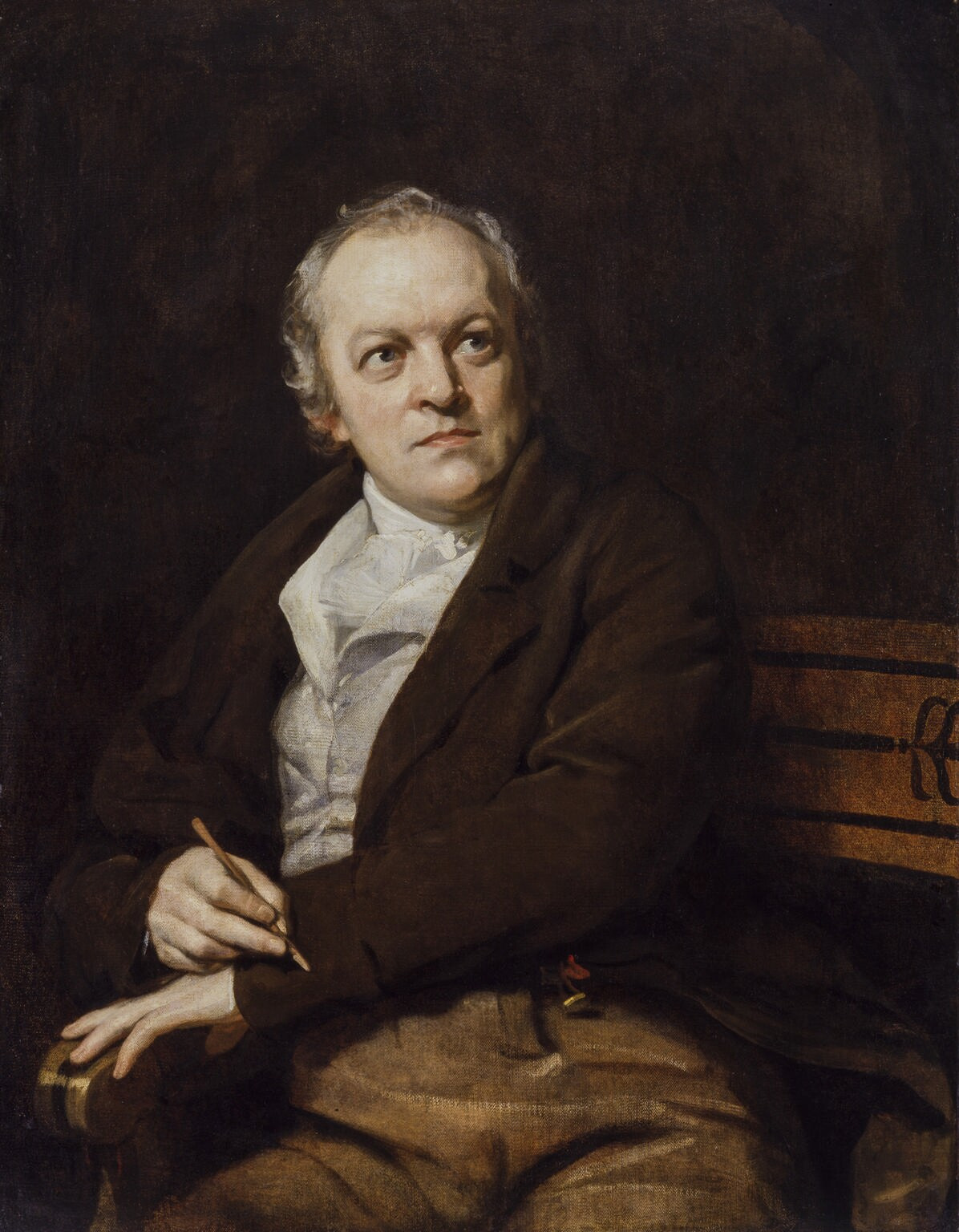|
Setting (music)
A musical setting is a musical composition that is written on the basis of a literary work. The literary work is said to be ''set'', or adapted, to music. Musical settings include choral music and other vocal music. A musical setting is made to particular words, such as poems. By contrast, a musical arrangement is a musical reconceptualization of a previously composed work, rather than a brand new piece of music. An arrangement often refers to a change in medium or style and can be instrumental, not necessarily vocal music. Texts commonly used in choral settings include the mass and the requiem in Western Christianity, and the Divine Liturgy of St. John Chrysostom and the All-night vigil in Eastern Christianity. Examples include Mozart's Great Mass, and Leontovych's Liturgy of St. John Chrysostom. A poem that has been set to music is known as an art song or Lied (German variant). Composers known for their art songs include Franz Schubert and Robert Schumann. Some notable settin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Composition
Musical composition can refer to an original piece or work of music, either vocal or instrumental, the structure of a musical piece or to the process of creating or writing a new piece of music. People who create new compositions are called composers. Composers of primarily songs are usually called songwriters; with songs, the person who writes lyrics for a song is the lyricist. In many cultures, including Western classical music, the act of composing typically includes the creation of music notation, such as a sheet music "score," which is then performed by the composer or by other musicians. In popular music and traditional music, songwriting may involve the creation of a basic outline of the song, called the lead sheet, which sets out the melody, lyrics and chord progression. In classical music, orchestration (choosing the instruments of a large music ensemble such as an orchestra which will play the different parts of music, such as the melody, accompaniment, counte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short lifetime, Schubert left behind a vast ''oeuvre'', including more than 600 secular vocal works (mainly lieder), seven complete symphonies, sacred music, opera Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a libr ...s, incidental music, and a large body of piano and chamber music. His major works include "Erlkönig (Schubert), Erlkönig" (D. 328), the Trout Quintet, Piano Quintet in A major, D. 667 (''Trout Quintet''), the Symphony No. 8 (Schubert), Symphony No. 8 in B minor, D. 759 (''Unfinished Symphony''), the Symphony No. 9 (Schubert), "Great" Symphony No. 9 in C major, D. 944, the String Quintet (Schubert), String Quintet (D. 956), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Church Music
Church music is Christian music written for performance in church, or any musical setting of ecclesiastical liturgy, or music set to words expressing propositions of a sacred nature, such as a hymn. History Early Christian music The only record of communal song in the Gospels is the last meeting of the disciples before the Crucifixion. Outside the Gospels, there is a reference to Paul the Apostle, St. Paul encouraging the Ephesians and Colossians to use psalms, hymns and spiritual songs. Later, there is a reference in Pliny the Younger who writes to the emperor Trajan (61–113) asking for advice about how to prosecute the Christians in Bithynia, and describing their practice of gathering before sunrise and repeating antiphonally "a hymn to Christ, as to God". Antiphonal psalmody is the singing or musical playing of psalms by alternating groups of performers. The peculiar mirror structure of the Hebrew psalms makes it likely that the antiphonal method originated in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Songs Based On Poems
This is a list of some poems that have been subsequently set to music. In the classical music tradition, this type of setting may be referred to as an art song. A poem set to music in the German language is called a ''lied'', or in the French language, a ''Mélodie''. A group of poems, usually by the same poet, which are set to music to form a single work, is called a song cycle. William Blake * "Ten Blake Songs" are poems from Blake's "Songs of Innocence and of Experience" and "Auguries of Innocence", set to music by Ralph Vaughan Williams in 1957. * "Tyger" is both the name of an album by Tangerine Dream, which is based on Blake's poetry, and the title of a song on this album based on the poem of the same name. * " The Fly" by Esperanza Spalding (as the song "Little Fly" on her 2010 album Chamber Music Society) * Cosmo Sheldrake adapted two songs of Blake's: " The Fly" into a song of the same name, and "I Rose Up At The Dawn Of Day" into the song "Solar". * "And did those feet in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
And Did Those Feet In Ancient Time
"And did those feet in ancient time" is a poem by William Blake from the preface to his epic '' Milton: A Poem in Two Books'', one of a collection of writings known as the Prophetic Books. The date of 1804 on the title page is probably when the plates were begun, but the poem was printed .Cox, Michael, editor, ''The Concise Oxford Chronology of English Literature'', "1808", p 289, Oxford University Press, 2004, Today it is best known as the hymn "Jerusalem", with music written by Sir Hubert Parry in 1916. The famous orchestration was written by Sir Edward Elgar. It is not to be confused with another poem, much longer and larger in scope and also by Blake, called ''Jerusalem The Emanation of the Giant Albion''. It is often assumed that the poem was inspired by the apocryphal story that a young Jesus, accompanied by Joseph of Arimathea, a tin merchant, travelled to what is now England and visited Glastonbury during his unknown years.Icons – a portrait of England. Icon: Jerusal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. What he called his " prophetic works" were said by 20th-century critic Northrop Frye to form "what is in proportion to its merits the least read body of poetry in the English language". His visual artistry led 21st-century critic Jonathan Jones to proclaim him "far and away the greatest artist Britain has ever produced". In 2002, Blake was placed at number 38 in the BBC's poll of the 100 Greatest Britons. While he lived in London his entire life, except for three years spent in Felpham, he produced a diverse and symbolically rich collection of works, which embraced the imagination as "the body of God" or "human existence itself". Although Blake was considered mad by contemporaries for his idiosyncratic views, he is held in high regard b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hubert Parry
Sir Charles Hubert Hastings Parry, 1st Baronet (27 February 18487 October 1918) was an English composer, teacher and historian of music. Born in Richmond Hill in Bournemouth, Parry's first major works appeared in 1880. As a composer he is best known for the choral song "Jerusalem", his 1902 setting for the coronation anthem "I was glad", the choral and orchestral ode '' Blest Pair of Sirens'', and the hymn tune "Repton", which sets the words "Dear Lord and Father of Mankind". His orchestral works include five symphonies and a set of Symphonic Variations. He also composed the music for ''Ode to Newfoundland'', the Newfoundland and Labrador provincial anthem (and former national anthem). After early attempts to work in insurance at his father's behest, Parry was taken up by George Grove, first as a contributor to Grove's massive '' Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' in the 1870s and '80s, and then in 1883 as professor of composition and musical history at the Royal College of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Requiem (Verdi)
The ''Messa da Requiem'' is a musical setting of the Catholic funeral mass (Requiem) for four soloists, double choir and orchestra by Giuseppe Verdi. It was composed in memory of Alessandro Manzoni, whom Verdi admired. The first performance, at the San Marco church in Milan on 22 May 1874, marked the first anniversary of Manzoni's death. The work was at one time referred to as the Manzoni Requiem. Considered too operatic to be performed in a liturgical setting, it is usually given in concert form of around 90 minutes in length. Musicologist David Rosen calls it "probably the most frequently performed major choral work composed since the compilation of Mozart's Requiem". Composition history After Gioachino Rossini's death in 1868, Verdi suggested that a number of Italian composers collaborate on a ''Requiem'' in Rossini's honor. He began the effort by submitting the concluding movement, the " Libera me". During the next year a '' Messa per Rossini'' was compiled by Verdi and twelv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giuseppe Verdi
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi (; 9 or 10 October 1813 – 27 January 1901) was an Italian composer best known for his operas. He was born near Busseto to a provincial family of moderate means, receiving a musical education with the help of a local patron. Verdi came to dominate the Italian opera scene after the era of Gioachino Rossini, Gaetano Donizetti, and Vincenzo Bellini, whose works significantly influenced him. In his early operas, Verdi demonstrated a sympathy with the Risorgimento movement which sought the unification of Italy. He also participated briefly as an elected politician. The chorus "Va, pensiero" from his early opera ''Nabucco'' (1842), and similar choruses in later operas, were much in the spirit of the unification movement, and the composer himself became esteemed as a representative of these ideals. An intensely private person, Verdi did not seek to ingratiate himself with popular movements. As he became professionally successful, he was able ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Die Forelle
"" (German for "The Trout"), Op. 32, 550. is a lied, or song, composed in early 1817 for solo voice and piano with music by the Austrian composer Franz Schubert (1797–1828). Schubert chose to set the text of a poem by Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart, first published in the ' in 1783. The full poem tells the story of a trout being caught by a fisherman, but in its final stanza reveals its purpose as a moral piece warning young women to guard against young men. When Schubert set the poem to music, he removed the last verse, which contained the moral, changing the song's focus and enabling it to be sung by male or female singers. Schubert produced six subsequent copies of the work, all with minor variations. Schubert wrote "" in the single key of D-flat major with a varied (or modified) strophic form. The first two verses have the same structure but change for the final verse to give a musical impression of the trout being caught. In the Deutsch catalogue of Schubert's works ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart
Christian Friedrich Daniel Schubart (24 March 1739 – 10 October 1791), was a German poet, organist, composer, and journalist. He was repeatedly punished for his social-critical writing and spent ten years in severe conditions in jail. Life Born at Obersontheim in Swabia, he entered the University of Erlangen in 1758 as a student of theology. He led a dissolute life, and after two years' stay was summoned home by his parents. After attempting to earn a livelihood as private tutor and as assistant preacher, his musical talents gained him the appointment of organist in Geislingen an der Steige. Meeting Schubart in Ludwigsburg in 1772, Charles Burney called him "the first, real great harpsichord player that I had hitherto met with in Germany ... He is formed on the Bach school; but is an enthusiast, and original in genius. Many of his pieces are printed in Holland; they are full of taste and fire. He played on the Clavichord, with great delicacy and expression; his finger is brillia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ave Verum Corpus (Mozart)
''Ave verum corpus'' (Hail, true body), ( K. 618), is a motet in D major composed by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart in 1791. It is a setting of the Latin hymn Ave verum corpus. Mozart wrote it for Anton Stoll, a friend who was the church musician of St. Stephan in Baden bei Wien. The motet was composed for the feast of Corpus Christi; the autograph is dated 17 June 1791. It is scored for SATB choir, string instruments and organ. History Mozart composed the motet in 1791 in the middle of writing his opera ''Die Zauberflöte''. He wrote it while visiting his wife Constanze, who was pregnant with their sixth child and staying in the spa Baden bei Wien. Mozart set the 14th century Eucharistic hymn in Latin "Ave verum corpus". He wrote the motet for Anton Stoll, a friend of his ."Ave Verum Corpus, K 618" '' |