|
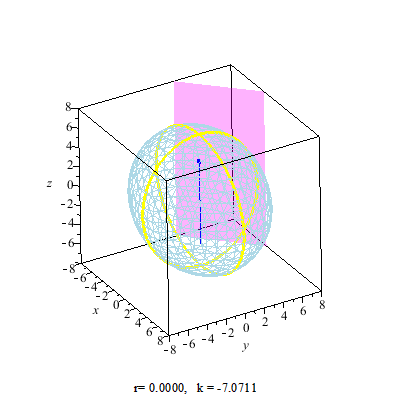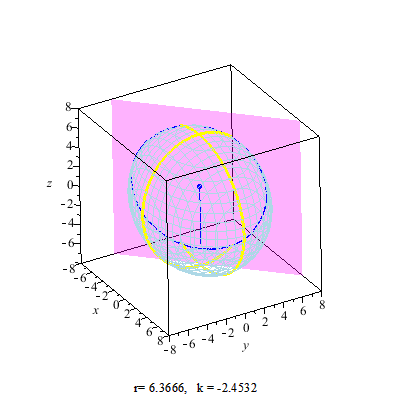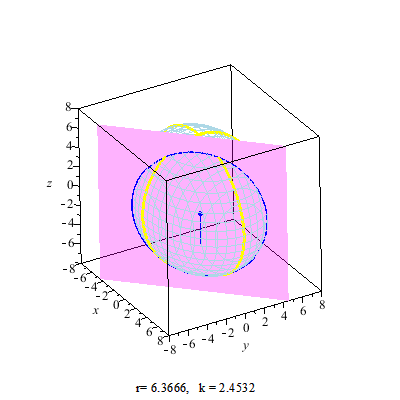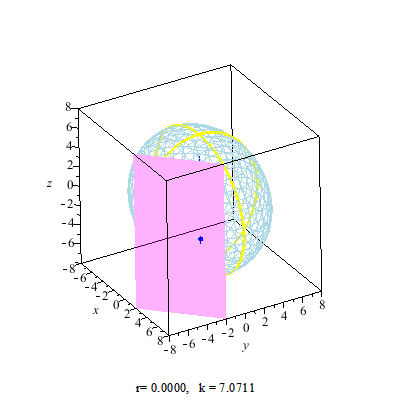
Secant Plane
A secant plane is a plane containing a nontrivial section of a sphere or an ellipsoid, or such a plane that a sphere is projected onto. Secant planes are similar to tangent planes, which contact the sphere's surface at a point, while secant planes contact the surface along curves. The two-dimensional representations of secant planes are secant lines, the lines that join two distinct points on a curve. Applications Secant planes are used in map projections. The secant plane intersects a globe along a small circle with no distortion, forming a standard parallel which has true scale. See also * Circular section * Circular segment * Spherical cap * Tangent space In mathematics, the tangent space of a manifold is a generalization of to curves in two-dimensional space and to surfaces in three-dimensional space in higher dimensions. In the context of physics the tangent space to a manifold at a point can be ... References {{Reflist External links Tangents and Secants in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid Circular Sections
An ellipsoid is a surface that can be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular axes of symmetry which intersect at a center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal axes'', or simply axes of the ellipsoid. If the three axes have different lengths, the figure is a triaxial ellipsoid ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plane (geometry)
In mathematics, a Euclidean plane is a Euclidean space of dimension two, denoted \textbf^2 or \mathbb^2. It is a geometric space in which two real numbers are required to determine the position of each point. It is an affine space, which includes in particular the concept of parallel lines. It has also metrical properties induced by a distance, which allows to define circles, and angle measurement. A Euclidean plane with a chosen Cartesian coordinate system is called a '' Cartesian plane''. The set \mathbb^2 of the ordered pairs of real numbers (the real coordinate plane), equipped with the dot product, is often called ''the'' Euclidean plane or ''standard Euclidean plane'', since every Euclidean plane is isomorphic to it. History Books I through IV and VI of Euclid's Elements dealt with two-dimensional geometry, developing such notions as similarity of shapes, the Pythagorean theorem (Proposition 47), equality of angles and areas, parallelism, the sum of the angles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cross Section (geometry)
In geometry and science, a cross section is the non-empty intersection (set theory), intersection of a solid body in three-dimensional space with a Plane (geometry), plane, or the analog in higher-dimensional spaces. Cutting an object into slices creates many parallel cross-sections. The boundary of a cross-section in three-dimensional space that is parallel to two of the Cartesian coordinate system, axes, that is, parallel to the plane determined by these axes, is sometimes referred to as a contour line; for example, if a plane cuts through mountains of a raised-relief map parallel to the ground, the result is a contour line in two-dimensional space showing points on the surface of the mountains of equal elevation. In technical drawing a cross-section, being a Planar projection, projection of an object onto a plane that intersects it, is a common tool used to depict the internal arrangement of a 3-dimensional object in two dimensions. It is traditionally crosshatched with th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere (from Ancient Greek, Greek , ) is a surface (mathematics), surface analogous to the circle, a curve. In solid geometry, a sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the center (geometry), ''center'' of the sphere, and the distance is the sphere's ''radius''. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental surface in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. The Earth is spherical Earth, often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ellipsoid
An ellipsoid is a surface that can be obtained from a sphere by deforming it by means of directional Scaling (geometry), scalings, or more generally, of an affine transformation. An ellipsoid is a quadric surface; that is, a Surface (mathematics), surface that may be defined as the zero set of a polynomial of degree two in three variables. Among quadric surfaces, an ellipsoid is characterized by either of the two following properties. Every planar Cross section (geometry), cross section is either an ellipse, or is empty, or is reduced to a single point (this explains the name, meaning "ellipse-like"). It is Bounded set, bounded, which means that it may be enclosed in a sufficiently large sphere. An ellipsoid has three pairwise perpendicular Rotational symmetry, axes of symmetry which intersect at a Central symmetry, center of symmetry, called the center of the ellipsoid. The line segments that are delimited on the axes of symmetry by the ellipsoid are called the ''principal ax ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secant Line
In geometry, a secant is a line (geometry), line that intersects a curve at a minimum of two distinct Point (geometry), points.. The word ''secant'' comes from the Latin word ''secare'', meaning ''to cut''. In the case of a circle, a secant intersects the circle at exactly two points. A Chord (geometry), chord is the line segment determined by the two points, that is, the interval (mathematics), interval on the secant whose ends are the two points. Circles A straight line can intersect a circle at zero, one, or two points. A line with intersections at two points is called a ''secant line'', at one point a ''tangent line'' and at no points an ''exterior line''. A ''chord'' is the line segment that joins two distinct points of a circle. A chord is therefore contained in a unique secant line and each secant line determines a unique chord. In rigorous modern treatments of plane geometry, results that seem obvious and were assumed (without statement) by Euclid in Euclid's Elements, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Map Projection
In cartography, a map projection is any of a broad set of Transformation (function) , transformations employed to represent the curved two-dimensional Surface (mathematics), surface of a globe on a Plane (mathematics), plane. In a map projection, coordinates, often expressed as latitude and longitude, of locations from the surface of the globe are transformed to coordinates on a plane. Projection is a necessary step in creating a two-dimensional map and is one of the essential elements of cartography. All projections of a sphere on a plane necessarily distort the surface in some way. Depending on the purpose of the map, some distortions are acceptable and others are not; therefore, different map projections exist in order to preserve some properties of the sphere-like body at the expense of other properties. The study of map projections is primarily about the characterization of their distortions. There is no limit to the number of possible map projections. More generally, proje ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Parallel (map Projections)
Standard may refer to: Symbols * Colours, standards and guidons, kinds of military signs * Standard (emblem), a type of a large symbol or emblem used for identification Norms, conventions or requirements * Standard (metrology), an object that bears a defined relationship to a unit of measure used for calibration of measuring devices * Standard (timber unit), an obsolete measure of timber used in trade * Breed standard (also called bench standard), in animal fancy and animal husbandry * BioCompute Standard, a standard for next generation sequencing * ''De facto'' standard, product or system with market dominance * Gold standard, a monetary system based on gold; also used metaphorically for the best of several options, against which the others are measured * Internet Standard, a specification ratified as an open standard by the Internet Engineering Task Force * Learning standards, standards applied to education content * Standard displacement, a naval term describing the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Section
In geometry, a circular section is a circle on a quadric surface (such as an ellipsoid or hyperboloid). It is a special plane (geometry), plane section of the quadric, as this circle is the intersection with the quadric of the plane containing the circle. Any plane section of a sphere is a circular section, if it contains at least 2 points. Any surface of revolution, quadric of revolution contains circles as sections with planes that are orthogonal to its axis; it does not contain any other circles, if it is not a sphere. More hidden are circles on other quadrics, such as tri-axial ellipsoids, elliptic cylinders, etc. Nevertheless, it is true that: *Any quadric surface which contains ellipses contains circles, too. Equivalently, all quadric surfaces contain circles except parabolic and hyperbolic cylinders and hyperbolic paraboloids. If a quadric contains a circle, then every intersection of the quadric with a plane parallel to this circle is also a circle, provided it contains at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circular Segment
In geometry, a circular segment or disk segment (symbol: ) is a region of a disk which is "cut off" from the rest of the disk by a straight line. The complete line is known as a '' secant'', and the section inside the disk as a '' chord''. More formally, a circular segment is a plane region bounded by a circular arc (of less than π radians by convention) and the circular chord connecting its endpoints. Formulae Let ''R'' be the radius of the arc which forms part of the perimeter of the segment, ''θ'' the central angle subtending the arc in radians, ''c'' the chord length, ''s'' the arc length, ''h'' the sagitta (height) of the segment, ''d'' the apothem of the segment, and ''a'' the area of the segment. Usually, chord length and height are given or measured, and sometimes the arc length as part of the perimeter, and the unknowns are area and sometimes arc length. These can't be calculated simply from chord length and height, so two intermediate quantities, the radius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spherical Cap
In geometry, a spherical cap or spherical dome is a portion of a sphere or of a ball (mathematics), ball cut off by a plane (mathematics), plane. It is also a spherical segment of one base, i.e., bounded by a single plane. If the plane passes through the center (geometry), center of the sphere (forming a great circle), so that the height of the cap is equal to the radius of the sphere, the spherical cap is called a ''Sphere#Hemisphere, hemisphere''. Volume and surface area The volume of the spherical cap and the area of the curved surface may be calculated using combinations of * The radius r of the sphere * The radius a of the base of the cap * The height h of the cap * The Spherical coordinate system, polar angle \theta between the rays from the center of the sphere to the apex of the cap (the pole) and the edge of the disk (mathematics), disk forming the base of the cap. These variables are inter-related through the formulas a = r \sin \theta, h = r ( 1 - \cos \theta ), 2hr = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangent Space
In mathematics, the tangent space of a manifold is a generalization of to curves in two-dimensional space and to surfaces in three-dimensional space in higher dimensions. In the context of physics the tangent space to a manifold at a point can be viewed as the space of possible velocities for a particle moving on the manifold. Informal description In differential geometry, one can attach to every point x of a differentiable manifold a ''tangent space''—a real vector space that intuitively contains the possible directions in which one can tangentially pass through x . The elements of the tangent space at x are called the ''tangent vectors'' at x . This is a generalization of the notion of a vector, based at a given initial point, in a Euclidean space. The dimension of the tangent space at every point of a connected manifold is the same as that of the manifold itself. For example, if the given manifold is a 2 -sphere, then one can picture the tangent space at a point ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |