|
Sendust
Sendust is a magnetic metal powder that was invented by Hakaru Masumoto at Tohoku Imperial University in Sendai, Japan circa 1936 as an alternative to permalloy in inductor applications for telephone networks. Sendust composition is typically 85% iron, 9% silicon and 6% aluminium. The powder is sintered into cores to manufacture inductors. Sendust cores have high magnetic permeability (up to 140 000), low loss, low coercivity (5 A/m) good temperature stability and saturation flux density up to 1 T. Due to its chemical composition and crystallographic structure Sendust exhibits simultaneously zero magnetostriction and zero magnetocrystalline anisotropy constant K1. Sendust is harder than permalloy, and is thus useful in abrasive wear applications such as magnetic recording heads. See also * Alperm External links Comparison of molybdenum permalloy with sendustas energy storage inductors (PDF Portable Document Format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Permeability
In electromagnetism, permeability is the measure of magnetization that a material obtains in response to an applied magnetic field. Permeability is typically represented by the (italicized) Greek letter ''μ''. The term was coined by William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin in 1872, and used alongside permittivity by Oliver Heaviside in 1885. The reciprocal of permeability is magnetic reluctivity. In SI units, permeability is measured in henries per meter (H/m), or equivalently in newtons per ampere squared (N/A2). The permeability constant ''μ''0, also known as the magnetic constant or the permeability of free space, is the proportionality between magnetic induction and magnetizing force when forming a magnetic field in a classical vacuum. A closely related property of materials is magnetic susceptibility, which is a dimensionless proportionality factor that indicates the degree of magnetization of a material in response to an applied magnetic field. Explanation In the ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permalloy
Permalloy is a nickel–iron magnetic alloy, with about 80% nickel and 20% iron content. Invented in 1914 by physicist Gustav Elmen at Bell Telephone Laboratories, it is notable for its very high magnetic permeability, which makes it useful as a magnetic core material in electrical and electronic equipment, and also in magnetic shielding to block magnetic fields. Commercial permalloy alloys typically have relative permeability of around 100,000, compared to several thousand for ordinary steel. In addition to high permeability, its other magnetic properties are low coercivity, near zero magnetostriction, and significant anisotropic magnetoresistance. The low magnetostriction is critical for industrial applications, allowing it to be used in thin films where variable stresses would otherwise cause a ruinously large variation in magnetic properties. Permalloy's electrical resistivity can vary as much as 5% depending on the strength and the direction of an applied magnetic field. P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recording Head
A recording head is the physical interface between a recording apparatus and a moving recording medium. Recording heads are generally classified according to the physical principle that allows them to impress their data upon their medium. A recording head is often mechanically paired with a playback head, which, though proximal to, is often discrete from the record head. Types The two most common forms of recording head are: * Magnetic - Magnetic recording heads use the principles of electromagnetism to coerce a paramagnetic recording medium, such as iron oxides, to orient in a readable manner such as magnetic tape. Record heads are constructed of laminated permalloy, ferrite, or sendust. As of 2006, this is the most dominant type of head in use. * Optical - Optical recording heads use the principles of optics and light to impart energy on a recording medium, which accepts the energy in a readable manner, e.g. by melting or photography. Note that Magneto-optical recording, though ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hakaru Masumoto
Hakaru Masumoto (1895–1987) was a pioneer in metal and alloy research. He discovered numerous superior and unique alloys, and contributed to improving the performance of precision machinery. A student of Kotaro Honda, Masumoto developed a magnetic metal powder Sendust in 1936,The Japanese Contributions to the English Language: An Historical Dictionary, by Garland Hampton Cannon, Nicholas W. Warren, page 205 and was the winner of the Imperial Prize of the Japan Academy The is a prestigious honor conferred to two of the recipients of the Japan Academy Prize. Overviews It is awarded in two categories: humanities and natural sciences. The Emperor and Empress visit the awarding ceremony and present a vase to ... in 1946. References {{DEFAULTSORT:Masumoto, Hakaru 1895 births 1987 deaths People from Hiroshima Japanese metallurgists Academic staff of Tohoku University Tohoku University alumni Grand Cordons of the Order of the Rising Sun Recipients of the Order ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Alloys
A magnetic alloy is a combination of various metals from the periodic table such as ferrite that contains at least one of the three main magnetic elements: iron (Fe), nickel (Ni), or cobalt (Co) etc.. Such an alloy must contain but is not limited to one or more of these metals. Magnetic alloys have become common, especially in the form of steel (iron and carbon), alnico (iron, nickel, cobalt, and aluminum), and permalloy (iron and nickel). So-called "neodymium magnets" are actually alloys of neodymium, iron and boron forming the crystal structure Nd2Fe14B . The strongest magnetic element is iron, which allows items made out of these alloys to attract to magnets. See also * Ferroalloy Ferroalloy refers to various alloys of iron with a high proportion of one or more other elements such as manganese (Mn), aluminium (Al), or silicon (Si). They are used in the production of steels and alloys. The alloys impart distinctive qualitie ... References External links Magnetic Alloys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alperm
Alperm (also alfenol or alfer) is a class of alloys comprising 83-90% of iron and 10-17% of aluminium. The most widely used composition is with 16% Al. An alloy with 13% Al is also sometimes referred to as alfer. It exhibits large magnetostriction and it is used in magnetoelastic sensors. Later during the WW2, Japanese used the alloy with 12.7-12.9% aluminium as a replacement of nickel for the magnetostrictive transducers used in their Type 93 model 5, Type 3, and Simple naval sonars. Alperm is magnetically soft and exhibits high magnetic permeability. The material can be produced in 0.5 mm thick sheets, as well as 50-60 μm thick ribbons. The coercivity is usually below 5 A/m (for alfer it is around 50 A/m) and permeability 55 000 (for alfer 4000). Saturation flux density is 0.8 T (for alfer 1.28 T). The addition of Al increases electrical resistivity of alloy up to 140 μΩm, which is almost four times the value in commonly used 3% SiFe electrical steel. For this reaso ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
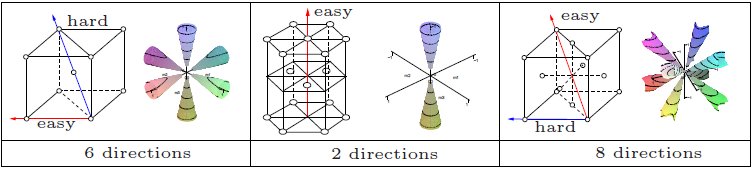
Magnetocrystalline Anisotropy
In physics, a ferromagnetic material is said to have magnetocrystalline anisotropy if it takes more energy to magnetize it in certain directions than in others. These directions are usually related to the principal axes of its crystal lattice. It is a special case of magnetic anisotropy. In other words, the excess energy required to magnetize a specimen in a particular direction over that required to magnetize it along the easy direction is called crystalline anisotropy energy. Causes The spin-orbit interaction is the primary source of magnetocrystalline anisotropy. It is basically the orbital motion of the electrons which couples with crystal electric field giving rise to the first order contribution to magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The second order arises due to the mutual interaction of the magnetic dipoles. This effect is weak compared to the exchange interaction and is difficult to compute from first principles, although some successful computations have been made. Pra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetostriction
Magnetostriction (cf. electrostriction) is a property of magnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of materials' magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ. The effect was first identified in 1842 by James Joule when observing a sample of iron. This effect causes energy loss due to frictional heating in susceptible ferromagnetic cores. The effect is also responsible for the low-pitched humming sound that can be heard coming from transformers, where oscillating AC currents produce a changing magnetic field. Explanation Internally, ferromagnetic materials have a structure that is divided into '' domains'', each of which is a region of uniform magnetization. When a magnetic field is applied, the boundaries between the domains shift and the domains rotate; both of these effects cause a change in the material's dimensions. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has a great affinity towards oxygen, and forms a protective layer of oxide on the surface when exposed to air. Aluminium visually resembles silver, both in its color and in its great ability to reflect light. It is soft, non-magnetic and ductile. It has one stable isotope, 27Al; this isotope is very common, making aluminium the twelfth most common element in the Universe. The radioactivity of 26Al is used in radiodating. Chemically, aluminium is a post-transition metal in the boron group; as is common for the group, aluminium forms compounds primarily in the +3 oxidation state. The aluminium cation Al3+ is small and highly charged; as such, it is polarizing, and bonds aluminium forms tend towards covalency. The strong affinity tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sintered
Clinker nodules produced by sintering Sintering or frittage is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by pressure or heat without melting it to the point of liquefaction. Sintering happens as part of a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plastics, and other materials. The atoms in the materials diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing the particles together and creating one solid piece. Because the sintering temperature does not have to reach the melting point of the material, sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points such as tungsten and molybdenum. The study of sintering in metallurgical powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy. An example of sintering can be observed when ice cubes in a glass of water adhere to each other, which is driven by the temperature difference between the water and the ice. Examples of pressure-driven sintering are the compact ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tohoku Imperial University
, or is a Japanese national university located in Sendai, Miyagi in the Tōhoku Region, Japan. It is informally referred to as . Established in 1907, it was the third Imperial University in Japan and among the first three Designated National Universities, along with the University of Tokyo and Kyoto University. Tohoku University is a Top Type university of the Top Global University Project, and since 2020 has been ranked the best university in Japan by Times Higher Education. In 2016, Tohoku University had 10 faculties, 16 graduate schools and 6 research institutes, with a total enrollment of 17,885 students. The university's three core values are "Research First (研究第一主義)," "Open-Doors (門戸開放)," and "Practice-Oriented Research and Education (実学尊重)." History On June 22, 1907(明治40年,''Mēji yonjyunen''), the university was established under the name by the Meiji government as the third Imperial University of Japan, following the Tokyo Imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic table: carbon is above it; and germanium, tin, lead, and flerovium are below it. It is relatively unreactive. Because of its high chemical affinity for oxygen, it was not until 1823 that Jöns Jakob Berzelius was first able to prepare it and characterize it in pure form. Its oxides form a family of anions known as silicates. Its melting and boiling points of 1414 °C and 3265 °C, respectively, are the second highest among all the metalloids and nonmetals, being surpassed only by boron. Silicon is the eighth most common element in the universe by mass, but very rarely occurs as the pure element in the Earth's crust. It is widely distributed in space in cosmic dusts, planetoids, and planets as various forms of silicon dioxide ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |