|
Saxagliptin Metformin
Saxagliptin, sold under the brand name Onglyza, is an oral hypoglycemic ( anti-diabetic drug) of the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor class. Early development was solely by Bristol-Myers Squibb; in 2007 AstraZeneca joined with Bristol-Myers Squibb to co-develop the final compound and collaborate on the marketing of the drug. In April 2016, the U.S. FDA added a warning about increased risk of heart failure. This was based on data in an article that concluded "DPP-4 inhibition with saxagliptin did not increase or decrease the rate of ischemic events, though the rate of hospitalization for heart failure was increased. Although saxagliptin improves glycemic control, other approaches are necessary to reduce cardiovascular risk in patients with diabetes." Medical uses Saxagliptin is used as monotherapy or in combination with other drugs for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. It does not appear to decrease the risk of heart attacks or strokes. It increases the risk of hospit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oral Administration
Oral administration is a route of administration where a substance is taken through the mouth. Per os abbreviated to P.O. is sometimes used as a direction for medication to be taken orally. Many medications are taken orally because they are intended to have a systemic effect, reaching different parts of the body via the bloodstream, for example. Oral administration can be easier and less painful than other routes, such as injection. However, the onset of action is relatively low, and the effectiveness is reduced if it is not absorbed properly in the digestive system, or if it is broken down by digestive enzymes before it can reach the bloodstream. Some medications may cause gastrointestinal side effects, such as nausea or vomiting, when taken orally. Oral administration can also only be applied to conscious patients, and patients willing and able to swallow. Terminology ''Per os'' (; ''P.O.'') is an adverbial phrase meaning literally from Latin "through the mouth" or "by mouth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulphonylurea
Sulfonylureas (UK: sulphonylurea) are a class of organic compounds used in medicine and agriculture, for example as antidiabetic drugs widely used in the management of diabetes mellitus type 2. They act by increasing insulin release from the beta cells in the pancreas. A number of sulfonylureas are also used as herbicides, because they can interfere with plant biosynthesis of certain amino acids. Sulfonylureas are also used experimentally to inhibit interleukin 1 beta release from the NALP3 (or NLRP3) inflammasome. Drugs * First-generation drugs include acetohexamide, carbutamide, chlorpropamide, glycyclamide (tolcyclamide), metahexamide, tolazamide and tolbutamide. * Second-generation drugs include glibenclamide (glyburide), glibornuride, gliclazide, glipizide, gliquidone, glisoxepide and glyclopyramide. * Third-generation drugs include glimepiride, although it is sometimes considered a second-generation agent. Medical uses Sulfonylureas are used primarily for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Peptide
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), also known as Gastric inhibitory polypeptide or gastric inhibitory peptide (also abbreviated as GIP), is an inhibiting hormone of the secretin family of hormones. While it is a weak inhibitor of gastric acid secretion, its main role is to stimulate insulin secretion. GIP, along with glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), belongs to a class of molecules referred to as incretins. Synthesis and transport GIP is derived from a 153-amino acid proprotein encoded by the GIP gene and circulates as a biologically active 42-amino acid peptide. It is synthesized by K cells, which are found in the mucosa of the duodenum and the jejunum of the gastrointestinal tract. Like all endocrine hormones, it is transported by blood. Gastric inhibitory polypeptide receptors are seven-transmembrane proteins found on beta-cells in the pancreas. Functions It has traditionally been named ''gastrointestinal inhibitory peptide'' or ''gastric inhibitory pept ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blood Glucose
Glycaemia, also known as blood sugar level, blood sugar concentration, or blood glucose level is the measure of glucose concentrated in the blood of humans or other animals. Approximately 4 grams of glucose, a simple sugar, is present in the blood of a 70 kg (154 lb) human at all times. The body tightly regulates blood glucose levels as a part of metabolic homeostasis. Glucose is stored in skeletal muscle and liver cells in the form of glycogen; in fasting individuals, blood glucose is maintained at a constant level at the expense of glycogen stores in the liver and skeletal muscle. In humans, a blood glucose level of 4 grams, or about a teaspoon, is critical for normal function in a number of tissues, and the human brain consumes approximately 60% of blood glucose in fasting, sedentary individuals. A persistent elevation in blood glucose leads to glucose toxicity, which contributes to cell dysfunction and the pathology grouped together as complications of diabetes. Gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
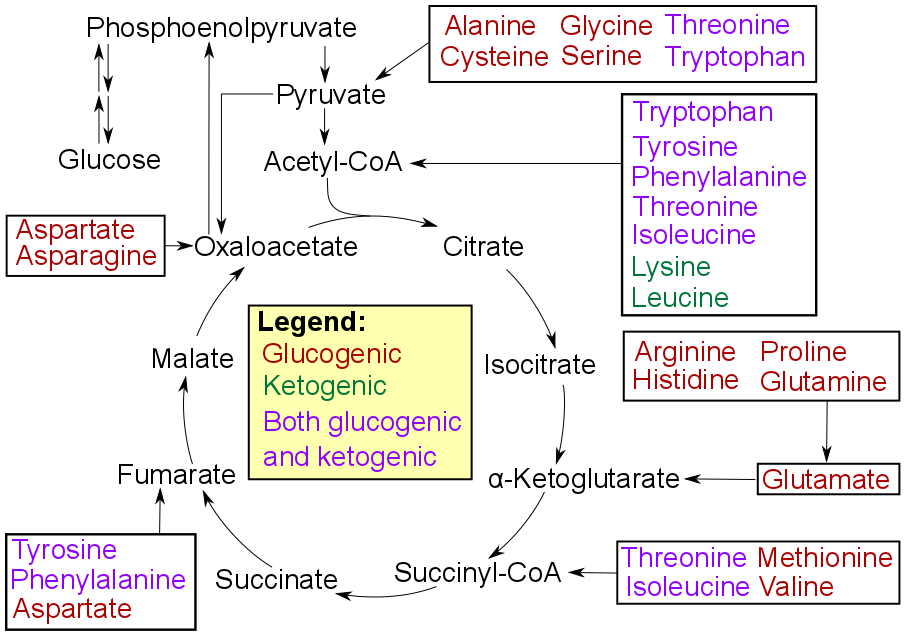
Gluconeogenesis
Gluconeogenesis (GNG) is a metabolic pathway that results in the generation of glucose from certain non-carbohydrate carbon substrates. It is a ubiquitous process, present in plants, animals, fungi, bacteria, and other microorganisms. In vertebrates, gluconeogenesis occurs mainly in the liver and, to a lesser extent, in the cortex of the kidneys. It is one of two primary mechanisms – the other being degradation of glycogen ( glycogenolysis) – used by humans and many other animals to maintain blood sugar levels, avoiding low levels (hypoglycemia). In ruminants, because dietary carbohydrates tend to be metabolized by rumen organisms, gluconeogenesis occurs regardless of fasting, low-carbohydrate diets, exercise, etc. In many other animals, the process occurs during periods of fasting, starvation, low-carbohydrate diets, or intense exercise. In humans, substrates for gluconeogenesis may come from any non-carbohydrate sources that can be converted to pyruvate or intermediates ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor
Inhibitors of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4 inhibitors or gliptins) are a class of oral hypoglycemics that block the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). They can be used to treat diabetes mellitus type 2. The first agent of the class – sitagliptin – was approved by the FDA in 2006. Glucagon increases blood glucose levels, and DPP-4 inhibitors reduce glucagon and blood glucose levels. The mechanism of DPP-4 inhibitors is to increase incretin levels ( GLP-1 and GIP), which inhibit glucagon release, which in turn increases insulin secretion, decreases gastric emptying, and decreases blood glucose levels. A 2018 meta-analysis found no favorable effect of DPP-4 inhibitors on all-cause mortality, cardiovascular mortality, myocardial infarction or stroke in patients with type 2 diabetes. Examples Drugs belonging to this class are: * Sitagliptin (FDA approved 2006, marketed by Merck & Co. as Januvia) * Vildagliptin (EU approved 2007, marketed in the EU by Novartis as Galvus) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incretin
Incretins are a group of metabolic hormones that stimulate a decrease in blood glucose levels. Incretins are released after eating and augment the secretion of insulin released from pancreatic beta cells of the islets of Langerhans by a blood-glucose–dependent mechanism. Some incretins (GLP-1) also inhibit glucagon release from the alpha cells of the islets of Langerhans. In addition, they slow the rate of absorption of nutrients into the blood stream by reducing gastric emptying and may directly reduce food intake. The two main candidate molecules that fulfill criteria for an incretin are the intestinal peptides glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and gastric inhibitory peptide (GIP, also known as: glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide). Both GLP-1 and GIP are rapidly inactivated by the enzyme dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4). Both GLP-1 and GIP are members of the glucagon peptide superfamily. Medical uses Medications based on incretins are used in the treatment of diabe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4
Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP4), also known as adenosine deaminase complexing protein 2 or CD26 (cluster of differentiation 26) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ''DPP4'' gene. DPP4 is related to FAP, DPP8, and DPP9. The enzyme was discovered in 1966 by Hopsu-Havu and Glenner, and as a result of various studies on chemism, was called dipeptidyl peptidase IV P IV Function The protein encoded by the ''DPP4'' gene is an enzyme expressed on the surface of most cell types and is associated with immune regulation, signal transduction, and apoptosis. It is a type II transmembrane glycoprotein, but a soluble form, which lacks the intracellular and transmembrane part, is present in blood plasma and various body fluids. DPP-4 is a serine exopeptidase that cleaves X-proline or X-alanine dipeptides from the N-terminus of polypeptides. Peptide bonds involving the cyclic amino acid proline cannot be cleaved by the majority of proteases and an N-terminal X-proline "shields" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Production Of Saxagliptin
Production may refer to: Economics and business * Production (economics) * Production, the act of manufacturing goods * Production, in the outline of industrial organization, the act of making products (goods and services) * Production as a statistic, gross domestic product * Production line Arts, entertainment, and media Motion pictures * Production, film distributor of a company * Production, phase of filmmaking * Production, video production Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Production'' (album), by Mirwais, 2000 * Production, category of illusory magic trick * Production, phase of video games development * Production, Record producer's role * Production, theatrical performance Science and technology * Production, deployment environment where changes go "live" and users interact with it * Production (computer science), formal-grammar concept * Primary production, the production of new biomass by autotrophs in ecosystems * Productivity (ecology), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boc Anhydride
Di-''tert''-butyl dicarbonate is a reagent widely used in organic synthesis. Since this compound can be regarded formally as the acid anhydride derived from a ''tert''-butoxycarbonyl (Boc) group, it is commonly referred to as Boc anhydride. This pyrocarbonate reacts with amines to give ''N''-''tert''-butoxycarbonyl or so-called Boc derivatives. These carbamate derivatives do not behave as amines, which allows certain subsequent transformations to occur that would be incompatible with the amine functional group. The Boc group can later be removed from the amine using moderately strong acids (e.g., trifluoroacetic acid). Thus, Boc serves as a protective group, for instance in solid phase peptide synthesis. Boc-protected amines are unreactive to most bases and nucleophiles, allowing for the use of the fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl group (Fmoc) as an orthogonal protecting group. Preparation Di-''tert''-butyl dicarbonate is inexpensive, so it is usually purchased. Classically, this comp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trifluoroacetic Anhydride
Trifluoroacetic anhydride (TFAA) is the acid anhydride of trifluoroacetic acid. It is the perfluorinated derivative of acetic anhydride. Preparation Trifluoroacetic anhydride was originally prepared by the dehydration of trifluoroacetic acid with phosphorus pentoxide. The dehydration might also be carried out with excess α-halogenated acid chlorides. For example, with dichloroacetyl chloride: : 2 CF3COOH + Cl2CHCOCl → (CF3CO)2O + Cl2CHCOOH + HCl Uses Trifluoroacetic anhydride has various uses in organic synthesis. It may be used to introduce the corresponding trifluoroacetyl group, for which it is more convenient than the corresponding acyl chloride, trifluoroacetyl chloride, which is a gas. It can be used to promote reactions of carboxylic acids, including nucleophilic acyl substitution, Friedel-Crafts acylation, and acylation of other unsaturated compounds. Other electrophilic aromatic substitution reactions can also be promoted with trifluoroacetic anhydride, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
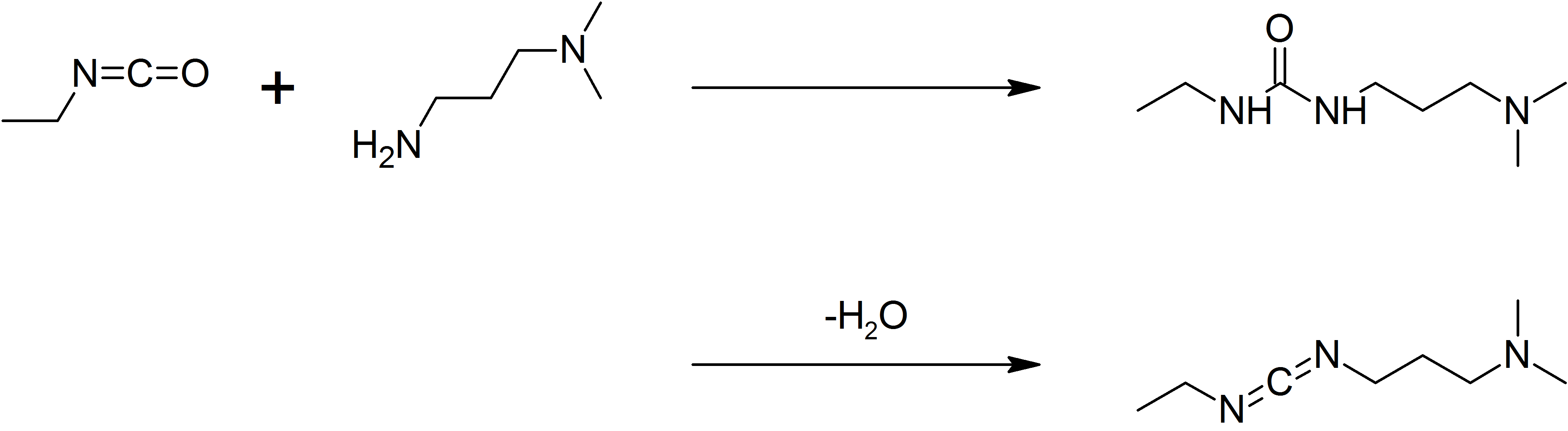
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
1-Ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide (EDC, EDAC or EDCI) is a water-soluble carbodiimide usually handled as the hydrochloride. It is typically employed in the 4.0-6.0 pH range. It is generally used as a carboxyl activating agent for the coupling of primary amines to yield amide bonds. While other carbodiimides like dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (DCC) or diisopropylcarbodiimide (DIC) are also employed for this purpose, EDC has the advantage that the urea byproduct formed (often challenging to remove in the case of DCC or DIC) can be washed away from the amide product using dilute acid. Additionally, EDC can also be used to activate phosphate groups in order to form phosphomonoesters and phosphodiesters. Common uses for this carbodiimide include peptide synthesis, protein crosslinking to nucleic acids, but also in the preparation of immunoconjugates. EDC is often used in combination with ''N''-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) for the immobilisation of large biomolecules. Recent work h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |