|
Rear-inflow Jet
The rear-inflow jet is a component of bow echoes in a mesoscale convective system that aids in creating a stronger cold pool and downdraft. The jet forms as a response to a convective circulation having upshear tilt and horizontal pressure gradients. The cold pool that comes from the outflow of a storm forms an area of high pressure at the surface. In response to the surface high and warmer temperatures aloft due to convection, a mid-level mesolow forms behind the leading edge of the storm. With a mid-level area of low pressure, air is drawn in under the trailing stratiform region of precipitation. As air is drawn in on the rear side of the storm, it begins to descend as it approaches the front line of the cells. Before reaching the leading edge, the jet descends to the surface as a strong downdraft, creating straight-line winds. Any mature mesoscale convective system is capable of developing its own rear-inflow jet, but questions remain as to what influences the strength of the j ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligne De Grain
The ''ligne'' ( ), or line or Paris line, is a historic unit of length used in France and elsewhere prior to the adoption of the metric system in the late 18th century, and used in various sciences after that time. The ''loi du 19 frimaire an VIII'' (Law of 10 December 1799) states that one metre is equal to exactly 443.296 French lines. It is vestigially retained today by French and Swiss watchmakers to measure the size of watch casings, in button making and in ribbon manufacture. Current use Watchmaking There are 12 ''lignes'' to one French inch (''pouce''). The standardized conversion for a ligne is 2.2558291 mm (1 mm = 0.443296 ''ligne''), and it is abbreviated with the letter L or represented by the triple prime, . One ligne is the equivalent of 0.0888 international inch. This is comparable in size to the British measurement called " line" (one-twelfth of an English inch), used prior to 1824. (The French inch at that time was slightly larger t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Melting
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which increases the substance's temperature to the melting point. At the melting point, the ordering of ions or molecules in the solid breaks down to a less ordered state, and the solid "melts" to become a liquid. Substances in the molten state generally have reduced viscosity as the temperature increases. An exception to this principle is the element sulfur, whose viscosity increases in the range of 160 °C to 180 °C due to polymerization. Some organic compounds melt through mesophases, states of partial order between solid and liquid. First order phase transition From a thermodynamics point of view, at the melting point the change in Gibbs free energy ''∆G'' of the substances is zero, but there are non-zero changes in the entha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesovortex
A mesovortex is a small-scale rotational feature found in a convective storm, such as a quasi-linear convective system (QLCS, i.e. squall line), a supercell, or the eyewall of a tropical cyclone. Mesovortices range in diameter from tens of miles to a mile or less and can be immensely intense. Eyewall mesovortex An ''eyewall mesovortex'' is a small-scale rotational feature found in an eyewall of an intense tropical cyclone. Eyewall mesovortices are similar, in principle, to small "suction vortices" often observed in multiple-vortex tornadoes. In these vortices, wind speed can be up to 10% higher than in the rest of the eyewall. Eyewall mesovortices are most common during periods of intensification in tropical cyclones. Eyewall mesovortices often exhibit unusual behavior in tropical cyclones. They usually revolve around the low pressure center, but sometimes they remain stationary. Eyewall mesovortices have even been documented to cross the eye of a storm. These phenomena have b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
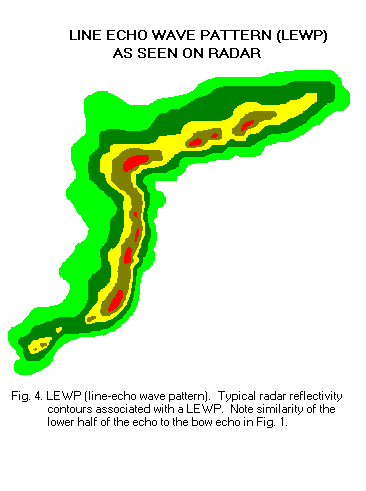
Line Echo Wave Pattern
A line echo wave pattern (LEWP) is a weather radar formation in which a single line of thunderstorms presenting multiple bow echoes forms south (or equatorward) of a mesoscale low-pressure area with a rotating "head". LEWP often are associated with a multiple-bow serial derecho and often produce tornadoes, some of which can be strong. The existence of a LEWP on radar means that a serial derecho has developed or is likely to develop soon, much as a hook echo indicates the same for a tornado. Formation A LEWP, according to the NWS, is defined as "a squall line that has developed into a wave-like pattern due to acceleration at one end of the line and deceleration along the portion immediately adjacent." A LEWP is an extension of the concept of the bow echo, which usually indicates a powerful convective windstorm. Areas hit by the apices of bows often see the worst weather, with the highest winds and very heavy rain. However, if the sides of the bows reach enough of an orientati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derecho
A ''derecho'' (, from es, derecho, link=no , 'straight') is a widespread, long-lived, straight-line wind storm that is associated with a fast-moving group of severe thunderstorms known as a mesoscale convective system. Derechos can cause hurricanic and tornadic-force winds, heavy rains, and flash floods. In many cases, convection-induced winds take on a bow echo (backward "C") form of squall line, often forming beneath an area of diverging upper tropospheric winds, and in a region of both rich low-level moisture and warm-air advection. Derechos move rapidly in the direction of movement of their associated storms, similar to an outflow boundary (gust front), except that the wind remains sustained for a greater period of time (often increasing in strength after onset), and may exceed hurricane-force. A derecho-producing convective system may remain active for many hours and, occasionally, over multiple days. A warm-weather phenomenon, derechos occur mostly in summer, especial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convective Storm Detection
Convective storm detection is the meteorological observation, and short-term prediction, of deep moist convection (DMC). DMC describes atmospheric conditions producing single or clusters of large vertical extension clouds ranging from cumulus congestus to cumulonimbus, the latter producing thunderstorms associated with lightning and thunder. Those two types of clouds can produce severe weather at the surface and aloft. The ability to discern the presence of deep moist convection in a storm significantly improves meteorologists' capacity to predict and monitor associated phenomena such as tornadoes, large hail, strong winds, and heavy rain leading to flash flooding. It relies on direct eyewitness observations, for example from storm spotters; and on remote sensing, especially weather radar. Some in situ measurements are used for direct detection as well, notably, wind speed reports from surface observation stations. It is part of the ''integrated warning system'', consisting of p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vortex
In fluid dynamics, a vortex ( : vortices or vortexes) is a region in a fluid in which the flow revolves around an axis line, which may be straight or curved. Vortices form in stirred fluids, and may be observed in smoke rings, whirlpools in the wake of a boat, and the winds surrounding a tropical cyclone, tornado or dust devil. Vortices are a major component of turbulent flow. The distribution of velocity, vorticity (the curl of the flow velocity), as well as the concept of circulation are used to characterise vortices. In most vortices, the fluid flow velocity is greatest next to its axis and decreases in inverse proportion to the distance from the axis. In the absence of external forces, viscous friction within the fluid tends to organise the flow into a collection of irrotational vortices, possibly superimposed to larger-scale flows, including larger-scale vortices. Once formed, vortices can move, stretch, twist, and interact in complex ways. A moving vortex ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when humidity affects rate of evaporation of water. When the molecules of the liquid collide, they transfer energy to each other based on how they collide. When a molecule near the surface absorbs enough energy to overcome the vapor pressure, it will escape and enter the surrounding air as a gas. When evaporation occurs, the energy removed from the vaporized liquid will reduce the temperature of the liquid, resulting in evaporative cooling. On average, only a fraction of the molecules in a liquid have enough heat energy to escape from the liquid. The evaporation will continue until an equilibrium is reached when the evaporation of the liquid is equal to its condensation. In an enclosed environment, a liquid will evaporate until the surrounding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sublimation (phase Transition)
Sublimation is the transition of a substance directly from the solid to the gas state, without passing through the liquid state. Sublimation is an endothermic process that occurs at temperatures and pressures below a substance's triple point in its phase diagram, which corresponds to the lowest pressure at which the substance can exist as a liquid. The reverse process of sublimation is deposition or desublimation, in which a substance passes directly from a gas to a solid phase. Sublimation has also been used as a generic term to describe a solid-to-gas transition (sublimation) followed by a gas-to-solid transition (deposition). While vaporization from liquid to gas occurs as evaporation from the surface if it occurs below the boiling point of the liquid, and as boiling with formation of bubbles in the interior of the liquid if it occurs at the boiling point, there is no such distinction for the solid-to-gas transition which always occurs as sublimation from the surface. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bow Echo
A bow echo is the characteristic radar return from a mesoscale convective system that is shaped like an archer's bow. These systems can produce severe straight-line winds and occasionally tornadoes, causing major damage. They can also become derechos or form Line echo wave pattern (LEWP). Research The term "bow echo" was first used by Theodore Fujita in his May 1978 paper "Manual of Downburst Identification for Project NIMROD." In 2004, research was done to better anticipate the formation of bow echoes, specifically the formation of bow echoes from weakly organized squall lines and supercells. Researchers determined that bow echoes were most likely to occur in weakly organized cells. A Midwest Bow Echo Workshop was held in 2007, at which meteorologists gathered to share their research to better understand bow echoes. Formation A bow echo is associated with squall lines or lines of convective thunderstorms. These echoes can range in size from 20 to 200 km, and have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_eye_close-up.jpg)