|
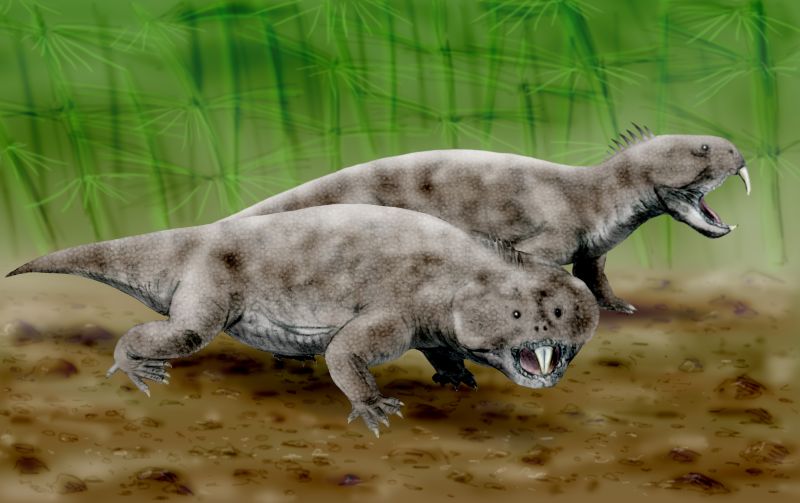
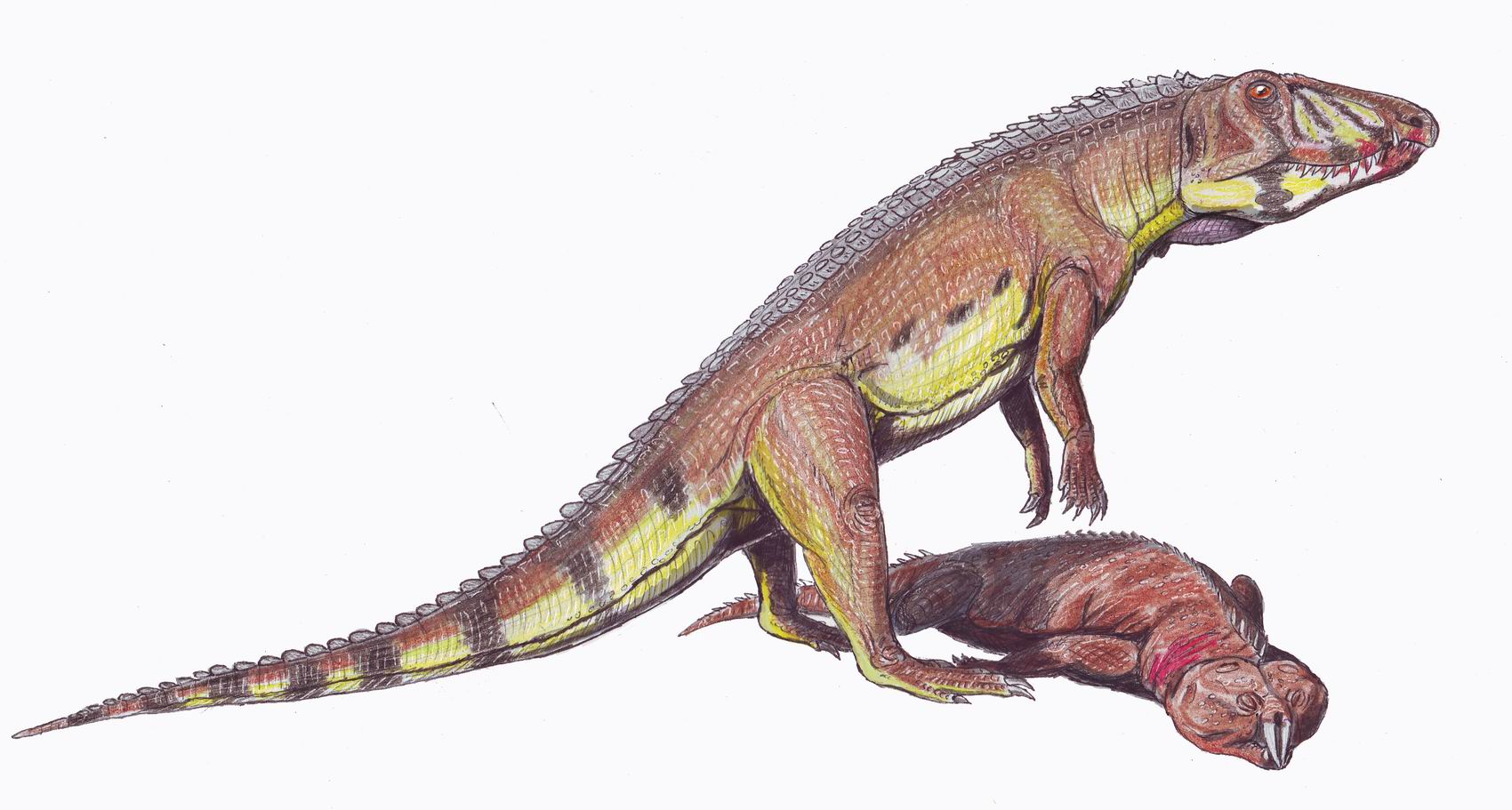
Rhynchosaur
Rhynchosaurs are a group of extinct herbivorous Triassic archosauromorph reptiles, belonging to the order Rhynchosauria. Members of the group are distinguished by their triangular skulls and elongated, beak like premaxillary bones. Rhynchosaurs first appeared in the Middle Triassic or possibly the Early Triassic, before becoming abundant and globally distributed during the Carnian stage of the Late Triassic. Description Rhynchosaurs were herbivores, and at times abundant (in some fossil localities accounting for 40 to 60% of specimens found), with stocky bodies and a powerful beak. Early primitive forms, like ''Mesosuchus'' and '' Howesia'', were generally small and more typically lizard-like in build, and had skulls rather similar to the early diapsid ''Youngina'', except for the beak and a few other features. Later and more advanced genera grew to medium to medium large size, up to two meters in length. The skull in these forms were short, broad, and triangular, becoming muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
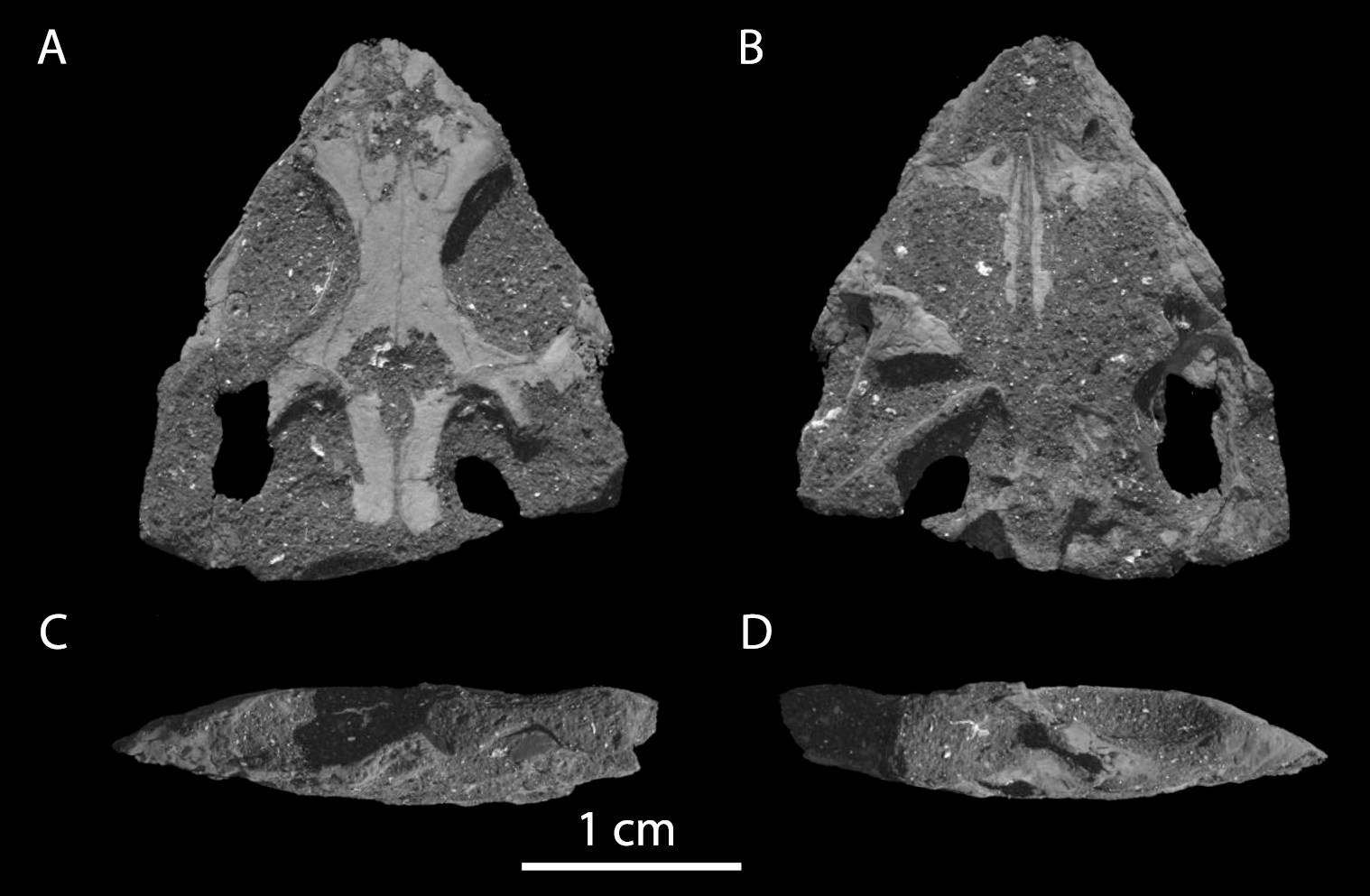
Colobops
''Colobops'' is a genus of reptile from the Late Triassic of Connecticut. Only known from a tiny skull (estimated total length of 2.8 centimeters or 1.1 inches long), this reptile has been interpreted to possess skull attachments for very strong jaw muscles. This may have given it a very strong bite, despite its small size. However, under some interpretations of the CT scan data, ''Colobopss bite force may not have been unusual compared to other reptiles. The generic name, ''Colobops'', is a combination of ''κολοβός'' (''kolobós''), meaning shortened, and ''ὤψ (ṓps),'' meaning face. This translation, "shortened face", refers to its short and triangular skull. ''Colobops'' is known from a single species, ''Colobops noviportensis''. The specific name, ''noviportensis'', is a latinization of New Haven, the name of both the geological setting of its discovery (the New Haven Arkose) as well as a nearby large city. The phylogenetic relations of ''Colobops'' are controver ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stenaulorhynchus
''Stenaulorhynchus'' (possibly meaning "narrow tube beak") is an extinct genus of hyperodapedontid rhynchosaur known from the Middle Triassic (late Anisian stage) deposits of Tanganyika Territory, Tanzania. It was found in the Lifua Member of the Manda Formation in the Karoo Supergroup. It was named and first described by Sidney Henry Haughton in 1932. The type species is ''Stenaulorhynchus stockleyi'', a beaked herbivore measuring 1–6 meters in length. Description Dentition The teeth of ''Stenaulorhynchus'' were conical, pointed, and composed mostly of dentine, although new unworn teeth may have had a thin layer of enamel. They were set deeply into and fused with the jaw bones. They are arranged with two-to-several rows of teeth on top and only a few on bottom. The middle row of maxillary teeth only occupied the posterior third of the jaw while the other rows extended all the way forwards and sometimes down the crest of the jaw. The teeth at the front of the mouth, by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archosauromorpha
Archosauromorpha (Greek for "ruling lizard forms") is a clade of diapsid reptiles containing all reptiles more closely related to archosaurs (such as crocodilians and dinosaurs, including birds) rather than lepidosaurs (such as tuataras, lizards, and snakes). Archosauromorphs first appeared during the late Middle Permian or Late Permian, though they became much more common and diverse during the Triassic period. Although Archosauromorpha was first named in 1946, its membership did not become well-established until the 1980s. Currently Archosauromorpha encompasses four main groups of reptiles: the stocky, herbivorous allokotosaurs and rhynchosaurs, the hugely diverse Archosauriformes, and a polyphyletic grouping of various long-necked reptiles including ''Protorosaurus'', tanystropheids, and ''Prolacerta''. Other groups including pantestudines (turtles and their extinct relatives) and the semiaquatic choristoderes have also been placed in Archosauromorpha by some authors. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eohyosaurus
''Eohyosaurus'' is an extinct genus of basal rhynchosaur known from the early Middle Triassic (early Anisian stage) Burgersdorp Formation of Free State, South Africa. It contains a single species, ''Eohyosaurus wolvaardti''. Discovery ''Eohyosaurus'' is known solely from the holotype SAM-PK-K10159, a partial skull missing the front end, with associated incomplete lower jaws currently housed at the Iziko South African Museum, Cape Town. The specimen was discovered by Frederik Petrus Wolvaardt in December 2000, loose on boulder-strewn slopes at the base of a cliff, at Farm Lemoenfontein 44, Rouxville District of the Free State Province. It was collected from the middle deposits of the Burgersdorp Formation of Beaufort Group. This horizon belongs to Subzone B of the ''Cynognathus'' Assemblage Zone, dating to the early Anisian stage of the early Middle Triassic period, about 246 million years ago. Farm Lemoenfontein 44 also yielded remains of the archosauriform ''Erythrosuchus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fodonyx
''Fodonyx'' (meaning "digging claw") is an extinct genus of rhynchosaur from the middle Triassic epoch of Devon in England. Its fossils (25 specimens) were discovered in Otter Sandstone Formation (late Anisian age) and were first assigned to '' Rhynchosaurus spenceri''. This species was reassigned to its own genus, ''Fodonyx'' (the type and only species is ''Fodonyx spenceri'') the holotype of which iEXEMS 60/1985/292, that described by David W. E. Hone and Michael J. Benton in 2008. More recently, one skull was reassigned to the new genus ''Bentonyx''. It is distinguished from other rhynchosaurs by a single autapomorphy, the ventral angling of the paraoccipital processes. In all other rhynchosaurs these processes angle dorsally or are horizontal. It is not known if this conferred any advantage to ''Fodonyx. Fodonyx'' was between 40 and 50 cm long. Features Skull and lower jaw The two premaxillae are very long and run up over the snout to meet the prefrontals at the or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperodapedontinae
Hyperodapedontinae is a subfamily of rhynchosaurs within the family Hyperodapedontidae. Fossils have been found from Argentina, Brazil, Canada, India, Madagascar, Scotland, Tanzania, United States and Zimbabwe. Phylogeny Hyperodapedontinae was erected by Sankar Chatterjee in 1969 as a coordinate name of the family Hyperodapedontidae Lydekker, 1985. Chatterjee (1969) originally named Hyperodapedontinae to include all Late Triassic rhynchosaurs known at that time, ''H. gordoni'', ''H. huxleyi'' and ''"Scaphonyx" fischeri'', and proposed a morphological diagnosis for the clade. ''Scaphonyx'' includes two additional species, ''S. africanus'' and ''S. australis'', all of which are currently believed to be dubious. As noted by Langer ''et al.'' (2000), using Chatterjee' morphological definition would exclude ''Teyumbaita'' and ''H. huenei'' from the clade, and thus it would be nested within ''Hyperodapedon''. To preserve the name, with its original stratigraphical meaning, Langer ''et a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperodapedon
''Hyperodapedon'' is a genus of rhynchosaurs (beaked, archosaur-like reptiles) from the Triassic, Late Triassic period (Carnian stage). Fossils of the genus have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe and North and South America. Its first discovery and naming was found by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1859. ''Hyperodapedon'' was a herbivore that used its beaked premaxilla and hindlimbs to dig for plants in dry land. Description ''Hyperodapedon'' was a heavily built, stocky, animal. ''H. gordoni'' had total length around with skull length of to , but largest species, ''H. huxleyi'' had lower jaw about and skull length is estimated about . Apart from its beak, it had several rows of heavy teeth on each side of the upper jaw, and a single row on each side of the lower jaw, creating a powerful chopping action when it ate. It is believed to have been herbivorous, feeding mainly on seed ferns, and died out when these plants became extinct at Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, the end of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scaphonyx
''Hyperodapedon'' is a genus of rhynchosaurs (beaked, archosaur-like reptiles) from the Late Triassic period (Carnian stage). Fossils of the genus have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe and North and South America. Its first discovery and naming was found by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1859. ''Hyperodapedon'' was a herbivore that used its beaked premaxilla and hindlimbs to dig for plants in dry land. Description ''Hyperodapedon'' was a heavily built, stocky, animal. ''H. gordoni'' had total length around with skull length of to , but largest species, ''H. huxleyi'' had lower jaw about and skull length is estimated about . Apart from its beak, it had several rows of heavy teeth on each side of the upper jaw, and a single row on each side of the lower jaw, creating a powerful chopping action when it ate. It is believed to have been herbivorous, feeding mainly on seed ferns, and died out when these plants became extinct at the end of the Triassic. The diagnosis of ''Hyperodapedon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noteosuchus
''Noteosuchus'' is an extinct genus of basal rhynchosaur known from the earliest Triassic deposits of Eastern Cape Province, South Africa. It was first named by David Meredith Seares Watson in 1912 and the type species is ''Eosuchus colletti''. The generic name ''Eosuchus'' is preoccupied by the generic name of '' Eosuchus lerichei'' Dollo, 1907, a gavialoid crocodilian known from northern France. Thus, an alternative generic name, ''Noteosuchus'', was proposed by Robert Broom in 1925. The generic name erected by Broom (1925) is a compound, meaning "Not ''Eosuchus''", while "Eosuchus" is derived from the name of Eos, the goddess of the dawn in Greek mythology, and ''suchus'', Latinized from the Greek ''souchos'', an Egyptian crocodile god, thus meaning "dawn crocodile". The specific name, ''colletti'', honors Mr. Collett for the discovery of the holotype and only known specimen. Discovery ''Noteosuchus'' is known solely from the holotype AM 3591, a well-preserved partial post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otischalkia
''Otischalkia'' is an extinct genus of archosauromoph from late Triassic (late Carnian stage) deposits of Howard County, Texas, US It is known from the holotype TMM 31025-263, left humerus and from the referred specimens TMM 31025-262, TMM 31025-266, TMM 31025-264, TMM 31185-92 and TMM 31185-93. It was found in the Lower Dockum Group near the abandoned settlement of Otis Chalk. It was first named by Adrian P. Hunt and Spencer G. Lucas in 1991 and the type species is ''Otischalkia elderae''. Originally described as a rhynchosaur, several recent studies found ''O. elderae'' to represent a ''nomen dubium''. Nesbitt ''et al.'' (2021) came to the conclusion that the holotype of ''Otischalkia'' actually belongs to an azendohsaurid Azendohsauridae is a family of allokotosaurian archosauromorphs that lived during the Middle to Late Triassic period, around 242-216 million years ago. The family was originally named solely for the eponymous '' Azendohsau ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brasinorhynchus
''Brasinorhynchus'' is an extinct genus of derived stenaulorhynchine known from the late Middle Triassic (Ladinian stage) Santa Maria Formation of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil.''Brasinorhynchus'' at .org It contains a single species, ''Brasinorhynchus mariantensis''. Description ''B. mariantensis'' is known from two specimens, including the UFRGS-PV-0168-T, a complete |
Langeronyx
''Langeronyx'' is an extinct genus of basal rhynchosaurid known from the early Middle Triassic (Anisian stage) Bromsgrove Sandstone Formation of Warwickshire, UK. It contains a single species, ''Langeronyx brodiei'', originally included in the genus ''Rhynchosaurus''. ''R. brodiei'' was first described and named by Michael Benton in 1990, but its redescription by Martín D. Ezcurra, Felipe Montefeltro and Richard J. Butler in 2016 recovered it as more closely related to the more advance hyperodapedontine than to the type species of ''Rhynchosaurus'' and thus it was moved to its own genus. The generic name ''Langeronyx'' honors the Brazilian paleontologist Max Cardoso Langer in recognition of his rhynchosaur research, combined with the Greek ''onyx'' (''óνυξ'') meaning "claw", a common suffix for rhynchosaur genera. ''L. brodiei'' is known solely from the holotype, a partial skull divided into the two specimenWARMS G6097/1and NHMUK PV R8495, housed in the Warwickshire Mu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |