|
Semiautomaton
In mathematics and theoretical computer science, a semiautomaton is a deterministic finite automaton having inputs but no output. It consists of a set ''Q'' of states, a set Σ called the input alphabet, and a function ''T'': ''Q'' × Σ → ''Q'' called the transition function. Associated with any semiautomaton is a monoid called the characteristic monoid, input monoid, transition monoid or transition system of the semiautomaton, which acts on the set of states ''Q''. This may be viewed either as an action of the free monoid of strings in the input alphabet Σ, or as the induced transformation semigroup of ''Q''. In older books like Clifford and Preston (1967) semigroup actions are called "operands". In category theory, semiautomata essentially are functors. Transformation semigroups and monoid acts : A transformation semigroup or transformation monoid is a pair (M,Q) consisting of a set ''Q'' (often called the "set of states") and a semigroup or monoid ''M'' of functions, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transformation Semigroup
In algebra, a transformation semigroup (or composition semigroup) is a collection of transformations ( functions from a set to itself) that is closed under function composition. If it includes the identity function, it is a monoid, called a transformation (or composition) monoid. This is the semigroup analogue of a permutation group. A transformation semigroup of a set has a tautological semigroup action on that set. Such actions are characterized by being faithful, i.e., if two elements of the semigroup have the same action, then they are equal. An analogue of Cayley's theorem shows that any semigroup can be realized as a transformation semigroup of some set. In automata theory, some authors use the term ''transformation semigroup'' to refer to a semigroup acting faithfully on a set of "states" different from the semigroup's base set. There is a correspondence between the two notions. Transformation semigroups and monoids A transformation semigroup is a pair (''X'',''S''), w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accept State
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of '' states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types— deterministic finite-state machines and non-deterministic finite-state machines. A deterministic finite-state machine can be constructed equivalent to any non-deterministic one. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions depending on a sequence of events with which they are presented. Simple examples are vending machines, which dispense p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finite State Machine
A finite-state machine (FSM) or finite-state automaton (FSA, plural: ''automata''), finite automaton, or simply a state machine, is a mathematical model of computation. It is an abstract machine that can be in exactly one of a finite number of '' states'' at any given time. The FSM can change from one state to another in response to some inputs; the change from one state to another is called a ''transition''. An FSM is defined by a list of its states, its initial state, and the inputs that trigger each transition. Finite-state machines are of two types— deterministic finite-state machines and non-deterministic finite-state machines. A deterministic finite-state machine can be constructed equivalent to any non-deterministic one. The behavior of state machines can be observed in many devices in modern society that perform a predetermined sequence of actions depending on a sequence of events with which they are presented. Simple examples are vending machines, which dispense p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoid Action
In algebra and theoretical computer science, an action or act of a semigroup on a set is a rule which associates to each element of the semigroup a transformation of the set in such a way that the product of two elements of the semigroup (using the semigroup operation) is associated with the composite of the two corresponding transformations. The terminology conveys the idea that the elements of the semigroup are ''acting'' as transformations of the set. From an algebraic perspective, a semigroup action is a generalization of the notion of a group action in group theory. From the computer science point of view, semigroup actions are closely related to automata: the set models the state of the automaton and the action models transformations of that state in response to inputs. An important special case is a monoid action or act, in which the semigroup is a monoid and the identity element of the monoid acts as the identity transformation of a set. From a category theoretic point of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semigroup Action
In algebra and theoretical computer science, an action or act of a semigroup on a set is a rule which associates to each element of the semigroup a transformation of the set in such a way that the product of two elements of the semigroup (using the semigroup operation) is associated with the composite of the two corresponding transformations. The terminology conveys the idea that the elements of the semigroup are ''acting'' as transformations of the set. From an algebraic perspective, a semigroup action is a generalization of the notion of a group action in group theory. From the computer science point of view, semigroup actions are closely related to automata: the set models the state of the automaton and the action models transformations of that state in response to inputs. An important special case is a monoid action or act, in which the semigroup is a monoid and the identity element of the monoid acts as the identity transformation of a set. From a category theoretic point of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting points of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Languages
In logic, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics, a formal language consists of string (computer science), words whose symbol (formal), letters are taken from an alphabet (formal languages), alphabet and are well-formedness, well-formed according to a specific set of rules. The alphabet of a formal language consists of symbols, letters, or tokens that concatenate into strings of the language. Each string concatenated from symbols of this alphabet is called a word, and the words that belong to a particular formal language are sometimes called ''well-formed words'' or ''well-formed formulas''. A formal language is often defined by means of a formal grammar such as a regular grammar or context-free grammar, which consists of its formation rules. In computer science, formal languages are used among others as the basis for defining the grammar of programming languages and formalized versions of subsets of natural languages in which the words of the language represent concepts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Category (mathematics)
In mathematics, a category (sometimes called an abstract category to distinguish it from a concrete category) is a collection of "objects" that are linked by "arrows". A category has two basic properties: the ability to compose the arrows associatively and the existence of an identity arrow for each object. A simple example is the category of sets, whose objects are sets and whose arrows are functions. '' Category theory'' is a branch of mathematics that seeks to generalize all of mathematics in terms of categories, independent of what their objects and arrows represent. Virtually every branch of modern mathematics can be described in terms of categories, and doing so often reveals deep insights and similarities between seemingly different areas of mathematics. As such, category theory provides an alternative foundation for mathematics to set theory and other proposed axiomatic foundations. In general, the objects and arrows may be abstract entities of any kind, and the n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alphabet (computer Science)
In formal language theory, an alphabet is a non-empty set of symbols/glyphs, typically thought of as representing letters, characters, or digits but among other possibilities the "symbols" could also be a set of phonemes (sound units). Alphabets in this technical sense of a set are used in a diverse range of fields including logic, mathematics, computer science, and linguistics. An alphabet may have any cardinality ("size") and depending on its purpose maybe be finite (e.g., the alphabet of letters "a" through "z"), countable (e.g., \), or even uncountable (e.g., \). Strings, also known as "words", over an alphabet are defined as a sequence of the symbols from the alphabet set. For example, the alphabet of lowercase letters "a" through "z" can be used to form English words like "iceberg" while the alphabet of both upper and lower case letters can also be used to form proper names like "Wikipedia". A common alphabet is , the binary alphabet, and a "00101111" is an example of a bin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kleene Star
In mathematical logic and computer science, the Kleene star (or Kleene operator or Kleene closure) is a unary operation, either on sets of strings or on sets of symbols or characters. In mathematics, it is more commonly known as the free monoid construction. The application of the Kleene star to a set V is written as ''V^*''. It is widely used for regular expressions, which is the context in which it was introduced by Stephen Kleene to characterize certain automata, where it means "zero or more repetitions". # If V is a set of strings, then ''V^*'' is defined as the smallest superset of V that contains the empty string \varepsilon and is closed under the string concatenation operation. # If V is a set of symbols or characters, then ''V^*'' is the set of all strings over symbols in V, including the empty string \varepsilon. The set ''V^*'' can also be described as the set containing the empty string and all finite-length strings that can be generated by concatenating arbitrary e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
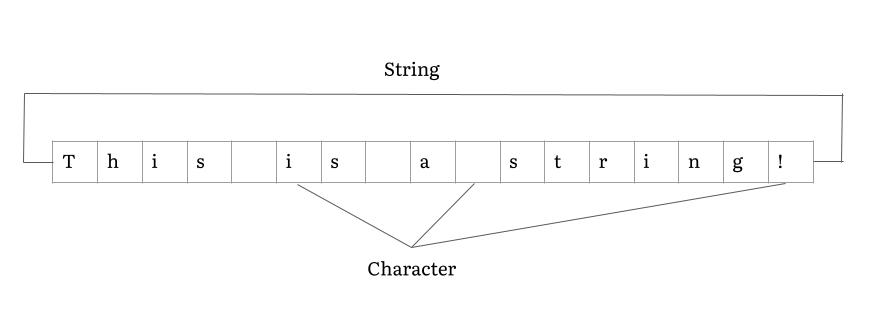
String (computer Science)
In computer programming, a string is traditionally a sequence of characters, either as a literal constant or as some kind of variable. The latter may allow its elements to be mutated and the length changed, or it may be fixed (after creation). A string is generally considered as a data type and is often implemented as an array data structure of bytes (or words) that stores a sequence of elements, typically characters, using some character encoding. ''String'' may also denote more general arrays or other sequence (or list) data types and structures. Depending on the programming language and precise data type used, a variable declared to be a string may either cause storage in memory to be statically allocated for a predetermined maximum length or employ dynamic allocation to allow it to hold a variable number of elements. When a string appears literally in source code, it is known as a string literal or an anonymous string. In formal languages, which are used in mathematical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empty Word
In formal language theory, the empty string, or empty word, is the unique string of length zero. Formal theory Formally, a string is a finite, ordered sequence of characters such as letters, digits or spaces. The empty string is the special case where the sequence has length zero, so there are no symbols in the string. There is only one empty string, because two strings are only different if they have different lengths or a different sequence of symbols. In formal treatments, the empty string is denoted with ε or sometimes Λ or λ. The empty string should not be confused with the empty language ∅, which is a formal language (i.e. a set of strings) that contains no strings, not even the empty string. The empty string has several properties: * , ε, = 0. Its string length is zero. * ε ⋅ s = s ⋅ ε = s. The empty string is the identity element of the concatenation operation. The set of all strings forms a free monoid with respect to ⋅ and ε. * εR = ε. Reversal of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |