|
Sea Fan
Alcyonacea, or soft corals, are an order of corals. In addition to the fleshy soft corals, the order Alcyonacea now contains all species previously known as "gorgonian corals", that produce a more or less hard skeleton, though quite different from "true" corals (Scleractinia). These can be found in suborders Holaxonia, Scleraxonia, and Stolonifera. They are sessile colonial cnidarians that are found throughout the oceans of the world, especially in the deep sea, polar waters, tropics and subtropics. Common names for subsets of this order are sea fans and sea whips; others are similar to the sea pens of related order Pennatulacea. Individual tiny polyps form colonies that are normally erect, flattened, branching, and reminiscent of a fan. Others may be whiplike, bushy, or even encrusting. A colony can be several feet high and across, but only a few inches thick. They may be brightly coloured, often purple, red, or yellow. Photosynthetic gorgonians can be successfully kept in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cladiella
''Cladiella'' is a genus of soft corals native to the Indo-Pacific region. These corals are commonly known as colt corals or finger leather corals and are often kept in reef aquaria. They grow fast, have short rounded or conical lobes and are sticky to the touch owing to the production of much mucus. They are creamy or pale grey in colour. The polyps are fully retractable and give the colony a fluffy look when extended. They may be a contrasting green or brown hue. Species The World Register of Marine Species lists the following species: *'' Cladiella arborea'' (Utinomi, 1954) *'' Cladiella arbusculoides'' Verseveldt & Benayahu, 1978 *'' Cladiella aspera'' Tixier-Durivault, 1970 *'' Cladiella australis'' (Macfadyen, 1936) *'' Cladiella bottai'' (Tixier-Durivault, 1943) *'' Cladiella brachyclados'' Ehrenberg, 1834 *'' Cladiella ceylonica'' (Pratt, 1905) *'' Cladiella conifera'' (Tixier-Durivault, 1943) *'' Cladiella crassa'' (Tixier-Durivault, 1943) *'' Cladiella daphnae'' van ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aquaculture
Aquaculture (less commonly spelled aquiculture), also known as aquafarming, is the controlled cultivation ("farming") of aquatic organisms such as fish, crustaceans, mollusks, algae and other organisms of value such as aquatic plants (e.g. lotus). Aquaculture involves cultivating freshwater, brackish water and saltwater populations under controlled or semi-natural conditions, and can be contrasted with commercial fishing, which is the harvesting of wild fish. Mariculture, commonly known as marine farming, refers specifically to aquaculture practiced in seawater habitats and lagoons, opposed to in freshwater aquaculture. Pisciculture is a type of aquaculture that consists of fish farming to obtain fish products as food. Aquaculture can also be defined as the breeding, growing, and harvesting of fish and other aquatic plants, also known as farming in water. It is an environmental source of food and commercial product which help to improve healthier habitats and used to recon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
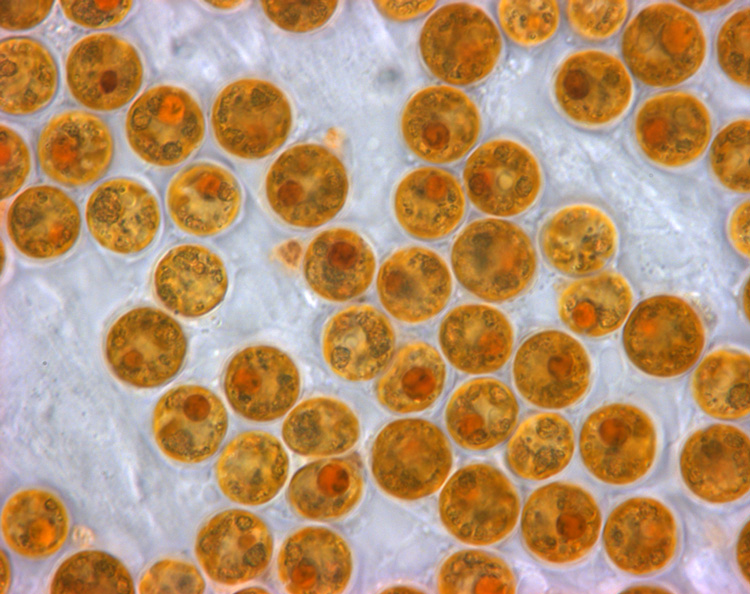
Zooxanthella
Zooxanthellae is a colloquial term for single-celled dinoflagellates that are able to live in symbiosis with diverse marine invertebrates including demosponges, corals, jellyfish, and nudibranchs. Most known zooxanthellae are in the genus ''Symbiodinium'', but some are known from the genus ''Amphidinium'', and other taxa, as yet unidentified, may have similar endosymbiont affinities. The true ''Zooxanthella'' K.brandt is a mutualist of the radiolarian ''Collozoum inerme'' (Joh.Müll., 1856) and systematically placed in Peridiniales. Another group of unicellular eukaryotes that partake in similar endosymbiotic relationships in both marine and freshwater habitats are green algae zoochlorellae. Zooxanthellae are photosynthetic organisms, which contain chlorophyll a and chlorophyll c, as well as the dinoflagellate pigments peridinin and diadinoxanthin. These provide the yellowish and brownish colours typical of many of the host species. During the day, they provide their host with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stony Coral
Scleractinia, also called stony corals or hard corals, are marine animals in the phylum Cnidaria that build themselves a hard skeleton. The individual animals are known as polyps and have a cylindrical body crowned by an oral disc in which a mouth is fringed with tentacles. Although some species are solitary, most are colonial. The founding polyp settles and starts to secrete calcium carbonate to protect its soft body. Solitary corals can be as much as across but in colonial species the polyps are usually only a few millimetres in diameter. These polyps reproduce asexually by budding, but remain attached to each other, forming a multi-polyp colony of clones with a common skeleton, which may be up to several metres in diameter or height according to species. The shape and appearance of each coral colony depends not only on the species, but also on its location, depth, the amount of water movement and other factors. Many shallow-water corals contain symbiont unicellular organi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinularia
''Sinularia'' is a genus of soft coral in the family Alcyoniidae. They are commonly known as leather corals and currently have 166 described species In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ... in the genus. Species Species include: References Encyclopedia of Life entry Alcyoniidae Octocorallia genera {{octocorallia-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sclerite
A sclerite (Greek , ', meaning "hard") is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly to the hardened parts of arthropod exoskeletons and the internal spicules of invertebrates such as certain sponges and soft corals. In paleontology, a scleritome is the complete set of sclerites of an organism, often all that is known from fossil invertebrates. Sclerites in combination Sclerites may occur practically isolated in an organism, such as the sting of a cone shell. Also, they can be more or less scattered, such as tufts of defensive sharp, mineralised bristles as in many marine Polychaetes. Or, they can occur as structured, but unconnected or loosely connected arrays, such as the mineral "teeth" in the radula of many Mollusca, the valves of Chitons, the beak of Cephalopod, or the articulated exoskeletons of Arthropoda. When ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrobiologia
''Hydrobiologia'', ''The International Journal of Aquatic Sciences'', is a peer-reviewed scientific journal publishing 21 issues per year, for a total of well over 4000 pages per year. ''Hydrobiologia'' publishes original research, reviews and opinions investigating the biology of freshwater and marine habitats, including the impact of human activities. Coverage includes molecular-, organism-, community -and ecosystem-level studies dealing with biological research in limnology and oceanography, including systematics and aquatic ecology. In addition to hypothesis-driven experimental research, it presents theoretical papers relevant to a broad hydrobiological audience, and collections of papers in special issues covering focused topics. History ''Hydrobiologia'' changed on the appointment of Henri Dumont to be its editor-in-chief. He introduced peer review, and expanded production from 6 issues per year to more than 20 per year. Koen Martens took over the responsibility as editor-in- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoceanography
Paleoceanography is the study of the history of the oceans in the geology, geologic past with regard to circulation, chemistry, biology, geology and patterns of sedimentation and biological productivity. Paleoceanographic studies using environment models and different proxies enable the scientific community to assess the role of the oceanic processes in the global climate by the re-construction of past climate at various intervals. Paleoceanographic research is also intimately tied to paleoclimatology. Source and methods of information Paleoceanography makes use of so-called proxy (climate), proxy methods as a way to infer information about the past state and evolution of the world's oceans. Several geochemical proxy tools include long-chain organic molecules (e.g. alkenones), stable and radioactive isotopes, and trace metals. Additionally, sediment cores can also be useful; the field of paleoceanography is closely related to sedimentology and paleontology. Sea-surface tem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleoclimatology
Paleoclimatology (British spelling, palaeoclimatology) is the study of climates for which direct measurements were not taken. As instrumental records only span a tiny part of Earth's history, the reconstruction of ancient climate is important to understand natural variation and the evolution of the current climate. Paleoclimatology uses a variety of proxy methods from Earth and life sciences to obtain data previously preserved within rocks, sediments, boreholes, ice sheets, tree rings, corals, shells, and microfossils. Combined with techniques to date the proxies, the paleoclimate records are used to determine the past states of Earth's atmosphere. The scientific field of paleoclimatology came to maturity in the 20th century. Notable periods studied by paleoclimatologists are the frequent glaciations that Earth has undergone, rapid cooling events like the Younger Dryas, and the rapid warming during the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum. Studies of past changes in the environm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |