|
Repetitive Tuning
Repetitive tunings are alternative tunings for the guitar. A repetitive tuning begins with a list of notes that is duplicated, either at unison or at higher octaves. Among regular tunings, there are four repetitive-tunings (besides trivially repetitive tunings such as C-C-C-C-C-C); this article discusses three minor-thirds tuning, major-thirds tuning, and augmented-fourths tuning (but not major seconds tuning, which is not repetitive on six strings). Among open tunings, there are repetitive versions of open C tuning and open G tuning, which have been associated with the English and Russian guitars, respectively. Repetition eases the learning of fretboard and chords and eases improvisation. For example, in major-thirds tuning, chords are raised an octave by shifting fingers by three strings on the same frets. Repetitive tunings are listed after their number of open pitches. For example, the repetitive open-C tuning C-E-G-C-E-G has three open-pitches, each of which is ass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
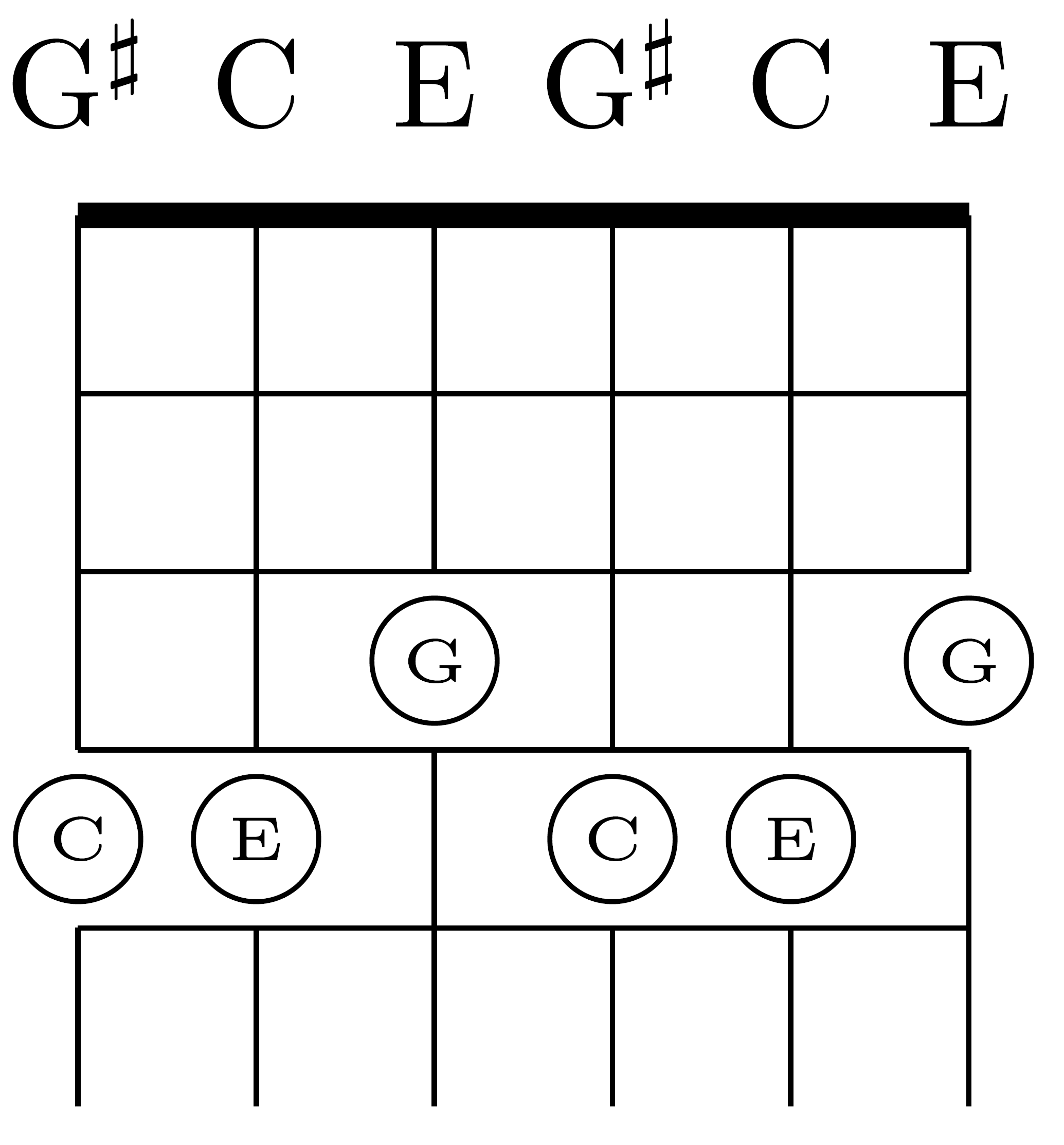
Shift C-major Chord Three Strings In Major Thirds Tuning On Six-string Guitar
Shift may refer to: Art, entertainment, and media Gaming * ''Shift'' (series), a 2008 online video game series by Armor Games * '' Need for Speed: Shift'', a 2009 racing video game ** '' Shift 2: Unleashed'', its 2011 sequel Literature * ''Shift'' (novel), a 2010 alternative history book by Tim Kring and Dale Peck * ''Shift'' (novella), a 2013 science fiction book, part two of the Silo trilogy by Hugh Howey * Shift the Ape, a character in ''The Chronicles of Narnia'' novel series Music * ''Shift'' (Nasum album), 2004 * Shift (The Living End album) * Shift (music), a change of level in music * Shift (string technique), a finger movement from one position to another on the same string Other uses in arts, entertainment, and media * ''Shift'' (magazine), a former Canadian technology and culture magazine * Shift (MSNBC), an online live-streaming video network * ''Shift'' (sculpture), an outdoor sculpture by American artist Richard Serra located in King City, Ontario, Canada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guitar Chord
In music, a guitar chord is a set of notes played on a guitar. A chord's notes are often played simultaneously, but they can be played sequentially in an arpeggio. The implementation of guitar chords depends on the guitar tuning. Most guitars used in popular music have six strings with the "standard" tuning of the Spanish classical guitar, namely E–A–D–G–B–E' (from the lowest pitched string to the highest); in standard tuning, the intervals present among adjacent strings are perfect fourths except for the major third (G,B). Standard tuning requires four chord-shapes for the major triads. There are separate chord-forms for chords having their root note on the third, fourth, fifth, and sixth strings. For a six-string guitar in standard tuning, it may be necessary to drop or omit one or more tones from the chord; this is typically the root or fifth. The layout of notes on the fretboard in standard tuning often forces guitarists to permute the tonal order of notes i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Major-thirds Tuning
Among alternative tunings for guitar, a major-thirds tuning is a regular tuning in which each interval between successive open strings is a major third ("M3" in musical abbreviation). Other names for major-thirds tuning include major-third tuning, M3 tuning, all-thirds tuning, and augmented tuning. By definition, a major-third interval separates two notes that differ by exactly four semitones (one-third of the twelve-note octave). The Spanish guitar's tuning mixes four perfect fourths (five semitones) and one major-third, the latter occurring between the G and B strings: :E–A–D–''G''–''B''–E. This tuning, which is used for acoustic and electric guitars, is called "''standard''" in English, a convention that is followed in this article. While standard tuning is irregular, mixing four fourths and one major third, M3 tunings are regular: Only major-third intervals occur between the successive strings of the M3 tunings, for example, the open augmente ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmented Chord In The Chromatic Circle
Augment or augmentation may refer to: Language *Augment (Indo-European), a syllable added to the beginning of the word in certain Indo-European languages *Augment (Bantu languages), a morpheme that is prefixed to the noun class prefix of nouns in certain Bantu languages *Augment, a name sometimes given to the verbal ''ō-'' prefix in Nahuatl grammar Technology * Augmentation (obstetrics), the process by which the first and/or second stages of an already established labour is accelerated or potentiated by deliberate and artificial means *Augmentation (pharmacology), the combination of two or more drugs to achieve better treatment results *Augmented reality, a live view of a physical, real-world environment whose elements are ''augmented'' by computer-generated sensory input *Augmented cognition, a research field that aims at creating revolutionary human-computer interactions * Augment (Tymshare), a hypertext system derived from Douglas Engelbart's oN-Line System, renamed "Augment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cittern
The cittern or cithren ( Fr. ''cistre'', It. ''cetra'', Ger. ''Cister,'' Sp. ''cistro, cedra, cítola'') is a stringed instrument dating from the Renaissance. Modern scholars debate its exact history, but it is generally accepted that it is descended from the Medieval citole (or cytole). Its flat-back design was simpler and cheaper to construct than the lute. It was also easier to play, smaller, less delicate and more portable. Played by people of all social classes, the cittern was a premier instrument of casual music-making much as is the guitar today. History Pre-modern citterns The cittern is one of the few metal-strung instruments known from the Renaissance period. It generally has four courses (single, pairs or threes) of strings, one or more courses being usually tuned in octaves, though instruments with more or fewer courses were made. The cittern may have a range of only an octave between its lowest and highest strings and employs a re-entrant tuning – a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritone
In music theory, the tritone is defined as a musical interval composed of three adjacent whole tones (six semitones). For instance, the interval from F up to the B above it (in short, F–B) is a tritone as it can be decomposed into the three adjacent whole tones F–G, G–A, and A–B. Narrowly defined, each of these whole tones must be a step in the scale, so by this definition, within a diatonic scale there is only one tritone for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned interval F–B is the only tritone formed from the notes of the C major scale. More broadly, a tritone is also commonly defined as any interval with a width of three whole tones (spanning six semitones in the chromatic scale), regardless of scale degrees. According to this definition, a diatonic scale contains two tritones for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned C major scale contains the tritones F–B (from F to the B above it, also called augmented fourth) and B–F (from B to the F above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Augmented-fourths Tuning
Among alternative tunings for guitar, each augmented-fourths tuning is a regular tuning in which the musical intervals between successive open-string notes are each '' augmented fourths''. Because augmented fourths are alternatively called " tritones" ("tri-tones") or " diminished fifths", augmented-fourths tuning is also called tritone tuning or diminished-fifths tuning. The standard guitar-tuning :E-A-d-g-b'-e' interjects exactly one major third amid four perfect fourths for the intervals between its successive open strings. In contrast, the augmented fourths tunings :C-F-c-f-c'-f ' and :B-F-b-f-b'-f' have only augmented-fourths intervals. The set of augmented-fourths tunings has three properties that simplify learning by beginners and improvisation by experts: Regular intervals, string repetition, and lefty-righty symmetry. These properties characterize augmented-fourths tunings among non-trivial tunings. Properties The set of augmented-fourths t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Tuning
Among alternative guitar-tunings, regular tunings have equal musical intervals between the paired notes of their successive open strings. ''Guitar tunings'' assign pitches to the open strings of guitars. Tunings can be described by the particular pitches that are denoted by notes in Western music. By convention, the notes are ordered from lowest to highest. The ''standard tuning'' defines the string pitches as E, A, D, G, B, and E. Between the open-strings of the standard tuning are three perfect-fourths (E–A, A–D, D–G), then the major third G–B, and the fourth perfect-fourth B–E. In contrast, regular tunings have constant intervals between their successive open-strings: * 3 semitones (minor third): Minor-thirds, or ''Diminished'' tuning * 4 semitones (major third): Major-thirds or ''Augmented'' tuning, * 5 semitones (perfect fourth): All-fourths tuning, * 6 semitones (augmented fourth, tritone, or diminished fifth): Augmented-fourth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unison
In music, unison is two or more musical parts that sound either the same pitch or pitches separated by intervals of one or more octaves, usually at the same time. ''Rhythmic unison'' is another term for homorhythm. Definition Unison or perfect unison (also called a prime, or perfect prime)Benward & Saker (2003), p. 53. may refer to the (pseudo-) interval formed by a tone and its duplication (in German, ''Unisono'', ''Einklang'', or ''Prime''), for example C–C, as differentiated from the second, C–D, etc. In the unison the two pitches have the ratio of 1:1 or 0 half steps and zero cents. Although two tones in unison are considered to be the same pitch, they are still perceivable as coming from separate sources, whether played on instruments of a different type: ; or of the same type: . This is because a pair of tones in unison come from different locations or can have different "colors" (timbres), i.e. come from different musical instruments or human voices. Voices w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostrich Guitar
The ostrich guitar or ostrich tuning is a type of trivial tuning. It assigns one note to all strings, e.g. E-E-e-e-e'-e' or D-D-D-D-d'-d'. The term "ostrich guitar" was coined by the Velvet Underground's Lou Reed after the pre-Velvet Underground song "The Ostrich" by Lou Reed and the Primitives, on which he first recorded using this tuning, the first known commercial composition to make use of a trivial guitar tuning. Musical theory The trivial tuning is a regular tuning based on the unison musical interval, which has zero semitones. It assigns exactly one pitch class (for example D, A, F or B) to all guitar-strings, tuned to the same note over two or three octaves. This creates an intense, chorused drone music, and interesting fingering potential. Among alternative tunings for the guitar, the trivial tuning is a regular and repetitive tuning. It is its own left-handed tuning.: Example To create a trivial D tuning from a standard guitar tuning: 1d ----- * downtuned to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tritone In The Chromatic Circle
In music theory, the tritone is defined as a musical interval composed of three adjacent whole tones (six semitones). For instance, the interval from F up to the B above it (in short, F–B) is a tritone as it can be decomposed into the three adjacent whole tones F–G, G–A, and A–B. Narrowly defined, each of these whole tones must be a step in the scale, so by this definition, within a diatonic scale there is only one tritone for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned interval F–B is the only tritone formed from the notes of the C major scale. More broadly, a tritone is also commonly defined as any interval with a width of three whole tones (spanning six semitones in the chromatic scale), regardless of scale degrees. According to this definition, a diatonic scale contains two tritones for each octave. For instance, the above-mentioned C major scale contains the tritones F–B (from F to the B above it, also called augmented fourth) and B–F (from B to the F above ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |