|
Ringed Cross
The ringed cross is a class of Christian cross symbols featuring a ring or nimbus. The concept exists in many variants and dates to early in the history of Christianity. One variant, the cruciform halo, is a special type of halo placed behind the head of Jesus in Christian art. Other common variants include the Celtic cross, used in the stone high crosses of Ireland and Britain; some forms of the Coptic cross; and ringed crosses from western France and Galicia. History The nimbus or ringed shape was appended to the Christian cross and other symbols relatively early. In these contexts it apparently derived from the earlier Roman garland of victory. The Chi Rho-in-circle motif was widespread in the Roman Empire by the late 4th century, and garlanded and ringed crosses were popular in imperial Ravenna by the 5th century, influencing the later versions. The cruciform halo or cross halo, a halo incorporating a cross, emerged as a distinctive type of halo painted behind the head ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earth Symbol (fixed Width)
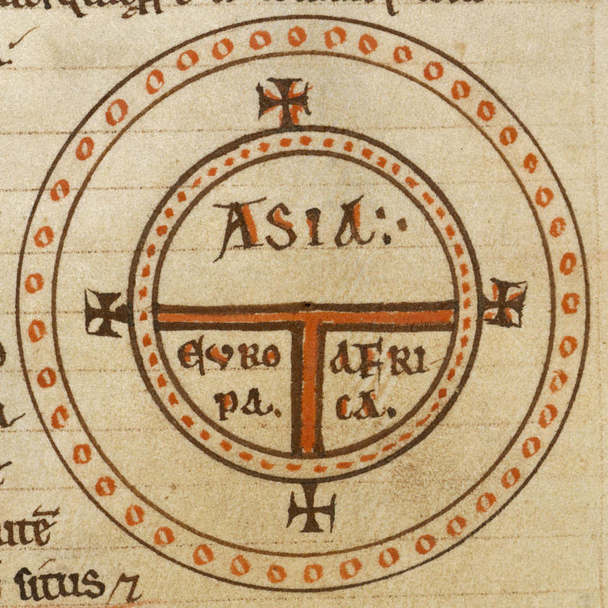
A variety of symbols or iconographic conventions are used to represent Earth, whether in the sense of planet Earth, or the inhabited world, or as a classical element. A circle representing the round world, with the rivers of Garden of Eden separating the four corners of the world, or rotated 45° to suggest the four continents, remains a common pictographic convention to express the notion of "worldwide". The current astronomical symbol for the planet is a circle with an intersecting cross, 20px, 🜨, alt=An equilateral cross enclosed in a circle. Although the International Astronomical Union (IAU) now discourages the use of planetary symbols, this is an exception, being used in abbreviations such as ''M''🜨 for Earth mass. History The earliest type of symbols are allegories, personifications or deifications, mostly in the form of an Earth goddess (in the case of Egyptian mythology a god, Geb). Before the recognition of the spherical shape of the Earth in the Hellenist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coptic Cross
The Coptic cross refers to a number of Christian cross variants associated in some way with Coptic Christians. Typical form The typical form of the "Coptic cross" used in the Coptic Church is made up of two bold lines of equal length that intersect at the middle at right angles. Each line terminates in three points, representing the Trinity of the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit. Altogether, the cross has 12 points symbolizing the Apostles, whose mission was to spread the Gospel message throughout the world. This form of Coptic cross is widely used in the Coptic church and the Ethiopian and Eritrean churches, and so this form of the cross may also be called the "Ethiopian cross" or " Axum cross". Bertran de la Farge dates it to the 4th century and cites it as a predecessor of the Occitan cross. History and variation Old Coptic crosses often incorporate a circle, as in the form called a "Coptic cross" by Rudolf Koch in his ''The Book of Signs'' (1933). Sometimes th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Middle Ages of European history, following the decline of the Western Roman Empire, and preceding the High Middle Ages ( 11th to 13th centuries). The alternative term ''late antiquity'', for the early part of the period, emphasizes elements of continuity with the Roman Empire, while ''Early Middle Ages'' is used to emphasize developments characteristic of the earlier medieval period. The period saw a continuation of trends evident since late classical antiquity, including population decline, especially in urban centres, a decline of trade, a small rise in average temperatures in the North Atlantic region and increased migration. In the 19th century the Early Middle Ages were often labelled the ''Dark Ages'', a characterization based on t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basilica Of Sant'Apollinare In Classe
The Basilica of Sant' Apollinare in Classe ("Saint Apollinaris in Classe") is a church in Classe, Ravenna, Italy, consecrated on 9 May 549 by the bishop Maximian and dedicated to Saint Apollinaris, the first bishop of Ravenna and Classe. An important monument of Byzantine art, in 1996 it was inscribed with seven other nearby monuments in the UNESCO World Heritage List, which described it as "an outstanding example of the early Christian basilica in its purity and simplicity of its design and use of space and in the sumptuous nature of its decoration". History Work on Sant'Apollinare in Classe started at the beginning of 6th century by order of Bishop Ursicinus, using money from the Roman banker Iulianus Argentarius. It was certainly located next to a Christian cemetery, and quite possibly on top of a pre-existing pagan one, as some of the ancient tombstones were re-used in its construction. At that time, Classe was located on the shore and was the ancient home port of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crux Gemmata
A ''crux gemmata'' (Latin for jewelled cross) is a form of cross typical of Early Christian and Early Medieval art, where the cross, or at least its front side, is principally decorated with jewels. In an actual cross, rather than a painted image of one, the reverse side often has engraved images of the Crucifixion of Jesus or other subjects. Examples in metalwork are the Cross of Justin II (6th century, in the Vatican Museums), the 'crumpled cross' in the Staffordshire Hoard (8th century), the Cross of Lothair (10th century, Aachen Cathedral Treasury), the Iberian Cross of the Angels and Victory Cross, and the Cross of Cong (1120s?, National Museum of Ireland). History of use In the Late Antique and Early Medieval periods, many objects of great significance, such as reliquaries, were studded with jewels in a style that in recent centuries has been restricted to crowns and other coronation regalia and small pieces of jewellery. In the case of the cross, such decorative em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mausoleum Of Galla Placidia
The Mausoleum of Galla Placidia is a Late Antique Roman building in Ravenna, Italy, built between 425 and 450. It was added to the World Heritage List together with seven other structures in Ravenna in 1996. Despite its common name, the empress Galla Placidia (d. 450) was not buried in the building, a misconception dating from the thirteenth century; she died in Rome and was buried there, probably alongside Honorius in the Mausoleum of Honorius at Old Saint Peter's Basilica. History The "mausoleum" of Galla Placidia, built 425–450, is a cruciform chapel or oratory that originally adjoined the narthex of the Church of the Holy Cross (''Santa Croce'') in Ravenna. It was probably dedicated to Saint Lawrence. Aelia Galla Placidia, the likely patron of the building's construction, was the daughter of Theodosius I and Galla, the daughter of Valentinian I. Raised by Serena, wife of Stilicho, she was made '' nobilissima'' in her youth and granted a palace by her father in Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Celestial Sphere
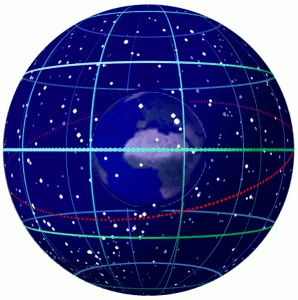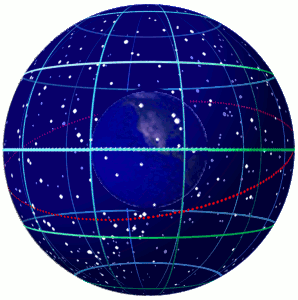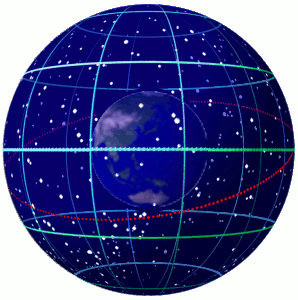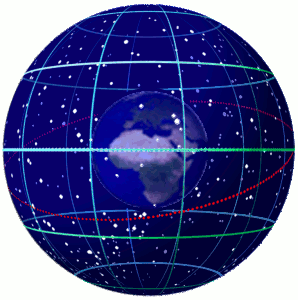
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, which may be centered on Earth or the observer. If centered on the observer, half of the sphere would resemble a hemispherical screen over the observing location. The celestial sphere is a conceptual tool used in spherical astronomy to specify the position of an object in the sky without consideration of its linear distance from the observer. The celestial equator divides the celestial sphere into northern and southern hemispheres. Introduction Because astronomical objects are at such remote distances, casual observation of the sky offers no information on their actual distances. All celestial objects seem equally far away, as if fixed onto the inside of a sphere with a large but unknown radius, which appears to rotate westward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holy Trinity
The Christian doctrine of the Trinity (, from 'threefold') is the central dogma concerning the nature of God in most Christian churches, which defines one God existing in three coequal, coeternal, consubstantial divine persons: God the Father, God the Son (Jesus Christ) and God the Holy Spirit, three distinct persons sharing one '' homoousion'' (essence) "each is God, complete and whole." As the Fourth Lateran Council declared, it is the Father who begets, the Son who is begotten, and the Holy Spirit who proceeds. In this context, the three persons define God is, while the one essence defines God is. This expresses at once their distinction and their indissoluble unity. Thus, the entire process of creation and grace is viewed as a single shared action of the three divine persons, in which each person manifests the attributes unique to them in the Trinity, thereby proving that everything comes "from the Father," "through the Son," and "in the Holy Spirit." This doc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Halo (religious Iconography)
A halo (from the Greek , ; also known as a nimbus, aureole, glory, or gloriole) is a crown of light rays, circle or disk of light that surrounds a person in art. It has been used in the iconography of many religions to indicate holy or sacred figures, and has at various periods also been used in images of rulers and heroes. In the religious art of Ancient Greece, Ancient Rome, Christianity, Hinduism, and Buddhism among other religions, sacred persons may be depicted with a halo in the form of a circular glow, or flames in Asian art, around the head or around the whole body—this last one is often called a mandorla. Halos may be shown as almost any colour or combination of colours, but are most often depicted as golden, yellow or white when representing light or red when representing flames. Ancient Mesopotamia Sumerian religious literature frequently speaks of (loaned into Akkadian as ), a "brilliant, visible glamour which is exuded by gods, heroes, sometimes by kings, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the capital of the Ostrogothic Kingdom until it was re-conquered in 540 by the Byzantine Empire. Afterwards, the city formed the centre of the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna until the last exarch was executed by the Lombards in 751. Although it is an inland city, Ravenna is connected to the Adriatic Sea by the Candiano Canal. It is known for its well-preserved late Roman and Byzantine architecture, with eight buildings comprising the UNESCO World Heritage Site "Early Christian Monuments of Ravenna". History The origin of the name ''Ravenna'' is unclear. Some have speculated that "Ravenna" is related to "Rasenna" (or "Rasna"), the term that the Etruscans used for themselves, but there is no agreement on this point. Ancient era The origins of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chi Rho
The Chi Rho (☧, English pronunciation ; also known as ''chrismon'') is one of the earliest forms of Christogram, formed by superimposing the first two (capital) letters—chi and rho (ΧΡ)—of the Greek word ( Christos) in such a way that the vertical stroke of the rho intersects the center of the chi. The Chi-Rho symbol was used by the Roman Emperor Constantine I (r. 306–337 AD) as part of a military standard ( vexillum). Constantine's standard was known as the Labarum. Early symbols similar to the Chi Rho were the Staurogram () and the IX monogram (). In pre-Christian times, the Chi-Rho symbol was also used to mark a particularly valuable or relevant passage in the margin of a page, abbreviating ''chrēston'' (good). Some coins of Ptolemy III Euergetes (r. 246–222 BC) were marked with a Chi-Rho. Although formed of Greek characters, the device (or its separate parts) is frequently found serving as an abbreviation in Latin text, with endings added appropriate t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laurel Wreath
A laurel wreath is a round wreath made of connected branches and leaves of the bay laurel (), an aromatic broadleaf evergreen, or later from spineless butcher's broom (''Ruscus hypoglossum'') or cherry laurel (''Prunus laurocerasus''). It is a symbol of triumph and is worn as a chaplet around the head, or as a garland around the neck. The symbol of the laurel wreath traces back to Ancient Greece. In Greek mythology, the god Apollo, who is patron of lyrical poetry, musical performance and skill-based athletics, is conventionally depicted wearing a laurel wreath on his head in all three roles. Wreaths were awarded to victors in athletic competitions, including the ancient Olympics; for victors in athletics they were made of wild olive tree known as ''" kotinos"'' (), (sc. at Olympia) – and the same for winners of musical and poetic competitions. In Rome they were symbols of martial victory, crowning a successful commander during his triumph. Whereas ancient laurel wreaths are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)
.jpeg/1200px-Gandhara_Buddha_(tnm).jpeg)
.png)