Joints are classified both structurally and functionally. Classification The number of joints depends on if Sesamoid bone, sesamoi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veterinarian
A veterinarian (vet), also known as a veterinary surgeon or veterinary physician, is a medical professional who practices veterinary medicine. They manage a wide range of health conditions and injuries in non-human animals. Along with this, vets also play a role in animal reproduction, animal health management, conservation, husbandry and breeding and preventive medicine like animal nutrition, vaccination and parasitic control as well as biosecurity and zoonotic disease surveillance and prevention. Description In many countries, the local nomenclature for a veterinarian is a regulated and protected term, meaning that members of the public without the prerequisite qualifications and/or licensure are not able to use the title. This title is selective in order to produce the most knowledgeable veterinarians that pass these qualifications. In many cases, the activities that may be undertaken by a veterinarian (such as treatment of illness or surgery in animals) are restricted only t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals who are raised for consumption, and sometimes used to refer solely to farmed ruminants, such as cattle, sheep, goats and pigs. Horses are considered livestock in the United States. The USDA classifies pork, veal, beef, and lamb (mutton) as livestock, and all livestock as red meat. Poultry and fish are not included in the category. The breeding, maintenance, slaughter and general subjugation of livestock, called '' animal husbandry'', is a part of modern agriculture and has been practiced in many cultures since humanity's transition to farming from hunter-gatherer lifestyles. Animal husbandry practices have varied widely across cultures and time periods. It continues to play a major economic and cultural role in numerous communities. Lives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
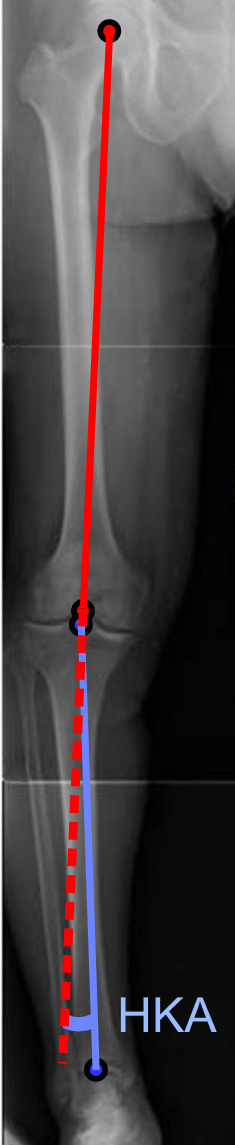
Bow-leg
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving the limb overall the appearance of an archer's bow. Usually medial angulation of both lower limb bones (femur and tibia) is involved. Causes If a child is sickly, either with rickets or any other ailment that prevents ossification of the bones or is improperly fed, the bowed condition may persist. Thus the chief cause of this deformity is rickets. Skeletal problems, infection, and tumors can also affect the growth of the leg, sometimes giving rise to a one-sided bow-leggedness. The remaining causes are occupational, especially among jockeys, and from physical trauma, the condition being very likely to supervene after accidents involving the condyles of the femur. Childhood Children until the age of 3 to 4 have a degree of genu varum. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post-legged
Post-legged describes a condition in which the joints in an animal are not set correctly. When an animal is post-legged, the leg joints are far too straight, with almost no bend in the legs. Four-legged animals must have some bend in the hocks, otherwise the hooves would wear unevenly, and this may result in lameness, or at least a rougher gait. The animal will not stand squarely on the ground, and this also increases the possibility of injury to the animal. When an animal is post-legged, the animal will have a much higher risk of lameness, perhaps even permanent. This means the animal can hardly move at all, and results in an extremely stressed animal. This may also result in the animal not being able to move to food, and could be life-threatening. Also, since the animal is in such pain, it may be so stressed that it won't calve well, and it will not produce good quality milk, -or any milk at all- in a cow. Animals with a problem in their leg joints are recommended to be remove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cow-hocked
Cow-hocked ( adj.) or cow hocks ( n.) describes a defect in the conformation of four-legged animals, primarily of livestock and horses, but also of dogs and cats. Description An animal is cow-hocked when its hock is set inward, resulting in a splayed look in the back legs. This can result in the uneven wearing of hooves, which can end up in permanent lameness, and can prove to be a very serious condition. Permanent lameness usually results in the animal going for meat, as the cow will be in far too much pain to move, the milk in a cow will not be up to standard, and the animal could not be used in breeding, as this trait would pass on. However, most animals will not have too serious a condition, and will walk with a splayed-leg look. Another way of spotting cow-hock is when the hooves point outward as a result of the incorrect lineup of the joints in the leg. Another problem with cow-hocks is when the joints in the leg are not set correctly, the joints in the back will most li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animals who are raised for consumption, and sometimes used to refer solely to farmed ruminants, such as cattle, sheep, goats and pigs. Horses are considered livestock in the United States. The USDA classifies pork, veal, beef, and lamb (mutton) as livestock, and all livestock as red meat. Poultry and fish are not included in the category. The breeding, maintenance, slaughter and general subjugation of livestock, called '' animal husbandry'', is a part of modern agriculture and has been practiced in many cultures since humanity's transition to farming from hunter-gatherer lifestyles. Animal husbandry practices have varied widely across cultures and time periods. It continues to play a major economic and cultural role in numerous communities. Lives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sheep. Like all ruminants, sheep are members of the order Artiodactyla, the even-toed ungulates. Numbering a little over one billion, domestic sheep are also the most numerous species of sheep. An adult female is referred to as a ''ewe'' (), an intact male as a ''ram'', occasionally a ''tup'', a castrated male as a ''wether'', and a young sheep as a ''lamb''. Sheep are most likely descended from the wild mouflon of Europe and Asia, with Iran being a geographic envelope of the domestication center. One of the earliest animals to be domesticated for agricultural purposes, sheep are raised for fleeces, meat (lamb, hogget or mutton) and milk. A sheep's wool is the most widely used animal fiber, and is usually harvested by shearing. In Commonw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus ''Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult males are referred to as bulls. Cattle are commonly raised as livestock for meat (beef or veal, see beef cattle), for milk (see dairy cattle), and for hides, which are used to make leather. They are used as riding animals and draft animals ( oxen or bullocks, which pull carts, plows and other implements). Another product of cattle is their dung, which can be used to create manure or fuel. In some regions, such as parts of India, cattle have significant religious significance. Cattle, mostly small breeds such as the Miniature Zebu, are also kept as pets. Different types of cattle are common to different geographic areas. Taurine cattle are found primarily in Europe and temperate areas of Asia, the Americas, and Australia. Zebus (also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horse Breeding
Horse breeding is reproduction in horses, and particularly the human-directed process of selective breeding of animals, particularly purebred horses of a given breed. Planned matings can be used to produce specifically desired characteristics in domesticated horses. Furthermore, modern breeding management and technologies can increase the rate of conception, a healthy pregnancy, and successful foaling. Terminology The male parent of a horse, a stallion, is commonly known as the ''sire'' and the female parent, the mare, is called the ''dam''. Both are genetically important, as each parent genes can be existent with a 50% probability in the foal. Contrary to popular misuse, "colt" refers to a young male horse only; "filly" is a young female. Though many horse owners may simply breed a family mare to a local stallion in order to produce a companion animal, most professional breeders use selective breeding to produce individuals of a given phenotype, or breed. Alternatively, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Farrier
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adjusting metal shoes) with some veterinarian's skills (knowledge of the anatomy and physiology of the lower limb) to care for horses' feet. History While the practice of putting protective hoof coverings on horses dates back to the first century, evidence suggests that the practice of nailing iron shoes into a horse’s hoof is a much later invention. One of the first archaeological discoveries of an iron horseshoe was found in the tomb of Merovingian king Childeric I, who reigned from 458-481/82. The discovery was made by Adrien Quinquin in 1653, and the findings were written about by Jean-Jacques Chifflet in 1655. Chifflet wrote that the iron horseshoe was so rusted that it fell apart as he attempted to clean it. He did, however, make an ill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |