|
Rock Cupule
Rock cupules () are artificially made depressions on rock surfaces that resemble the shape of an inverse spherical cap or dome. They were made by direct percussion with hand-held hammer-stones, on vertical, sloping or horizontal rock surfaces. Cupules are widely believed to be the world's most common rock art motifs, found in huge numbers in every continent except Antarctica. They were produced in many cultures, from the Lower Paleolithic to the 20th century, and they can be found on most lithologies. Similar artifacts from lithic Native American cultures are also known as cupstones. The name cupule derives from the Late Latin ''cūpula'', “little cask”. Appearances Cupules are usually between in diameter, although larger specimens are occasionally seen. They occur commonly in groupings that may number several hundred; they may be arranged in geometric formations, such as aligned sets, or they occur in unstructured, random groups. Some specimens in the southern Kalahari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slagsta
Slagsta is a municipal district and a residential area of Botkyrka Municipality, Stockholm County, southeastern Sweden. It is located between the E4 south and part of Lake Mälaren A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much larger ... in the north. The area is named after Slagsta farm. Gallery File:Slagstabadet 2012a.jpg, Slagstabadet File:Slagsta gård 2009a.jpg, Slagsta gård File:Slagstaristningen 2009.jpg, Slagsta hällristning References Populated places in Botkyrka Municipality Södermanland {{Stockholm-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mortar And Pestle
Mortar and pestle is a set of two simple tools used from the Stone Age to the present day to prepare ingredients or substances by crushing and grinding them into a fine paste or powder in the kitchen, laboratory, and pharmacy. The ''mortar'' () is characteristically a bowl, typically made of hard wood, metal, ceramic, or hard stone such as granite. The ''pestle'' (, also ) is a blunt, club-shaped object. The substance to be ground, which may be wet or dry, is placed in the mortar where the pestle is pounded, pressed, and rotated into the substance until the desired texture is achieved. Mortars and pestles have been used in cooking since prehistory; today they are typically associated with the profession of pharmacy due to their historical use in preparing medicines. They are used in chemistry settings for pulverizing small amounts of chemicals; in arts and cosmetics for pulverizing pigments, binders, and other substances; in ceramics for making grog; in masonry and in other typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock Art
In archaeology, rock art is human-made markings placed on natural surfaces, typically vertical stone surfaces. A high proportion of surviving historic and prehistoric rock art is found in caves or partly enclosed rock shelters; this type also may be called cave art or parietal art. A global phenomenon, rock art is found in many culturally diverse regions of the world. It has been produced in many contexts throughout human history. In terms of technique, the four main groups are: * cave paintings, * petroglyphs, which are carved or scratched into the rock surface, * sculpted rock reliefs, and * geoglyphs, which are formed on the ground. The oldest known rock art dates from the Upper Palaeolithic period, having been found in Europe, Australia, Asia, and Africa. Anthropologists studying these artworks believe that they likely had magico-religious significance. The archaeological sub-discipline of rock art studies first developed in the late-19th century among Francophone scholar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Energy Metamorphosis
Kinetic energy metamorphosis (KEM) is a recently discovered tribological process of gradual crystal re-orientation and foliation of component minerals in certain rocks. It is caused by very high, localized application of kinetic energy. The required energy may be provided by prolonged battery of fluvially propelled bed load of cobbles, by glacial abrasion, tectonic deformation, and even by human action. It can result in the formation of laminae on specific metamorphic rocks that, while being chemically similar to the protolith, differ significantly in appearance and in their resistance to weathering or deformation. These tectonite layers are of whitish color and tend to survive granular or mass exfoliation much longer than the surrounding protolith. KEM in cupules The products of KEM were first identified in 2015 in cupules, a form of rock art consisting of spherical cap or dome-shaped depressions created by percussion with hammer-stones. KEM laminae, caused by solid state re-met ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vickers Test
The Vickers hardness test was developed in 1921 by Robert L. Smith and George E. Sandland at Vickers Ltd as an alternative to the Brinell method to measure the hardness of materials. The Vickers test is often easier to use than other hardness tests since the required calculations are independent of the size of the indenter, and the indenter can be used for all materials irrespective of hardness. The basic principle, as with all common measures of hardness, is to observe a material's ability to resist plastic deformation from a standard source. The Vickers test can be used for all metals and has one of the widest scales among hardness tests. The unit of hardness given by the test is known as the Vickers Pyramid Number (HV) or Diamond Pyramid Hardness (DPH). The hardness number can be converted into units of pascals, but should not be confused with pressure, which uses the same units. The hardness number is determined by the load over the surface area of the indentation and not t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brinell Scale
The Brinell scale characterizes the indentation hardness of materials through the scale of penetration of an indenter, loaded on a material test-piece. It is one of several definitions of hardness in materials science. History Proposed by Swedish engineer Johan August Brinell in 1900, it was the first widely used and standardised hardness test in engineering and metallurgy. The large size of indentation and possible damage to test-piece limits its usefulness. However, it also had the useful feature that the hardness value divided by two gave the approximate UTS in ksi for steels. This feature contributed to its early adoption over competing hardness tests. Test details The typical test uses a diameter steel ball as an indenter with a force. For softer materials, a smaller force is used; for harder materials, a tungsten carbide ball is substituted for the steel ball. The indentation is measured and hardness calculated as: :\operatorname=\frac where: :BHN = Brinell Hardne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rosiwal Scale
The Rosiwal scale is a hardness scale in mineralogy, with its name given in memory of the Austrian geologist August Karl Rosiwal. The Rosiwal scale attempts to give more quantitative values of scratch hardness, unlike the Mohs scale which is a qualitative measurement with relative values. The Rosiwal method (also called the Delesse-Rosiwal method) is a method of petrographic analysis and is performed by scratching a polished surface under a known load using a scratch-tip with a known geometry. The hardness is calculated by finding the volume of removed material, but this measurement can be difficult and must sample a large enough number of grain in order to have statistical significance. Rosiwal scale values Measures the scratch hardness of a mineral expressed on a quantitative scale. These measurements must be performed in a laboratory, since the surfaces must be flat and smooth. The base value of the Rosiwal scale is defined as corundum set to 1000 (unitless). See also * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Querns
Quern-stones are stone tools for hand-grinding a wide variety of materials. They are used in pairs. The lower stationary stone of early examples is called a saddle quern, while the upper mobile stone is called a muller, rubber or handstone. The upper stone was moved in a back-and-forth motion across the saddle quern. Later querns are known as rotary querns. The central hole of a rotary quern is called the eye, and a dish in the upper surface is known as the hopper. A handle slot contained a handle which enabled the rotary quern to be rotated. They were first used in the Neolithic era to grind cereals into flour. Uses of quern-stones An old Gaelic proverb is "The quern performs best when the grindstone has been pitted." Design of quern-stones The upper stones were usually concave while the lower ones were convex. Quern-stones are frequently identifiable by their grooved working surfaces which enabled the movement of flour. Sometimes a millrind was present as a piece of wood (or o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
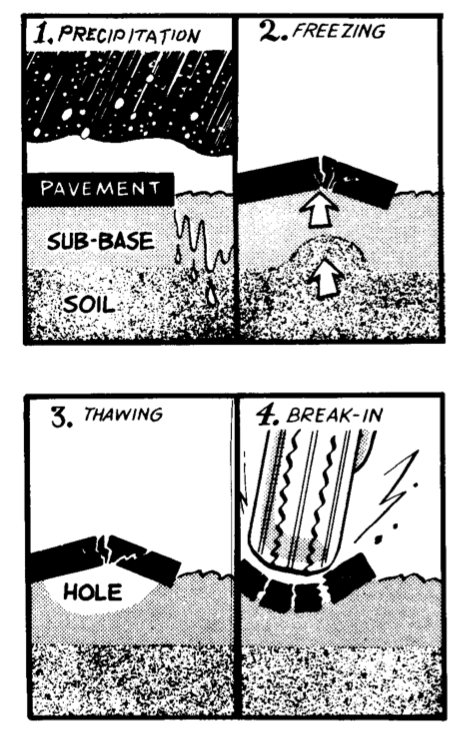
Potholes
A pothole is a depression in a road surface, usually asphalt pavement, where traffic has removed broken pieces of the pavement. It is usually the result of water in the underlying soil structure and traffic passing over the affected area. Water first weakens the underlying soil; traffic then fatigues and breaks the poorly supported asphalt surface in the affected area. Continued traffic action ejects both asphalt and the underlying soil material to create a hole in the pavement. Formation According to the US Army Corps of Engineers's Cold Regions Research and Engineering Laboratory, pothole formation requires two factors to be present at the same time: water and traffic. Water weakens the soil beneath the pavement while traffic applies the loads that stress the pavement past the breaking point. Potholes form progressively from fatigue of the road surface which can lead to a precursor failure pattern known as crocodile (or alligator) cracking. Eventually, chunks of pavement b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
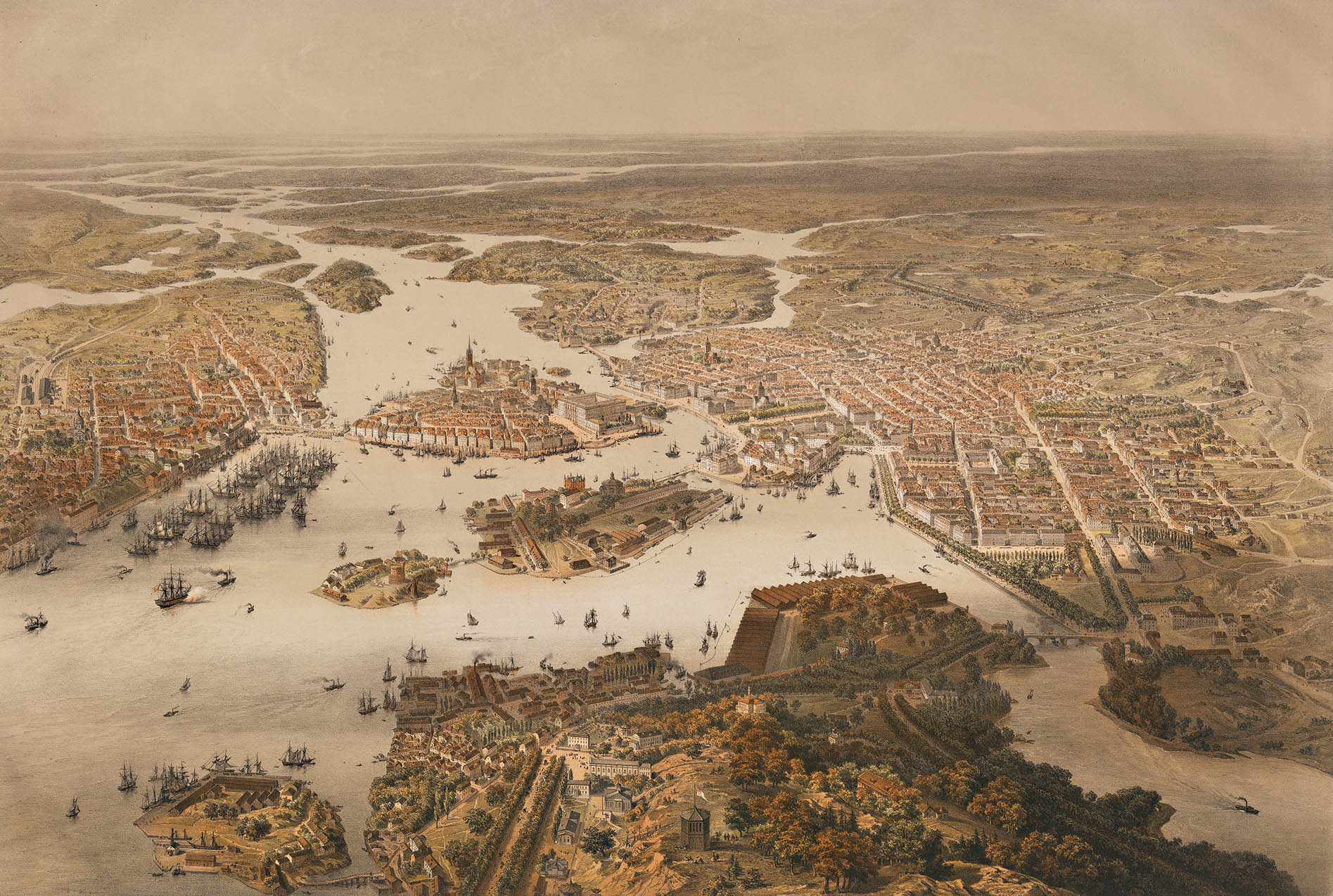
Stockholm
Stockholm () is the Capital city, capital and List of urban areas in Sweden by population, largest city of Sweden as well as the List of urban areas in the Nordic countries, largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the Stockholm Municipality, municipality, with 1.6 million in the Stockholm urban area, urban area, and 2.4 million in the Metropolitan Stockholm, metropolitan area. The city stretches across fourteen islands where Mälaren, Lake Mälaren flows into the Baltic Sea. Outside the city to the east, and along the coast, is the island chain of the Stockholm archipelago. The area has been settled since the Stone Age, in the 6th millennium BC, and was founded as a city in 1252 by Swedish statesman Birger Jarl. It is also the county seat of Stockholm County. For several hundred years, Stockholm was the capital of Finland as well (), which then was a part of Sweden. The population of the municipality of Stockholm is expected to reach o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithophone
A lithophone is a musical instrument consisting of a rock or pieces of rock which are struck to produce musical notes. Notes may be sounded in combination (producing harmony) or in succession (melody). It is an idiophone comparable to instruments such as the glockenspiel, vibraphone, xylophone and marimba. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, lithophones are designated as '111.22' – directly-struck percussion plaques. Notable examples A rudimentary form of lithophone is the "rock gong", usually a natural rock formation opportunistically adapted to produce musical tones, such as that on Mfangano Island, in Lake Victoria, Kenya. The Great Stalacpipe Organ of Luray Caverns, Virginia, USA uses 37 stalactites to produce the Western scale. Other stalactite lithophones are at Tenkasi in South India, and at Ringing Rocks Park in Pennsylvania. An example that is no longer used is at Cave of the Winds, in Colorado Springs. The Txalaparta (or Chalaparta), a tradition ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Menhir Fraisse Mas-Saint-Chely Causse Mejean 2
A menhir (from Brittonic languages: ''maen'' or ''men'', "stone" and ''hir'' or ''hîr'', "long"), standing stone, orthostat, or lith is a large human-made upright stone, typically dating from the European middle Bronze Age. They can be found individually as monoliths, or as part of a group of similar stones. Menhirs' size can vary considerably, but they often taper toward the top. They are widely distributed across Europe, Africa and Asia, but are most numerous in Western Europe; particularly in Ireland, Great Britain, and Brittany, where there are about 50,000 examples, and northwestern France, where there are some 1,200 further examples. Standing stones are usually difficult to date. They were constructed during many different periods across pre-history as part of the larger megalithic cultures in Europe and near areas. Some menhirs stand next to buildings that have an early or current religious significance. One example is the South Zeal Menhir in Devon, which formed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_1934.jpg)