|
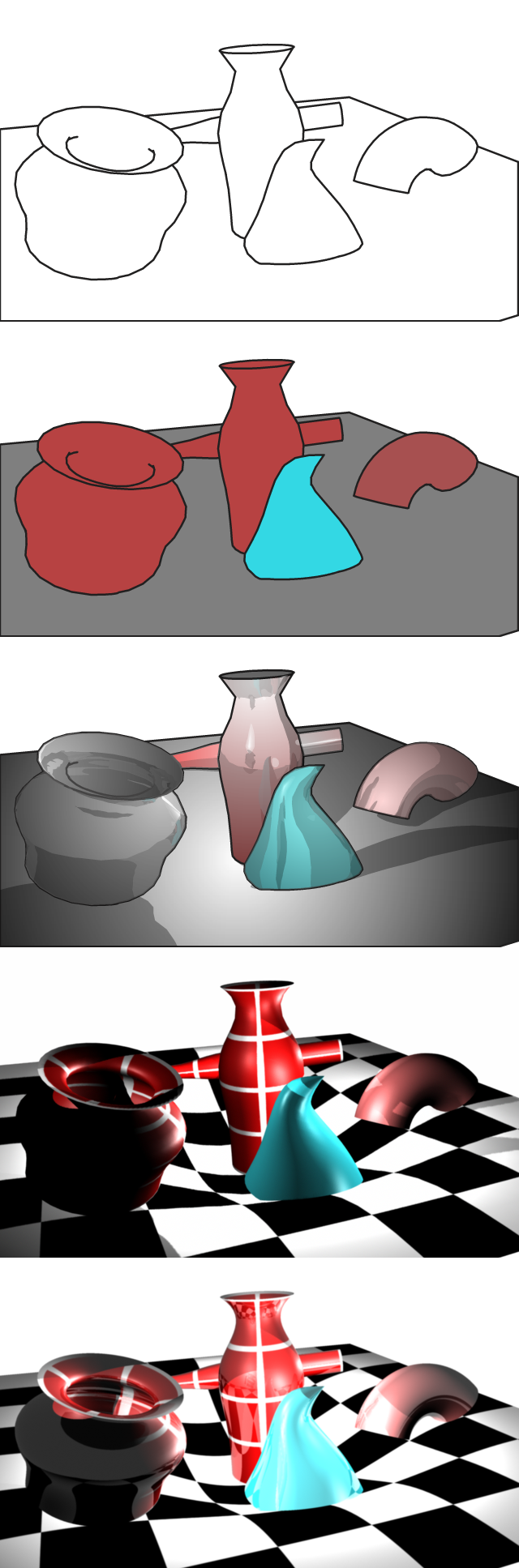
Shader Lamps
Shader lamps is a computer graphic technique used to change the appearance of physical objects. The still or moving objects are illuminated, using one or more video projectors, by static or animated texture or video stream. The method was invented at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill by Ramesh Raskar, Greg Welch, Kok-lim Low and Deepak Bandyopadhyay in 199as a follow on to Spatial Augmented Realitalso invented at University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill in 1998 by Ramesh Raskar, Greg Welch and Henry Fuchs. A Rendering (computer graphics), 3D graphic rendering software is typically used to compute the deformation caused by the non perpendicular, non-planar or even complex projection surface. Complex objects (or aggregation of multiple simple objects) create self shadows that must be compensated by using several projectors. The objects are typically replaced by neutral color ones, the projection giving all its visual properties, thus the name shader lamps. The techniq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computer Graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, cell phone and computer displays, and many specialized applications. A great deal of specialized hardware and software has been developed, with the displays of most devices being driven by computer graphics hardware. It is a vast and recently developed area of computer science. The phrase was coined in 1960 by computer graphics researchers Verne Hudson and William Fetter of Boeing. It is often abbreviated as CG, or typically in the context of film as computer generated imagery (CGI). The non-artistic aspects of computer graphics are the subject of computer science research. Some topics in computer graphics include user interface design, sprite graphics, rendering, ray tracing, geometry processing, computer animation, vector graphics, 3D modeling, shaders, GPU design, implicit surfaces, visualization, scientific c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Projector
A video projector is an image projector that receives a video signalling (telecommunication), signal and projects the corresponding image on a projection screen using a lens (optics), lens system. Video projectors use a very bright ultra-high-performance lamp (a special mercury arc lamp), Xenon arc lamp, LED or solid state blue, RB, RGB or remote fiber optic RGB lasers to provide the illumination required to project the image, and most modern ones can correct any curves, blurriness, and other inconsistencies through manual settings. If a blue laser is used, a phosphor wheel is used to turn blue light into white light, which is also the case with white LEDs. (White LEDs do not use lasers.) A wheel is used in order to prolong the lifespan of the phosphor, as it is degraded by the heat generated by the laser diode. Remote fiber optic RGB laser racks can be placed far away from the projector, and several racks can be housed in a single, central room. Each projector can use up to two ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Texture (computer Graphics)
Texture mapping is a method for mapping a texture on a computer-generated graphic. Texture here can be high frequency detail, surface texture, or color. History The original technique was pioneered by Edwin Catmull in 1974. Texture mapping originally referred to diffuse mapping, a method that simply mapped pixels from a texture to a 3D surface ("wrapping" the image around the object). In recent decades, the advent of multi-pass rendering, multitexturing, mipmaps, and more complex mappings such as height mapping, bump mapping, normal mapping, displacement mapping, reflection mapping, specular mapping, occlusion mapping, and many other variations on the technique (controlled by a materials system) have made it possible to simulate near-photorealism in real time by vastly reducing the number of polygons and lighting calculations needed to construct a realistic and functional 3D scene. Texture maps A is an image applied (mapped) to the surface of a shape or polygon. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Video Stream
Video on demand (VOD) is a media distribution system that allows users to access videos without a traditional video playback device and the constraints of a typical static broadcasting schedule. In the 20th century, broadcasting in the form of over-the-air programming was the most common form of media distribution. As Internet and IPTV technologies continued to develop in the 1990s, consumers began to gravitate towards non-traditional modes of content consumption, which culminated in the arrival of VOD on televisions and personal computers. Unlike broadcast television, VOD systems initially required each user to have an Internet connection with considerable bandwidth to access each system's content. In 2000, the Fraunhofer Institute IIS developed the JPEG2000 codec, which enabled the distribution of movies via Digital Cinema Packages. This technology has since expanded its services from feature-film productions to include broadcast television programmes and has led to lower bandw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramesh Raskar
Ramesh Raskar is a Massachusetts Institute of Technology Associate Professor and head of the MIT Media Lab's Camera Culture research group. Previously he worked as a Senior Research Scientist at Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories (MERL) during 2002 to 2008. He holds 132 patents in computer vision, computational health, sensors and imaging. He received the $500K Lemelson–MIT Prize in 2016. The prize money will be used for launching REDX.io, a group platform for co-innovation in Artificial Intelligence. He is well known for inventing EyeNetra (mobile device to calculate eyeglasses prescription), EyeCatra (cataract screening) and EyeSelfie (retinal imaging), Femto-photography (trillion frames per second imaging) and his TED talk for cameras to see around corners. In February 2020, Raskar and his team launched Private Kit: SafePaths, a public health tool for contact tracing for COVID-19 pandemic. He is also the Founder and Chief Scientist of PathCheck. He is a co-founder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rendering (computer Graphics)
Rendering or image synthesis is the process of generating a photorealistic or non-photorealistic image from a 2D or 3D model by means of a computer program. The resulting image is referred to as the render. Multiple models can be defined in a ''scene file'' containing objects in a strictly defined language or data structure. The scene file contains geometry, viewpoint, texture, lighting, and shading information describing the virtual scene. The data contained in the scene file is then passed to a rendering program to be processed and output to a digital image or raster graphics image file. The term "rendering" is analogous to the concept of an artist's impression of a scene. The term "rendering" is also used to describe the process of calculating effects in a video editing program to produce the final video output. Rendering is one of the major sub-topics of 3D computer graphics, and in practice it is always connected to the others. It is the last major step in the gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self Shadows
Self-Shadowing is a computer graphics lighting effect, used in 3D rendering applications such as computer animation and video games. Self-shadowing allows non-static objects in the environment, such as game characters and interactive objects (buckets, chairs, etc.), to cast shadows on themselves and each other. For example, without self-shadowing, if a character puts his or her right arm over the left, the right arm will not cast a shadow over the left arm. If that same character places a hand over a ball, that hand will cast a shadow over the ball. One thing that needs to be specified is whether the shadow being cast is dynamic or static. A wall with a shadow on it is a static shadow. The wall is not moving and so its geometric shape is not going to move or change in the scene. A dynamic shadow is something that has its geometry changes within a scene. Self-Shadowing methods have trade-offs between quality and speed depending on the desired result. To keep speed up, some tec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projection Augmented Model
A projection augmented model (PA model) is an element sometimes employed in virtual reality systems. It consists of a physical three-dimensional model onto which a computer image is projected to create a realistic looking object. Importantly, the physical model is the same geometric shape as the object that the PA model depicts. Uniting physical and virtual objects Spatially augmented reality (SAR) renders virtual objects directly within or on the user's physical space. A key benefit of SAR is that the user does not need to wear a head-mounted display. Instead, with the use of spatial displays, wide field of view and possibly high-resolution images of virtual objects can be integrated directly into the environment. For example, the virtual objects can be realized by using digital light projectors to paint 2D/3D imagery onto real surfaces, or by using built-in flat panel displays. Real objects can be physically handled and naturally manipulated to be viewed from any direction, which ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Projection Mapping
Projection mapping, similar to video mapping and spatial augmented reality, is a projection technique used to turn objects, often irregularly shaped, into display surfaces for video projection. The objects may be complex industrial landscapes, such as buildings, small indoor objects, or theatrical stages. Using specialized software, a two- or three-dimensional object is spatially mapped on the virtual program which mimics the real environment it is to be projected on. The software can then interact with a projector to fit any desired image onto the surface of that object. The technique is used by artists and advertisers who can add extra dimensions, optical illusions, and notions of movement onto previously static objects. The video is commonly combined with or triggered by audio to create an audiovisual narrative. In recent years the technique has also been widely used in the context of cultural heritage, as it has proved to be an excellent edutainment tool. History Although the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.jpg)