|
Magnetostriction
Magnetostriction is a property of magnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of materials' magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ. The effect was first identified in 1842 by James Joule when observing a sample of iron. Magnetostriction applies to magnetic fields, while electrostriction applies to electric fields. Magnetostriction causes energy loss due to frictional heating in susceptible ferromagnetic cores, and is also responsible for the low-pitched humming sound that can be heard coming from transformers, where alternating currents produce a changing magnetic field. Explanation Internally, ferromagnetic materials have a structure that is divided into '' domains'', each of which is a region of uniform magnetization. When a magnetic field is applied, the boundaries between the domains shift and the domains rota ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetostrictive Hysteresis Loop Of Mn-Zn Ferrite
Magnetostriction is a property of magnet, magnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of materials' magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ. The effect was first identified in 1842 by James Joule when observing a sample of iron. Magnetostriction applies to magnetic fields, while electrostriction applies to electric fields. Magnetostriction causes energy loss due to frictional heating in susceptible ferromagnetic cores, and is also responsible for the low-pitched humming sound that can be heard coming from transformers, where alternating currents produce a changing magnetic field. Explanation Internally, ferromagnetic materials have a structure that is divided into ''magnetic domain, domains'', each of which is a region of uniform magnetization. When a magnetic field is applied, the boundaries between the domains shift ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetostrictive Transducer
Magnetostriction is a property of magnetic materials that causes them to change their shape or dimensions during the process of magnetization. The variation of materials' magnetization due to the applied magnetic field changes the magnetostrictive strain until reaching its saturation value, λ. The effect was first identified in 1842 by James Joule when observing a sample of iron. Magnetostriction applies to magnetic fields, while electrostriction applies to electric fields. Magnetostriction causes energy loss due to frictional heating in susceptible ferromagnetic cores, and is also responsible for the low-pitched humming sound that can be heard coming from transformers, where alternating currents produce a changing magnetic field. Explanation Internally, ferromagnetic materials have a structure that is divided into '' domains'', each of which is a region of uniform magnetization. When a magnetic field is applied, the boundaries between the domains shift and the domains rotate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terfenol-D
Terfenol-D, an alloy of the formula (''x'' ≈ 0.3), is a magnetostrictive material. It was initially developed in the 1970s by the Naval Ordnance Laboratory in the United States. The technology for manufacturing the material efficiently was developed in the 1980s at Ames Laboratory under a U.S. Navy-funded program. It is named after terbium, iron (Fe), Naval Ordnance Laboratory (NOL), and the D comes from dysprosium. Physical properties The alloy has the highest magnetostriction of any alloy, up to 0.002 m/m at saturation; it expands and contracts in a magnetic field. Terfenol-D has a large magnetostriction force, high energy density, low sound velocity, and a low Young's modulus. At its most pure form, it also has low ductility and a low fracture resistance. Terfenol-D is a gray alloy that has different possible ratios of its elemental components that always follow a formula of . The addition of dysprosium made it easier to induce magnetostrictive responses by making ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Villari Effect
The inverse magnetostrictive effect, magnetoelastic effect or Villari effect, after its discoverer Emilio Villari, is the change of the magnetic susceptibility of a material when subjected to a mechanical stress. Explanation The magnetostriction \lambda characterizes the shape change of a ferromagnetic material during magnetization, whereas the inverse magnetostrictive effect characterizes the change of sample magnetization M(for given magnetizing field strength H) when mechanical stresses \sigma are applied to the sample. Qualitative explanation of magnetoelastic effect Under a given uni-axial mechanical stress \sigma, the flux density B for a given magnetizing field strength H may increase or decrease. The way in which a material responds to stresses depends on its saturation magnetostriction \lambda_s. For this analysis, compressive stresses \sigma are considered as negative, whereas tensile stresses are positive. According to Le Chatelier's principle: \left(\frac\right)_= ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Domain
A magnetic domain is a region within a magnetic material in which the magnetization is in a uniform direction. This means that the individual magnetic moments of the atoms are aligned with one another and they point in the same direction. When cooled below a temperature called the Curie temperature, the magnetization of a piece of ferromagnetic material spontaneously divides into many small regions called magnetic domains. The magnetization within each domain points in a uniform direction, but the magnetization of different domains may point in different directions. Magnetic domain structure is responsible for the magnetic behavior of ferromagnetic materials like iron, nickel, cobalt and their alloys, and ferrimagnetic materials like Ferrite (magnet), ferrite. This includes the formation of permanent magnets and the attraction of ferromagnetic materials to a magnetic field. The regions separating magnetic domains are called Domain wall (magnetism), domain walls, where the mag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
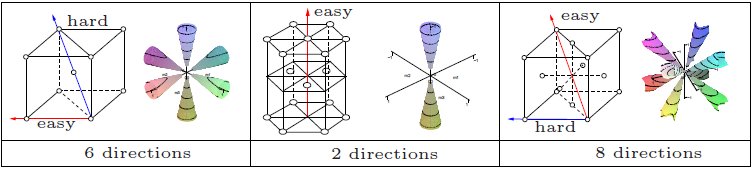
Magnetocrystalline Anisotropy
In physics, a ferromagnetic material is said to have magnetocrystalline anisotropy if it takes more energy to magnetization, magnetize it in certain directions than in others. These directions are usually related to the crystal structure, principal axes of its crystal lattice. It is a special case of magnetic anisotropy. In other words, the excess energy required to magnetize a specimen in a particular direction over that required to magnetize it along the easy direction is called crystalline anisotropy energy. Causes The spin-orbit interaction is the primary source of magnetocrystalline anisotropy. It is basically the orbital motion of the electrons which couples with crystal electric field giving rise to the first order contribution to magnetocrystalline anisotropy. The second order arises due to the mutual interaction of the magnetic dipoles. This effect is weak compared to the exchange interaction and is difficult to compute from first principles, although some successful co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces a varying magnetic flux in the transformer's core, which induces a varying electromotive force, electromotive force (EMF) across any other coils wound around the same core. Electrical energy can be transferred between separate coils without a metallic (conductive) connection between the two circuits. Faraday's law of induction, discovered in 1831, describes the induced voltage effect in any coil due to a changing magnetic flux encircled by the coil. Transformers are used to change Alternating current, AC voltage levels, such transformers being termed step-up or step-down type to increase or decrease voltage level, respectively. Transformers can also be used to provide galvanic isolation between circuits as well as to couple stages of signa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dysprosium
Dysprosium is a chemical element; it has symbol Dy and atomic number 66. It is a rare-earth element in the lanthanide series with a metallic silver luster. Dysprosium is never found in nature as a free element, though, like other lanthanides, it is found in various minerals, such as xenotime. Naturally occurring dysprosium is composed of seven isotopes, the most abundant of which is 164Dy. Dysprosium was first identified in 1886 by Paul Émile Lecoq de Boisbaudran, but it was not isolated in pure form until the development of ion-exchange techniques in the 1950s. Dysprosium is used to produce neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets, which are crucial for electric vehicle motors and the efficient operation of wind turbines. It is used for its high thermal neutron absorption cross-section in making control rods in nuclear reactors, for its high magnetic susceptibility () in data-storage applications, and as a component of Terfenol-D (a magnetostrictive material). Soluble dyspr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Joule
James Prescott Joule (; 24 December 1818 11 October 1889) was an English physicist. Joule studied the nature of heat and discovered its relationship to mechanical work. This led to the law of conservation of energy, which in turn led to the development of the first law of thermodynamics. The International System of Units, SI unit of energy, the joule (J), is named after him. He worked with Lord Kelvin to develop an absolute thermodynamic temperature scale, which came to be called the Kelvin scale. Joule also made observations of magnetostriction, and he found the relationship between the electric current, current through a resistor and the heat dissipation, dissipated, which is also called Joule's first law. His experiments about energy transformations were first published in 1843. Early years James Joule was born in 1818, the son of Benjamin Joule (1784–1858), a wealthy brewer, and his wife, Alice Prescott, on New Bailey Street in City of Salford, Salford. Joule was tutor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrostriction
In electromagnetism, electrostriction is a property of all electrical non- conductor or dielectrics. Electrostriction causes these materials to change their shape under the application of an electric field. It is the dual property to magnetostriction. Explanation Electrostriction is a property of all dielectric materials, and is caused by displacement of ions in the crystal lattice upon being exposed to an external electric field. The cause of electrostrictive is linked to anharmonic effects. Positive ions will be displaced in the direction of the field, while negative ions will be displaced in the opposite direction. This displacement will accumulate throughout the bulk material and result in an overall strain (elongation) in the direction of the field. The thickness will be reduced in the orthogonal directions characterized by Poisson's ratio. All insulating materials consisting of more than one type of atom will be ionic to some extent due to the difference of electronegativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terbium
Terbium is a chemical element; it has Symbol (chemistry), symbol Tb and atomic number 65. It is a silvery-white, rare earth element, rare earth metal that is malleable and ductile. The ninth member of the lanthanide series, terbium is a fairly electropositive metal that reacts with water, evolving hydrogen gas. Terbium is never found in nature as a free element, but it is contained in many minerals, including cerite, gadolinite, monazite, xenotime and euxenite. Swedish chemist Carl Gustaf Mosander discovered terbium as a chemical element in 1843. He detected it as an impurity in Yttrium(III) oxide, yttrium oxide (). Yttrium and terbium, as well as erbium and ytterbium, are named after the village of Ytterby in Sweden. Terbium was not isolated in pure form until the advent of ion exchange techniques. Terbium is used to dopant, dope calcium fluoride, calcium tungstate and strontium molybdate in solid-state devices, and as a crystal stabilizer of fuel cells that operate at elevated t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiedemann Effect
The Wiedemann effect is the twisting of a ferromagnetic rod through which an electric current is flowing when the rod is placed in a longitudinal magnetic field, caused by the total helical magnetic field. It is the inverse of the Matteucci effect. It was discovered by the German physicist Gustav Wiedemann in 1858 . The Wiedemann effect is one of the manifestations of magnetostriction in a field formed by the combination of a longitudinal magnetic field and a circular magnetic field that is created by an electric current. If the electric current (or the magnetic field) is alternating, the rod will begin torsional oscillation. In linear approach angle of rod torsion ''α'' does not depend on its cross-section form and is defined only by current density and magnetoelastic properties of the rod: :\alpha = j \frac, where * j is current density; * h_ is magnetoelastic parameter, proportional to longitudinal magnetic field value; * G is the shear modulus. Applications Magnetostric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |