|
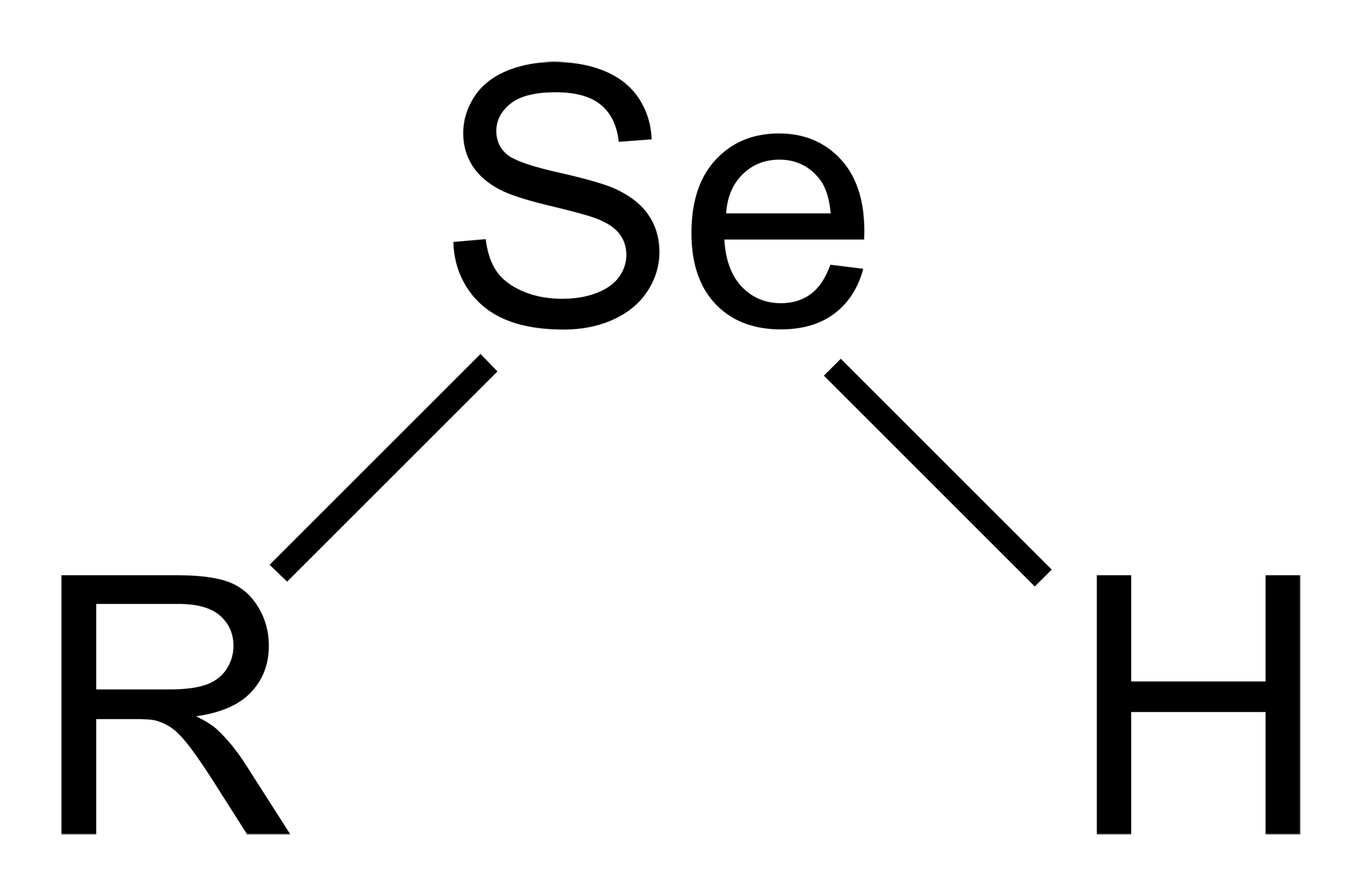
Selenol
Selenols are organic compounds that contain the functional group with the connectivity C– Se–H. Selenols are sometimes also called selenomercaptans and selenothiols. Selenols are one of the principal classes of organoselenium compounds. The best known member of the group is the amino acid selenocysteine. Structure, bonding, properties Selenols are structurally similar to thiols, but the C-Se bond is about 8% longer at 196 pm. The C–Se–H angle approaches 90°. The bonding involves almost pure p-orbitals on Se, hence the near 90 angles. The Se–H bond energy is weaker than the S–H bond, consequently selenols are easily oxidized and serve as H-atom donors. The Se-H bond is much weaker than the S-H bond as reflected in their respective bond dissociation energy (BDE). For C6H5Se-H, the BDE is 326 kJ/mol, while for C6H5S-H, the BDE is 368 kJ/mol. Selenol acids are about 1000 times stronger than thiols: the p''K''a of CH3SeH is 5.2 vs 8.3 for CH3SH. Deprotonation affords the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenenic Acid
A selenenic acid is an organoselenium compound and an oxoacid with the general formula RSeOH, where R ≠ H. It is the first member of the family of organoselenium oxoacids, which also include seleninic acids and selenonic acids, which are RSeO2H and RSeO3H, respectively. Selenenic acids derived from selenoenzymes are thought to be responsible for the antioxidant activity of these enzymes. This functional group is sometimes called SeO-selenoperoxol. Properties In contrast to selenonic and seleninic acids, selenenic acids are unstable with respect to a self-condensation reaction to form the corresponding selenoseleninates or disproportionation into corresponding seleninic acids and diselenides: :2 RSeOH → RSe(O)SeR + H2O :2 RSeOH → RSeO2H + 1/2 RSeSeR Even the very bulky 2,4,6-tri-''tert''-butylbenzeneselenenic acid disproportionates readily. A stable selenenic acid was synthesized by burying the SeOH functional group within the cavity of a ''p''-''tert''-butyl rene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organoselenium Compound
Organoselenium compounds (or seleno-organic) are chemical compounds containing carbon-to-selenium chemical bonds. Organoselenium chemistry is the corresponding science exploring their properties and reactivity. Selenium belongs with oxygen and sulfur to the group 16 elements or chalcogens, and similarities in chemistry are to be expected. Organoselenium compounds are found at trace levels in ambient waters, soils and sediments. Selenium can exist with oxidation state −2, +2, +4, +6. Se(II) is the dominant form in organoselenium chemistry. Down the group 16 column, the bond strength becomes increasingly weaker (234 kJ/ mol for the C−Se bond and 272 kJ/mol for the C−S bond) and the bond lengths longer (C−Se 198 pm, C−S 181 pm and C−O 141 pm). Selenium compounds are more nucleophilic than the corresponding sulfur compounds and also more acidic. The p''K''a values of XH2 are 16 for oxygen, 7 for sulfur and 3.8 for selenium. In contrast to sulfoxides, the corresponding se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenocysteine
Selenocysteine (symbol Sec or U, in older publications also as Se-Cys) is the 21st proteinogenic amino acid. Selenoproteins contain selenocysteine residues. Selenocysteine is an analogue of the more common cysteine with selenium in place of the sulfur. Selenocysteine is present in several enzymes (for example glutathione peroxidases, tetraiodothyronine 5′ deiodinases, thioredoxin reductases, formate dehydrogenases, glycine reductases, selenophosphate synthetase 2, methionine-''R''-sulfoxide reductase B1 ( SEPX1), and some hydrogenases). It occurs in all three domains of life, including important enzymes (listed above) present in humans. Selenocysteine was discovered by biochemist Thressa Stadtman at the National Institutes of Health. Chemistry Selenocysteine is the Se-analogue of cysteine. It is rarely encountered outside of living tissue (and is not available commercially) because it is very susceptible to air-oxidation. More common is the oxidized derivative selenocys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenophenol
Benzeneselenol, also known as selenophenol, is the organoselenium compound with the formula C6H5SeH, often abbreviated PhSeH. It is the selenium analog of phenol. This colourless, malodorous compound is a reagent in organic synthesis. Synthesis Benzeneselenol is prepared by the reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide and selenium: :PhMgBr + Se → PhSeMgBr :PhSeMgBr + HCl → PhSeH + MgBrCl Since benzeneselenol does not have a long shelflife, it is often generated in situ. A common method is by reduction of diphenyldiselenide. A further reason for this conversion is that often, it is the anion that is sought. Reactions More so than thiophenol, benzeneselenol is easily oxidized by air. The facility of this reaction reflects the weakness of the Se-H bond, bond dissociation energy of which is estimated to be between 67 and 74 kcal/mol. In contrast, the S-H BDE for thiophenol is near 80 kcal/mol. The product is diphenyl diselenide as shown in this idealized equation: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzeneselenol
Benzeneselenol, also known as selenophenol, is the organoselenium compound with the formula C6H5SeH, often abbreviated PhSeH. It is the selenium analog of phenol. This colourless, malodorous compound is a reagent in organic synthesis. Synthesis Benzeneselenol is prepared by the reaction of phenylmagnesium bromide and selenium: :PhMgBr + Se → PhSeMgBr :PhSeMgBr + HCl → PhSeH + MgBrCl Since benzeneselenol does not have a long shelflife, it is often generated in situ. A common method is by reduction of diphenyldiselenide. A further reason for this conversion is that often, it is the anion that is sought. Reactions More so than thiophenol, benzeneselenol is easily oxidized by air. The facility of this reaction reflects the weakness of the Se-H bond, bond dissociation energy of which is estimated to be between 67 and 74 kcal/mol. In contrast, the S-H BDE for thiophenol is near 80 kcal/mol. The product is diphenyl diselenide as shown in this idealized equation: : ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metallomics (journal)
''Metallomics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal covering the growing research field of metallomics. The journal's scope is aimed at "elucidating the identification, distribution, dynamics, role and impact of metals and metalloids in biological systems". It is published by the Royal Society of Chemistry. The executive editor is Jeanne Andres, while the current chair of the editorial board is David Giedroc at Indiana University Bloomington. Abstracting and indexing The journal is abstracted and indexed in: * Chemical Abstracts Service/CASSI * PubMed/MEDLINE * Science Citation Index * Scopus According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citations of articles published in the last two years in a given journal, as ... of 4.526. References External links * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenourea
Selenourea is the organoselenium compound with the formula SeC(NH2)2. It is a white solid. This compound features a rare example of a stable, unhindered carbon-selenium double bond. The compound is used in the synthesis of selenium heterocycles. Compared to urea, the oxo-analog of selenourea, few studies have been done on the compound due to the instability and toxicity of selenium compounds. Selenourea is toxic if inhaled or consumed. Synthesis The compound was first synthesized in 1884 by Auguste Verneuil by the reaction of hydrogen selenide and cyanamide: :H2Se + NCNH2 → SeC(NH2)2 While this reaction has even found use in industrial synthesis of selenourea, more modern methods concern themselves with synthesis of substituted selenoureas. These can be synthesized using organic isoselenocyanates and secondary amines: :RN=C=Se + NHR′R″ → Se=C(NRH)(NR′R″H) Alternatively, a substituted carbodiimide could be used as follows: :RN=C=NR′ Se=C(NRH)(NR′H) Proper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkylation
Alkylation is the transfer of an alkyl group from one molecule to another. The alkyl group may be transferred as an alkyl carbocation, a free radical, a carbanion, or a carbene (or their equivalents). Alkylating agents are reagents for effecting alkylation. Alkyl groups can also be removed in a process known as dealkylation. Alkylating agents are often classified according to their nucleophilic or electrophilic character. In oil refining contexts, alkylation refers to a particular alkylation of isobutane with olefins. For upgrading of petroleum, alkylation produces a premium blending stock for gasoline. In medicine, alkylation of DNA is used in chemotherapy to damage the DNA of cancer cells. Alkylation is accomplished with the class of drugs called alkylating antineoplastic agents. Nucleophilic alkylating agents Nucleophilic alkylating agents deliver the equivalent of an alkyl anion ( carbanion). The formal "alkyl anion" attacks an electrophile, forming a new coval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Syntheses
''Organic Syntheses'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that was established in 1921. It publishes detailed and checked procedures for the synthesis of organic compounds. A unique feature of the review process is that all of the data and experiments reported in an article must be successfully repeated in the laboratory of a member of the editorial board as a check for reproducibility prior to publication. The journal is published by Organic Syntheses, Inc., a non-profit A nonprofit organization (NPO) or non-profit organisation, also known as a non-business entity, not-for-profit organization, or nonprofit institution, is a legal entity organized and operated for a collective, public or social benefit, in co ... corporation. An annual print version is published by John Wiley & Sons on behalf of Organic Syntheses, Inc. History Prior to World War I, work on synthetic organic chemistry in the United States had been quite limited, and most of the reagents used in labora ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylmagnesium Bromide
Phenylmagnesium bromide, with the simplified formula , is a magnesium-containing organometallic compound. It is commercially available as a solution in diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran (THF). Phenylmagnesium bromide is a Grignard reagent. It is often used as a synthetic equivalent for the phenyl "Ph−" synthon. Preparation Phenylmagnesium bromide is commercially available as solutions of diethyl ether or THF. Laboratory preparation involves treating bromobenzene with magnesium metal, usually in the form of turnings. A small amount of iodine may be used to activate the magnesium to initiate the reaction. Coordinating solvents such as ether or THF, are required to solvate (complex) the magnesium(II) center. The solvent must be aprotic since alcohols and water contain an acidic proton and thus react with phenylmagnesium bromide to give benzene. Carbonyl-containing solvents, such as acetone and ethyl acetate, are also incompatible with the reagent. Structure Although phen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grignard Reagent
A Grignard reagent or Grignard compound is a chemical compound with the general formula , where X is a halogen and R is an organic group, normally an alkyl or aryl. Two typical examples are methylmagnesium chloride and phenylmagnesium bromide . They are a subclass of the organomagnesium compounds. Grignard compounds are popular reagents in organic synthesis for creating new carbon-carbon bonds. For example, when reacted with another halogenated compound in the presence of a suitable catalyst, they typically yield and the magnesium halide as a byproduct; and the latter is insoluble in the solvents normally used. In this aspect, they are similar to organolithium reagents. Pure Grignard reagents are extremely reactive solids. They are normally handled as solutions in solvents such as diethyl ether or tetrahydrofuran; which are relatively stable as long as water is excluded. In such a medium, a Grignard reagent is invariably present as a complex with the magnesium atom co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |