|
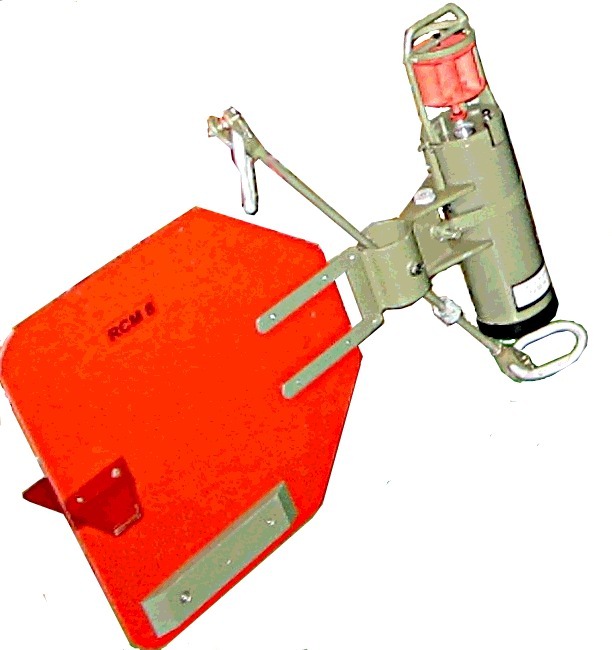
Rotor Current Meter
A rotor current meter (RCM) is a mechanical current meter, an oceanography, oceanographic device deployed within an Mooring (oceanography), oceanographic mooring Flow meter, measuring the flow within the world oceans to learn more about ocean currents. Many RCMs have been replaced by instruments measuring the flow by hydroacoustics, the so-called Acoustic Doppler Current Profilers. However, for instance in Fram Strait, the Alfred Wegener Institute still uses RCMs for long-term monitoring the inflow into the Arctic Ocean. Measurement principle A RCM usually consists of the recording unit, a propeller to detect the water velocity and vane to determine the direction of the flow. The gimbal rings of the RCM-instruments allow to compensate a tilt of up to 40° of the mooring line. The recording unit houses a battery pack for energy supply, the Analog-to-digital converter, possible additional sensors for other variables (like the standard parameters conductivity, temperature, depth, C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic North Pole Positions
Magnetism is the class of physical attributes that are mediated by a magnetic field, which refers to the capacity to induce attractive and repulsive phenomena in other entities. Electric currents and the magnetic moments of elementary particles give rise to a magnetic field, which acts on other currents and magnetic moments. Magnetism is one aspect of the combined phenomena of electromagnetism. The most familiar effects occur in ferromagnetic materials, which are strongly attracted by magnetic fields and can be magnetized to become permanent magnets, producing magnetic fields themselves. Demagnetizing a magnet is also possible. Only a few substances are ferromagnetic; the most common ones are iron, cobalt, and nickel and their alloys. The rare-earth metals neodymium and samarium are less common examples. The prefix ' refers to iron because permanent magnetism was first observed in lodestone, a form of natural iron ore called magnetite, Fe3O4. All substances exhibit some type of m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bremerhaven
Bremerhaven (, , Low German: ''Bremerhoben'') is a city at the seaport of the Free Hanseatic City of Bremen, a state of the Federal Republic of Germany. It forms a semi-enclave in the state of Lower Saxony and is located at the mouth of the River Weser on its eastern bank, opposite the town of Nordenham. Though a relatively new city, it has a long history as a trade port and today is one of the most important German ports, playing a role in Germany's trade. History in 1827, but neighboring settlements such as Lehe were in the vicinity as early as the 12th century, and Geestendorf was "mentioned in documents of the ninth century". p. 8. Fourth revised edition. Translated into English from the original German edition titled ''Bremerhaven – tätige Stadt im Noordseewind'' These tiny villages were built on small islands in the swampy estuary. In 1381, the city of Bremen established ''de facto'' rule over the lower Weser stream, including Lehe, later therefore called Bremer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Maritime Museum
The German Maritime Museum (german: Deutsches Schifffahrtsmuseum (DSM)) is a museum in Bremerhaven, Germany. It is part of the Gottfried Wilhelm Leibniz Scientific Community. The main museum building was opened on 5 September 1975 by then-president of Germany Walter Scheel, though scientific work already had started in 1971. In 2000, celebrating the 25th anniversary of the museum, the ''Hansekogge'', a ship constructed around 1380 that was found in the Weser river in 1962, was presented to the public after having undergone a lengthy process of conservation in a large preservative-filled basin. The museum consists of the building planned by Hans Scharoun as well as several museum ships in the Old Harbour of Bremerhaven, including the ''Seute Deern'' windjammer. Since 2005, the buildings and 8 ships are listed as protected heritage ensemble. History The German Maritime Museum (DSM) was founded in Bremerhaven in 1971 to replace the Museum of Marine Science in Berlin, which had b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction: *Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of two solid surfaces in contact. Dry friction is subdivided into ''static friction'' ("stiction") between non-moving surfaces, and ''kinetic friction'' between moving surfaces. With the exception of atomic or molecular friction, dry friction generally arises from the interaction of surface features, known as asperities (see Figure 1). *Fluid friction describes the friction between layers of a viscous fluid that are moving relative to each other. *Lubricated friction is a case of fluid friction where a lubricant fluid separates two solid surfaces. *Skin friction is a component of drag, the force resisting the motion of a fluid across the surface of a body. *Internal friction is the force resisting motion between the elements making up a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inertia
Inertia is the idea that an object will continue its current motion until some force causes its speed or direction to change. The term is properly understood as shorthand for "the principle of inertia" as described by Newton in his first law of motion. After some other definitions, Newton states in his first law of motion: The word "perseveres" is a direct translation from Newton's Latin. Other, less forceful terms such as "to continue" or "to remain" are commonly found in modern textbooks. The modern use follows from some changes in Newton's original mechanics (as stated in the ''Principia'') made by Euler, d'Alembert, and other Cartesians. The term inertia comes from the Latin word ''iners'', meaning idle, sluggish. The term inertia may also refer to the resistance of any physical object to a change in its velocity. This includes changes to the object's speed or direction of motion. An aspect of this property is the tendency of objects to keep moving in a straight li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ADCP
An acoustic Doppler current profiler (ADCP) is a hydroacoustic current meter similar to a sonar, used to measure water current velocities over a depth range using the Doppler effect of sound waves scattered back from particles within the water column. The term ADCP is a generic term for all acoustic current profilers, although the abbreviation originates from an instrument series introduced by RD Instruments in the 1980s. The working frequencies range of ADCPs range from 38 kHz to several megahertz. The device used in the air for wind speed profiling using sound is known as '' SODAR'' and works with the same underlying principles. Working principle ADCPs contain piezoelectric transducers to transmit and receive sound signals. The traveling time of sound waves gives an estimate of the distance. The frequency shift of the echo is proportional to the water velocity along the acoustic path. To measure 3D velocities, at least three beams are required. In rivers, only the 2D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Of The Art
The state of the art (sometimes cutting edge or leading edge) refers to the highest level of general development, as of a device, technique, or scientific field achieved at a particular time. However, in some contexts it can also refer to a level of development reached at any particular time as a result of the common methodologies employed at the time. The term has been used since 1910, and has become both a common term in advertising and marketing, and a legally significant phrase with respect to both patent law and tort liability. In advertising, the phrase is often used to convey that a product is made with the best or latest available technology, but it has been noted that "the term 'state of the art' requires little proof on the part of advertisers", as it is considered mere puffery. The use of the term in patent law "does not connote even superiority, let alone the superlative quality the ad writers would have us ascribe to the term". Origin and history The origin of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metre Per Second
The metre per second is the unit of both speed (a scalar (physics), scalar quantity) and velocity (a Vector (mathematics and physics), vector quantity, which has direction and magnitude) in the International System of Units (SI), equal to the speed of a body covering a distance of one metre in a time of one second. The International System of Units, SI unit symbols are m/s, m·s−1, m s−1, or . Sometimes it is abbreviated as "mps". Conversions is equivalent to: : = 3.6 kilometres per hour, km/h (exactly) : ≈ 3.2808 feet per second (approximately) : ≈ 2.2369 miles per hour (approximately) : ≈ 1.9438 knot (unit), knots (approximately) 1 feet per second, foot per second = (exactly) 1 miles per hour, mile per hour = (exactly) 1 kilometres per hour, km/h = (exactly) Relation to other measures The benz, named in honour of Karl Benz, has been proposed as a name for one metre per second. Although it has seen some support as a practical unit, primarily from German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accuracy And Precision
Accuracy and precision are two measures of ''observational error''. ''Accuracy'' is how close a given set of measurements ( observations or readings) are to their ''true value'', while ''precision'' is how close the measurements are to each other. In other words, ''precision'' is a description of '' random errors'', a measure of statistical variability. ''Accuracy'' has two definitions: # More commonly, it is a description of only '' systematic errors'', a measure of statistical bias of a given measure of central tendency; low accuracy causes a difference between a result and a true value; ISO calls this ''trueness''. # Alternatively, ISO defines accuracy as describing a combination of both types of observational error (random and systematic), so high accuracy requires both high precision and high trueness. In the first, more common definition of "accuracy" above, the concept is independent of "precision", so a particular set of data can be said to be accurate, precise, both, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Declination
Magnetic declination, or magnetic variation, is the angle on the horizontal plane between magnetic north (the direction the north end of a magnetized compass needle points, corresponding to the direction of the Earth's magnetic field lines) and true north (the direction along a meridian towards the geographic North Pole). This angle varies depending on position on the Earth's surface and changes over time. Somewhat more formally, Bowditch defines variation as “the angle between the magnetic and geographic meridians at any place, expressed in degrees and minutes east or west to indicate the direction of magnetic north from true north. The angle between magnetic and grid meridians is called grid magnetic angle, grid variation, or grivation.” By convention, declination is positive when magnetic north is east of true north, and negative when it is to the west. ''Isogonic lines'' are lines on the Earth's surface along which the declination has the same constant value, and line ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Pole
The North Pole, also known as the Geographic North Pole or Terrestrial North Pole, is the point in the Northern Hemisphere where the Earth's axis of rotation meets its surface. It is called the True North Pole to distinguish from the Magnetic North Pole. The North Pole is by definition the northernmost point on the Earth, lying antipodally to the South Pole. It defines geodetic latitude 90° North, as well as the direction of true north. At the North Pole all directions point south; all lines of longitude converge there, so its longitude can be defined as any degree value. No time zone has been assigned to the North Pole, so any time can be used as the local time. Along tight latitude circles, counterclockwise is east and clockwise is west. The North Pole is at the center of the Northern Hemisphere. The nearest land is usually said to be Kaffeklubben Island, off the northern coast of Greenland about away, though some perhaps semi-permanent gravel banks lie slightly clos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



