|
Ram-air
A ram-air intake is any intake design which uses the dynamic air pressure created by vehicle motion, or ram pressure, to increase the static air pressure inside of the intake manifold on an internal combustion engine, thus allowing a greater massflow through the engine and hence increasing engine power. Design features The ram-air intake works by reducing the intake air velocity by increasing the cross-sectional area of the intake ducting. When gas velocity goes down the dynamic pressure is reduced, while the static pressure is increased. The increased static pressure in the plenum chamber has a positive effect on engine power, both because of the pressure itself and the increased air density that this higher pressure gives. Ram-air systems are used on high-performance vehicles, most often on motorcycles and performance cars. The 1990 Kawasaki Ninja ZX-11 C1 model used a ram-air intake, the very first on any production motorcycle. Ram-air was a feature on some cars in the sixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Ram Intake
A ram-air intake is any intake design which uses the dynamic air pressure created by vehicle motion, or ram pressure, to increase the static air pressure inside of the intake manifold on an internal combustion engine, thus allowing a greater massflow through the engine and hence increasing engine power. Design features The ram-air intake works by reducing the intake air velocity by increasing the cross-sectional area of the intake ducting. When gas velocity goes down the dynamic pressure is reduced, while the static pressure is increased. The increased static pressure in the plenum chamber has a positive effect on engine power, both because of the pressure itself and the increased air density that this higher pressure gives. Ram-air systems are used on high-performance vehicles, most often on motorcycles and performance cars. The 1990 Kawasaki Ninja ZX-11 C1 model used a ram-air intake, the very first on any production motorcycle. Ram-air was a feature on some cars in the sixt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TA-4SU Super Skyhawk
The ST Aerospace A-4SU Super Skyhawk is a major upgrade project of the Douglas A-4S Skyhawk attack aircraft undertaken by Singapore Aircraft Industries (SAI, now ST Aerospace) in the 1980s. It was used exclusively by the Republic of Singapore Air Force (RSAF), serving in the fighter-bomber role from 1989 until retirement from front line service in 2005. Since mid-1999, the A-4SU took on the additional role of being the designated advanced jet trainer (AJT) aircraft for the RSAF's AJT training program/detachment in Cazaux, France."Inauguration of the 150 Squadron Building in Cazaux Air Base, France." '' Singaporean Ministry of Defence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
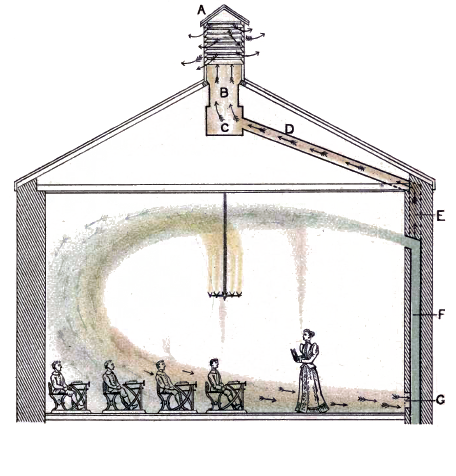
Plenum Chamber
A plenum chamber is a pressurised housing containing a fluid (typically air) at positive pressure. One of its functions is to equalise pressure for more even distribution, compensating for irregular supply or demand. It is typically relatively large in volume and thus has relatively low velocity compared to the system's other components. In wind tunnels, rockets, and many flow applications, it is a chamber upstream on the fluid flow where the fluid initially resides (approximately at rest). It can also work as an acoustic silencer. Examples of plenum chambers include those used with: * Superchargers * Hovercraft * Corliss steam engines * Raised floors and false ceilings in equipment rooms * Some organs (to supplement the bellows) * A number of aerophones, such as the bag of bagpipes and the ''slow air chamber'' of the Native American flute * Plenum chamber anesthetic vaporizers * Rocket motor combustion chambers, which may have a section near the nozzle that is free of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cold Air Intake
A cold air intake (CAI) is usually an aftermarket assembly of parts used to bring relatively cool air into a car's internal-combustion engine. Most vehicles manufactured from the mid-1970s until the mid-1990s have thermostatic air intake systems that regulate the temperature of the air entering the engine's intake tract, providing warm air when the engine is cold and cold air when the engine is warm to maximize performance, efficiency, and fuel economy. With the advent of advanced emission controls and more advanced fuel injection methods, modern vehicles do not have a thermostatic air intake system and the factory-installed air intake draws unregulated cold air. Aftermarket cold air intake systems are marketed with claims of increased engine efficiency and performance. The putative principle behind a cold air intake is that cooler air has a higher density, thus containing more oxygen per volume unit than warmer air. Design features Some strategies used in designing aftermark ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kawasaki Ninja ZX-11
The ZZ-R1100 or ZX-11 is a sport bike in Kawasaki's Ninja series made from 1990 to 2001, as the successor to the 1988–1990 Tomcat ZX-10. With a top speed of , it was the fastest production motorcycle from its introduction until 1996, surpassed by the Honda CBR1100XX. It was marketed as the ZX-11 Ninja in North America and the ZZ-R1100 in the rest of the world. The C-model ran from 1990 to 1993 while the D-model ran from 1993 to 2001, when it was replaced by the ZZ-R1200 (ZX-12C) 2002-2005 Competition for fastest production motorcycle With a record top speed of the ZX-11 was the fastest production motorcycle for six years, from its introduction in 1990 through 1995, when it was surpassed by the 1996 Honda CBR1100XX. When the bike was introduced in 1990, the nearest production bike top speed was slower and it belonged to the ZX-10, the bike that Kawasaki was replacing with the ZX-11. The ZX-11 also had a ram air induction system. The 1990 ZX-11 C1 model got a Ram-air ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ram Pressure
Ram pressure is a pressure exerted on a body moving through a fluid medium, caused by relative bulk motion of the fluid rather than random thermal motion. It causes a drag force to be exerted on the body. Ram pressure is given in tensor form as :P_\text= \rho u_i u_j, where \rho is the density of the fluid; P_\text is the momentum flux per second in the i direction through a surface with normal in the j direction. u_i,u_j are the components of the fluid velocity in these directions. The total Cauchy stress tensor \sigma_ is the sum of this ram pressure and the isotropic thermal pressure (in the absence of viscosity). In the simple case when the relative velocity is normal to the surface, and momentum is fully transferred to the object, the ram pressure becomes :P_\text = \rho u^2. Derivation The Eulerian form of the Cauchy momentum equation for a fluid is :\rho\frac = -\vec \nabla p - \rho(\vec u \cdot \vec \nabla)\vec u + \rho \vec g for isotropic pressure p, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pitot Tube
A pitot ( ) tube (pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by a French engineer, Henri Pitot, in the early 18th century, and was modified to its modern form in the mid-19th century by a French scientist, Henry Darcy. It is widely used to determine the airspeed of aircraft; the water speed of boats; and the flow velocity of liquids, air, and gases in industry. Theory of operation The basic pitot tube consists of a tube pointing directly into the fluid flow. As this tube contains fluid, a pressure can be measured; the moving fluid is brought to rest (stagnates) as there is no outlet to allow flow to continue. This pressure is the stagnation pressure of the fluid, also known as the total pressure or (particularly in aviation) the pitot pressure. The measured stagnation pressure cannot itself be used to determine the fluid flow velocity (airspeed in aviation). However, Bernoulli's equation states: :Stagnation pressure = static pressure + dynamic pressure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Airspeed
In aviation, airspeed is the speed of an aircraft relative to the air. Among the common conventions for qualifying airspeed are: * Indicated airspeed ("IAS"), what is read on an airspeed gauge connected to a Pitot-static system; * Calibrated airspeed ("CAS"), indicated airspeed adjusted for pitot system position and installation error; * Equivalent airspeed ("EAS"), calibrated airspeed adjusted for compressibility effects; * True airspeed ("TAS"), equivalent airspeed adjusted for air density, and is also the speed of the aircraft through the air in which it is flying. Calibrated airspeed is typically within a few knots of indicated airspeed, while equivalent airspeed decreases slightly from CAS as aircraft altitude increases or at high speeds. With EAS constant, true airspeed increases as aircraft altitude increases. This is because air density decreases with higher altitude. The measurement and indication of airspeed is ordinarily accomplished on board an aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Engine Knocking
In spark ignition internal combustion engines, knocking (also knock, detonation, spark knock, pinging or pinking) occurs when combustion of some of the air/fuel mixture in the cylinder does not result from propagation of the flame front ignited by the spark plug, but one or more pockets of air/fuel mixture explode outside the envelope of the normal combustion front. The fuel-air charge is meant to be ignited by the spark plug only, and at a precise point in the piston's stroke. Knock occurs when the peak of the combustion process no longer occurs at the optimum moment for the four-stroke cycle. The shock wave creates the characteristic metallic "pinging" sound, and cylinder pressure increases dramatically. Effects of engine knocking range from inconsequential to completely destructive. Knocking should not be confused with pre-ignition—they are two separate events. However, pre-ignition can be followed by knocking. The phenomenon of detonation was described in November 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Combustion Engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high- temperature and high- pressure gases produced by combustion applies direct force to some component of the engine. The force is typically applied to pistons (piston engine), turbine blades ( gas turbine), a rotor (Wankel engine), or a nozzle (jet engine). This force moves the component over a distance, transforming chemical energy into kinetic energy which is used to propel, move or power whatever the engine is attached to. This replaced the external combustion engine for applications where the weight or size of an engine was more important. The first commercially successful internal combustion engine was created by Étienne Lenoir around 1860, and the first modern internal combustion engine, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between those layers. Turbulence is commonly observed in everyday phenomena such as surf, fast flowing rivers, billowing storm clouds, or smoke from a chimney, and most fluid flows occurring in nature or created in engineering applications are turbulent. Turbulence is caused by excessive kinetic energy in parts of a fluid flow, which overcomes the damping effect of the fluid's viscosity. For this reason turbulence is commonly realized in low viscosity fluids. In general terms, in turbulent flow, unsteady vortices appear of many sizes which interact with each other, consequently drag due to friction effects increases. This increases the energy needed to pump fluid through a pipe. The onset of turbulence can be predicted by the dimensionless Rey ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |