|
Raid On Pickawillany
"ash people" , settlement_type = Historic Native American village , image_skyline = , imagesize = , image_alt = , image_map1 = OHMap-doton-Piqua.png , mapsize1 = 220px , map_caption1 = Location of Pickawillany Village , image_caption = , nickname = , coordinates = , established_title = Founded , established_date = 1747 , established_title2 = Demolished , established_date2 = 21 June, 1752 , established_title3 = , established_date3 = , population_total = , population_est = 400 families (1200–1600 people) , pop_est_as_of = 1750 , subdivision_type = State , subdivision_name = Ohio , subdivision_type1 = Present-day community , subdivision_name1 = Piqua, Ohio , subdivision_type2 = County , subdivision_name2 = Miami , image_map = Ohio in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 206 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 UN member states, 2 UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and 11 other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (16 states, of which there are 6 UN member states, 1 UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and 9 de facto states), and states having a special political status (2 states, both in free association with New Zealand). Compiling a list such as this can be a complicated and controversial process, as there is no definition that is binding on all the members of the community of nations concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
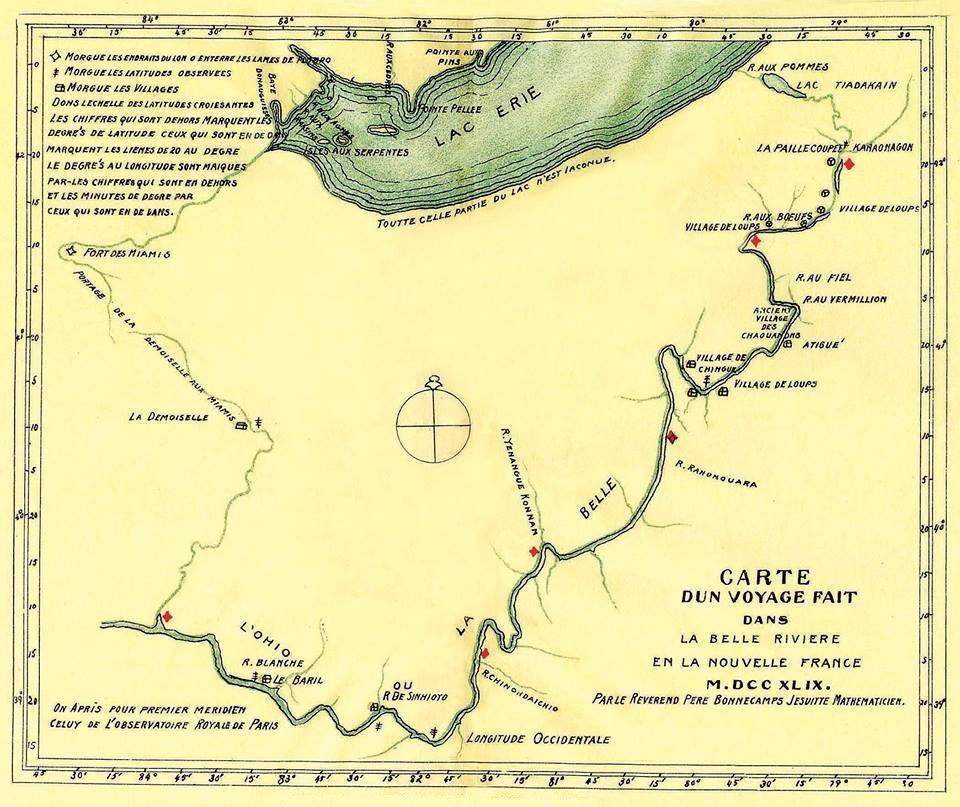
Fort Miami (Indiana)
Fort Miami, originally called Fort St. Philippe or Fort des Miamis, was the name of a pair of French palisade forts built at Kekionga, the principal village of the Miami. It was situated where the St. Joseph River and St. Marys River merge to form the Maumee River in Northeastern Indiana, where present day Fort Wayne is located. The first construct was a small trading post built by Jean Baptiste Bissot, Sieur de Vincennes around 1706, while the first fortified fort was finished in 1722, and the second in 1750. It is the predecessor to the Fort Wayne. Prehistory and original settlement Fort Miami within the village of Kekionga was one of the first posts established by the French along the Wabash- Maumee route. Some of the earliest known European contact in the area occurred in the 1690s by the French, who described the Miami controlled portage connecting the Maumee to the Wabash as the "Toll road swamp". In 1702, Vincennes was known to have began visiting the growing Miami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nanticokes
The Nanticoke people are a Native American Algonquian people, whose traditional homelands are in Chesapeake Bay and Delaware. Today they live in the Northeastern United States and Canada, especially Delaware; in Ontario; and in Oklahoma. The Nanticoke people consisted of several tribes: The Nanticoke proper (the subject of this article), the Choptank, the Assateague, the Piscataway, and the Doeg. History The Nanticoke people may have originated in Labrador, Canada, and migrated through the Great Lakes region and the Ohio Valley to the east, along with the Shawnee and Lenape peoples. In 1608, the Nanticoke came into European contact, with the arrival of British captain John Smith. They allied with the British and traded beaver pelts with them. They were located in today's Dorchester, Somerset and Wicomico counties. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twightwee Treaty Of Lancaster - DPLA - A7eba5170b87fbfb63c0e75a4eb6f2e2 (page 2)
The Miami (Miami-Illinois: ''Myaamiaki'') are a Native American nation originally speaking one of the Algonquian languages. Among the peoples known as the Great Lakes tribes, they occupied territory that is now identified as North-central Indiana, southwest Michigan, and western Ohio. The Miami were historically made up of several prominent subgroups, including the Piankeshaw, Wea, Pepikokia, Kilatika, Mengakonkia, and Atchakangouen. In modern times, Miami is used more specifically to refer to the Atchakangouen. By 1846, most of the Miami had been forcefully displaced to Indian Territory (initially to what is now Kansas, and later to what is now part of Oklahoma). The Miami Tribe of Oklahoma are the federally recognized tribe of Miami Indians in the United States. The Miami Nation of Indiana, a nonprofit organization of descendants of Miamis who were exempted from removal, have unsuccessfully sought separate recognition. Name The name Miami derives from ''Myaamia'' (plural ''My ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coureur Des Bois
A coureur des bois (; ) or coureur de bois (; plural: coureurs de(s) bois) was an independent entrepreneurial French-Canadian trader who travelled in New France and the interior of North America, usually to trade with First Nations peoples by exchanging various European items for furs. Some learned the trades and practices of the indigenous peoples. These expeditions were part of the beginning of the fur trade in the North American interior. Initially they traded for beaver coats and furs. However, as the market grew, ''coureurs de bois'' were trapping and trading prime beavers whose skins were to be felted in Europe. Evolution While French settlers had lived and traded alongside Indigenous people since the earliest days of New France, coureurs des bois reached their apex during the second half of the 17th century. After 1681, the independent coureur des bois was gradually replaced by state-sponsored voyageurs, who were workers associated with licensed fur traders. They trave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Trent
William Trent (February 13, 1715–1787) was an American fur trader and merchant based in colonial Pennsylvania. He was commissioned as a captain of the Virginia Regiment in the early stages of the French and Indian War, when he served on the western frontier with the young Lt. Colonel George Washington. Trent led an advance group who built forts and improved roads for troop access and defense of the western territory. He was later promoted to the rank of major. Trent had gone into fur trading by 1740, aided by capital from his father, a wealthy shipping merchant of Philadelphia who was the founder of Trenton, New Jersey. The younger Trent took on George Croghan, an Irish immigrant, as his partner, as he was effective in developing trading networks with Native Americans. Some of Trent’s first land deals were of modest size, with the first three involving no more than four hundred acres of land each. In 1744, Trent purchased vast lands in the Ohio Country west of the Appalachia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Illinois (people)
The Illinois Confederation, also referred to as the Illiniwek or Illini, were made up of 12 to 13 tribes who lived in the Mississippi River Valley. Eventually member tribes occupied an area reaching from Lake Michicigao (Michigan) to Iowa, Illinois, Missouri, and Arkansas. The five main tribes were the Cahokia, Kaskaskia, Michigamea, Peoria, and Tamaroa. The name of the confederation was derived from the transliteration by French explorers of to ''Illinois'', more in keeping with the sounds of their own language. The tribes are estimated to have had tens of thousands of members, before the advancement of European contact in the 17th century that inhibited their growth and resulted in a marked decline in population. The Illinois, like many Native American groups, sustained themselves through agriculture, hunting, and fishing. A partially nomadic group, the Illinois often lived in longhouses and wigwams, according to the season and resources that were available to them in the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kickapoo People
The Kickapoo people ( Kickapoo: ''Kiikaapoa'' or ''Kiikaapoi''; es, Kikapú) are an Algonquian-speaking Native American and Indigenous Mexican tribe, originating in the region south of the Great Lakes. Today, three federally recognized Kickapoo tribes are in the United States: the Kickapoo Tribe in Kansas, the Kickapoo Tribe of Oklahoma, and the Kickapoo Traditional Tribe of Texas. The Oklahoma and Texas bands are politically associated with each other. The Kickapoo in Kansas came from a relocation from southern Missouri in 1832 as a land exchange from their reserve there. Around 3,000 people are enrolled tribal members. Another band, the Tribu Kikapú, resides in Múzquiz Municipality in the northern Mexican state of Coahuila. Smaller bands live in Sonora, to the west, and Durango, to the southwest. Name and etymology According to some sources, the name "Kickapoo" (''Giiwigaabaw'' in the Anishinaabe language and its Kickapoo cognate ''Kiwikapawa'') means "stands here a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potawatomi
The Potawatomi , also spelled Pottawatomi and Pottawatomie (among many variations), are a Native American people of the western Great Lakes region, upper Mississippi River and Great Plains. They traditionally speak the Potawatomi language, a member of the Algonquin family. The Potawatomi call themselves ''Neshnabé'', a cognate of the word ''Anishinaabe''. The Potawatomi are part of a long-term alliance, called the Council of Three Fires, with the Ojibway and Odawa (Ottawa). In the Council of Three Fires, the Potawatomi are considered the "youngest brother" and are referred to in this context as ''Bodwéwadmi'', a name that means "keepers of the fire" and refers to the council fire of three peoples. In the 18th century, they were pushed to the west by European/American encroachment and eventually removed from their lands in the Great Lakes region to reservations in Oklahoma. Under Indian Removal, they eventually ceded many of their lands, and most of the Potawatomi relocated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
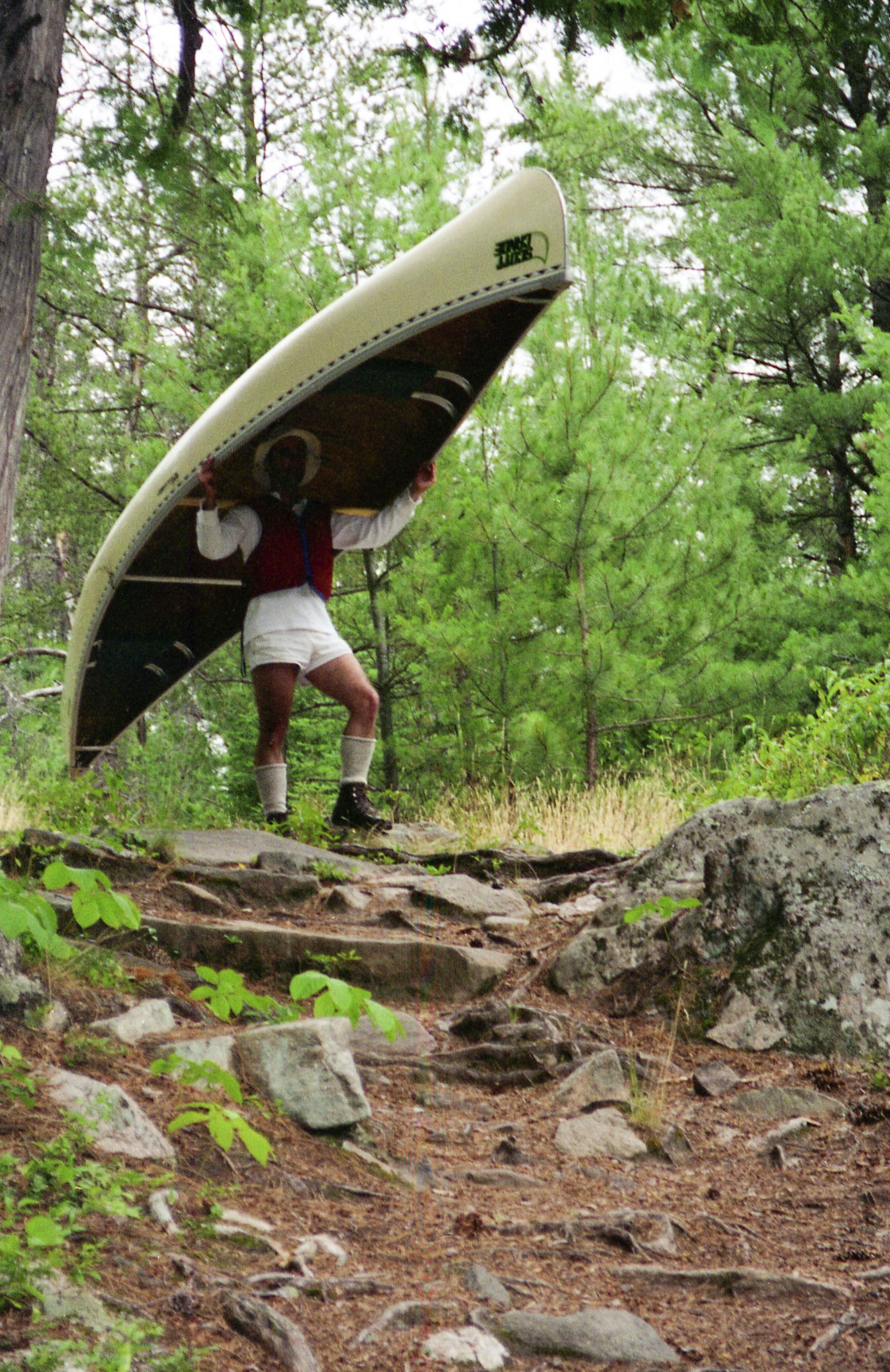
Portage
Portage or portaging (Canada: ; ) is the practice of carrying water craft or cargo over land, either around an obstacle in a river, or between two bodies of water. A path where items are regularly carried between bodies of water is also called a ''portage.'' The term comes from French, where means "to carry," as in "portable". In Canada, the term "carrying-place" was sometimes used. Early French explorers in New France and French Louisiana encountered many rapids and cascades. The Native Americans carried their canoes over land to avoid river obstacles. Over time, important portages were sometimes provided with canals with locks, and even portage railways. Primitive portaging generally involves carrying the vessel and its contents across the portage in multiple trips. Small canoes can be portaged by carrying them inverted over one's shoulders and the center strut may be designed in the style of a yoke to facilitate this. Historically, voyageurs often employed tump lines on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loramie Creek
Loramie Creek is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed May 19, 2011 tributary of the Great Miami River in western Ohio in the United States. Via the Great Miami and Ohio rivers, it is part of the watershed of the Mississippi River, draining an area of . According to the Geographic Names Information System, the stream has also been known historically as "Laramie Creek," "Loramie Ditch," "Loramies Creek," and "Lonamie Creek." It is named after Louis Lorimier, a French-Canadian fur trader who had a trading post in the area in the 18th century. Loramie Creek rises in northern Shelby County and initially flows southwestwardly, passing through a dam which causes the creek to form Lake Loramie, along which a state park is located. Near Fort Loramie the creek turns southeastwardly, flowing through Lockington Dam (a dry dam) and past the community of Lockington. It flows into the Great Miami River in northern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maumee River
The Maumee River (pronounced ) ( sjw, Hotaawathiipi; mia, Taawaawa siipiiwi) is a river running in the United States Midwest from northeastern Indiana into northwestern Ohio and Lake Erie. It is formed at the confluence of the St. Joseph and St. Marys rivers, where Fort Wayne, Indiana has developed, and meanders northeastwardly for U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed May 19, 2011 through an agricultural region of glacial moraines before flowing into the Maumee Bay of Lake Erie. The city of Toledo is located at the mouth of the Maumee. The Maumee was designated an Ohio State Scenic River on July 18, 1974. The Maumee watershed is Ohio’s breadbasket; it is two-thirds farmland, mostly corn and soybeans. It is the largest watershed of any of the rivers feeding the Great Lakes, and supplies five percent of Lake Erie’s water. History Historically the river was also known as the ''Miami'' in United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)





