|
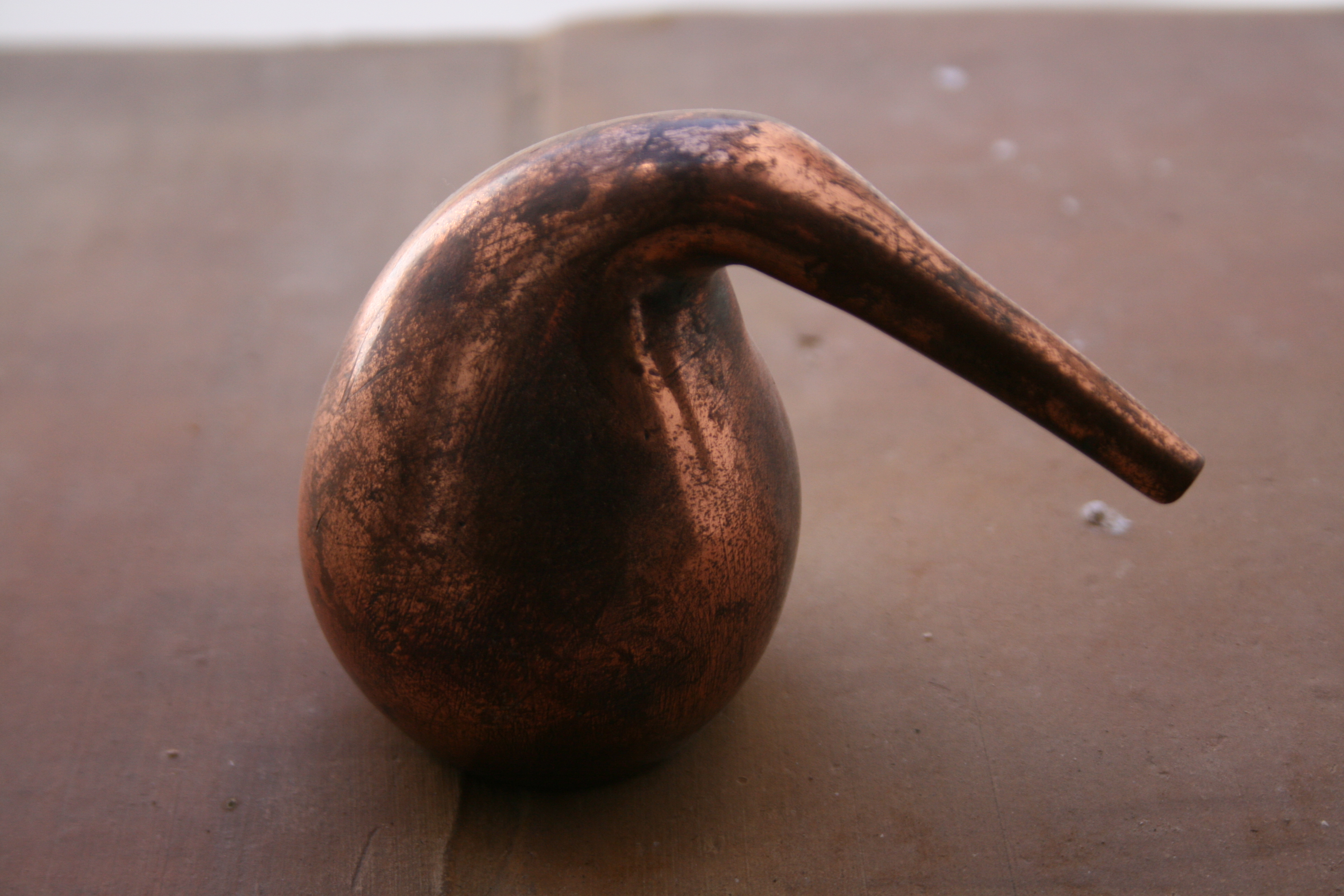
Retort
In a chemistry laboratory, a retort is a device used for distillation or dry distillation of substances. It consists of a spherical vessel with a long downward-pointing neck. The liquid to be distilled is placed in the vessel and heated. The neck acts as a condenser, allowing the vapors to condense and flow along the neck to a collection vessel placed underneath. In the chemical industry, a retort is an airtight vessel in which substances are heated for a chemical reaction producing gaseous products to be collected in a collection vessel or for further processing. Such industrial-scale retorts are used in shale oil extraction, the production of charcoal and in the recovery of mercury in gold mining processes and hazardous waste. A process of heating oil shale to produce shale oil, oil shale gas, and spent shale is commonly called retorting. Airtight vessels to apply pressure as well as heat are called autoclaves. In the food industry, pressure cookers are often referred to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retort Stand
In chemistry, a retort stand, also called a clamp stand,Laboratory-Equipment.com (2020):Large Clamp Stand, for Q700. Online catalog item 5323-07. Accessed on 202-02-18. a ring stand, or a support stand,Fischer Scientific (2020):American Educational Products Tripod Base Support Stands Online catalog entry S47809. Accessed on 202-02-18. is a piece of scientific equipment intended to support other pieces of equipment and glassware — for instance, burettes, test tubes and Laboratory flask, flasks. The typical ring stand consists of a heavy base and a vertical rod, both usually made of metal. A number of accessories, such as clamp (tool), clamps of various types and Iron ring (laboratory), iron rings, can be attached to the rod by Thumbscrew (fastener), thumbscrews, at whatever heights and orientations are necessary to support the target equipment. Structure Retort stands commonly have a cast iron base of around 200 x 125 mm. The rod may be up to 750 mm and screws into a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retort Pouch
A retort pouch or retortable pouch is a type of food packaging made from a laminate of flexible plastic and metal foils. It allows the sterile packaging of a wide variety of food and drink handled by aseptic processing, and is used as an alternative to traditional industrial canning methods. Packaged foods range from water to fully cooked, thermo-stabilized (heat-treated) high-caloric (1,300 kcal on average) meals such as Meals, Ready-to-Eat (MREs), which can be eaten cold, warmed by submersing in hot water, or through the use of a flameless ration heater, a meal component introduced by the military in 1992. Retort pouches are used in field rations, space food, fish products, camping food, instant noodles, and brands such as Capri Sun and Tasty Bite. Some varieties have a bottom gusset and are known as stand-up pouches. Origin The retort pouch was invented by the United States Army Natick R&D Command, Reynolds Metals Company, and Continental Flexible Packaging, who jointly rece ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shale Oil Extraction
Shale oil extraction is an industrial process for unconventional oil production. This process converts kerogen in oil shale into shale oil by pyrolysis, hydrogenation, or thermal dissolution. The resultant shale oil is used as fuel oil or upgraded to meet refinery feedstock specifications by adding hydrogen and removing sulfur and nitrogen impurities. Shale oil extraction is usually performed above ground (''ex situ'' processing) by mining the oil shale and then treating it in processing facilities. Other modern technologies perform the processing underground (on-site or ''in situ'' processing) by applying heat and extracting the oil via oil wells. The earliest description of the process dates to the 10th century. In 1684, Great Britain granted the first formal extraction process patent. Extraction industries and innovations became widespread during the 19th century. The industry shrank in the mid-20th century following the discovery of large reserves of conventional oil, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distillation By Retort
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the heating of solid materials to produce gaseous products (which may condense into liquids or solids); this may involve chemical changes such as destructive distillation or cracking. Distillation may result in essentially complete separation (resulting in nearly pure components), or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components; in either case, the process exploits differences in the relative volatility of the mixture's components. In industrial applications, distillation is a unit operation of practically universal importance, but is a physical separation process, not a chemical reaction. An installation used for distillation, especially of distilled beverages, is a distillery. Distillation includes the fol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Charcoal
Charcoal is a lightweight black carbon residue produced by strongly heating wood (or other animal and plant materials) in minimal oxygen to remove all water and volatile constituents. In the traditional version of this pyrolysis process, called charcoal burning, often by forming a charcoal kiln, the heat is supplied by burning part of the starting material itself, with a limited supply of oxygen. The material can also be heated in a closed retort. Modern "charcoal" briquettes used for outdoor cooking may contain many other additives, e.g. coal. This process happens naturally when combustion is incomplete, and is sometimes used in radiocarbon dating. It also happens inadvertently while burning wood, as in a fireplace or wood stove. The visible flame in these is due to combustion of the volatile gases exuded as the wood turns into charcoal. The soot and smoke commonly given off by wood fires result from incomplete combustion of those volatiles. Charcoal burns at a higher temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Distillation
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separation process, separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the heating of solid materials to produce gaseous products (which may condense into liquids or solids); this may involve chemical changes such as destructive distillation or Cracking (chemistry), cracking. Distillation may result in essentially complete separation (resulting in nearly pure components), or it may be a partial separation that increases the concentration of selected components; in either case, the process exploits differences in the relative volatility of the mixture's components. In Chemical industry, industrial applications, distillation is a unit operation of practically universal importance, but is a physical separation process, not a chemical reaction. An installation used for distillation, especially of distilled ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shale Oil
Shale oil is an unconventional oil produced from oil shale rock fragments by pyrolysis, hydrogenation, or thermal dissolution. These processes convert the organic matter within the rock (kerogen) into synthetic oil and gas. The resulting oil can be used immediately as a fuel or upgraded to meet refinery feedstock specifications by adding hydrogen and removing impurities such as sulfur and nitrogen. The refined products can be used for the same purposes as those derived from crude oil. The term "shale oil" is also used for crude oil produced from shales of other unconventional, very low permeability formations. However, to reduce the risk of confusion of shale oil produced from oil shale with crude oil in oil-bearing shales, the term "tight oil" is preferred for the latter. The International Energy Agency recommends to use the term "light tight oil" and World Energy Resources 2013 report by the World Energy Council uses the term "tight oil" for crude oil in oil-bearing sha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spent Shale
Spent shale or spent oil shale (also known as retorted shale) is a solid residue from the shale oil extraction process of producing synthetic shale oil from oil shale. It consists of inorganic compounds (minerals) and remaining organic matter known as char—a carbonaceous residue formed from kerogen. Depending on the extraction process and the amount of remaining organic matter, spent shale may be classified as oil shale coke, semi-coke or coke-ash residue, known also as oil shale ash. According to the European Union waste list all these types of spent shale are classified as hazardous waste. Oil shale coke is created by chamber ovens which were used for oil shale gas production. Vertical retorts create mainly semi-coke. Most solid heat carrier processes create coke-ash residue as the semi-coke created during the process is combusted for the process's energy needs. Spent shale can be used as ingredients in cement or brick manufacture. In Jordan, usage of spent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canning
Canning is a method of food preservation in which food is processed and sealed in an airtight container (jars like Mason jars, and steel and tin cans). Canning provides a shelf life that typically ranges from one to five years, although under specific circumstances, it can be much longer. A freeze-dried canned product, such as canned dried lentils, could last as long as 30 years in an edible state. In 1974, samples of canned food from the wreck of the ''Bertrand'', a steamboat that sank in the Missouri River in 1865, were tested by the National Food Processors Association. Although appearance, smell, and vitamin content had deteriorated, there was no trace of microbial growth and the 109-year-old food was determined to be still safe to eat. History and development French origins During the first years of the Napoleonic Wars, the French government offered a hefty cash award of 12,000 francs to any inventor who could devise a cheap and effective method of preserving l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alembic
An alembic (from ar, الإنبيق, al-inbīq, originating from grc, ἄμβιξ, ambix, 'cup, beaker') is an alchemical still consisting of two vessels connected by a tube, used for distillation of liquids. Description The complete distilling apparatus consists of three parts: the "cucurbit" (Arabic: ; Greek: , ), the still pot containing the liquid to be distilled, which is heated by a flame; the "head" or "cap" (, ; Greek , ) which fits over the mouth of the cucurbit to receive the vapors, with an attached downward-sloping "tube" (, ); and the "receiver" (, ; , or , ) container. In the case of another distilling vessel, the retort, the "cap" and the "cucurbit" have been combined to form a single vessel. The anbik is also called the raʾs (head) of the cucurbit. The liquid in the cucurbit is heated or boiled; the vapour rises into the anbik, where it cools by contact with the walls and condenses, running down the spout into the receiver. A modern descendant of the alemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrolysis
The pyrolysis (or devolatilization) process is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures, often in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change of chemical composition. The word is coined from the Greek-derived elements ''pyro'' "fire", "heat", "fever" and '' lysis'' "separating". Pyrolysis is most commonly used in the treatment of organic materials. It is one of the processes involved in charring wood.''Burning of wood'' , InnoFireWood's website. Accessed on 2010-02-06. In general, pyrolysis of organic substances produces volatile products and leaves , a carbon-rich solid residue. Extreme pyrolysis, which leaves mostly |
Laboratory Techniques
A laboratory (; ; colloquially lab) is a facility that provides controlled conditions in which scientific or technological research, experiments, and measurement may be performed. Laboratory services are provided in a variety of settings: physicians' offices, clinics, hospitals, and regional and national referral centers. Overview The organisation and contents of laboratories are determined by the differing requirements of the specialists working within. A physics laboratory might contain a particle accelerator or vacuum chamber, while a metallurgy laboratory could have apparatus for casting or refining metals or for testing their strength. A chemist or biologist might use a wet laboratory, while a psychologist's laboratory might be a room with one-way mirrors and hidden cameras in which to observe behavior. In some laboratories, such as those commonly used by computer scientists, computers (sometimes supercomputers) are used for either simulations or the analysis of data. Scienti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |