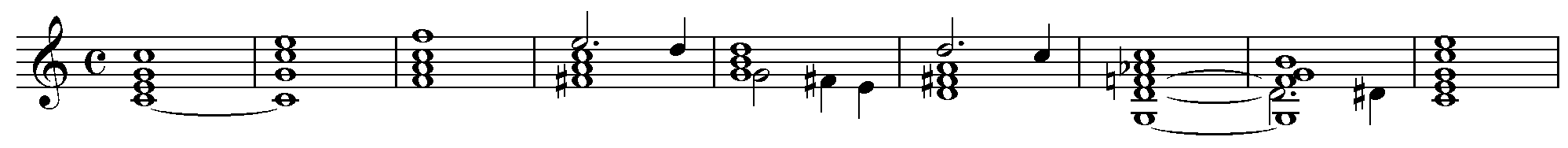|
Reaching Over
Schenkerian analysis is a method of analyzing tonal music based on the theories of Heinrich Schenker (1868–1935). The goal is to demonstrate the organic coherence of the work by showing how it relates to an abstracted deep structure, the ''Ursatz''. This primal structure is roughly the same for any tonal work, but a Schenkerian analysis shows how, in an individual case, that structure develops into a unique work at the "foreground", the level of the score itself. A key theoretical concept is "tonal space". The intervals between the notes of the tonic triad in the background form a ''tonal space'' that is filled with passing and neighbour tones, producing new triads and new tonal spaces that are open for further elaborations until the "surface" of the work (the score) is reached. The analysis uses a specialized symbolic form of musical notation. Although Schenker himself usually presents his analyses in the generative direction, starting from the fundamental structure (''Ursatz'') t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Analysis
Musical analysis is the study of musical structure in either compositions or performances. According to music theorist Ian Bent, music analysis "is the means of answering directly the question 'How does it work?'". The method employed to answer this question, and indeed exactly what is meant by the question, differs from analyst to analyst, and according to the purpose of the analysis. According to Bent, "its emergence as an approach and method can be traced back to the 1750s. However it existed as a scholarly tool, albeit an auxiliary one, from the Middle Ages onwards." The principle of analysis has been variously criticized, especially by composers, such as Edgard Varèse's claim that, "to explain by means of nalysisis to decompose, to mutilate the spirit of a work". Analyses Some analysts, such as Donald Tovey (whose '' Essays in Musical Analysis'' are among the most accessible musical analyses) have presented their analyses in prose. Others, such as Hans Keller (who devised ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Max Reger
Johann Baptist Joseph Maximilian Reger (19 March 187311 May 1916) was a German composer, pianist, organist, conductor, and academic teacher. He worked as a concert pianist, as a musical director at the Paulinerkirche, Leipzig, Leipzig University Church, as a professor at the Leipzig Conservatory, Royal Conservatory in Leipzig, and as a music director at the court of Duke Georg II of Saxe-Meiningen. Reger first composed mainly ''Lieder'', chamber music, choral music and works for piano and organ. He later turned to orchestral compositions, such as the popular ''Variations and Fugue on a Theme by Mozart'' (1914), and to works for choir and orchestra such as ''Gesang der Verklärten'' (1903), ' (1909), ''Der Einsiedler'' and the ''Requiem (Reger), Hebbel Requiem'' (both 1915). Biography Born in Brand, Bavaria, Brand, Kingdom of Bavaria, Bavaria, Reger was the first child of Josef Reger, a school teacher and amateur musician, and his wife Katharina Philomena. The devout Catholic fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The New Grove Dictionary Of Music And Musicians
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language ''Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and theory of music. Earlier editions were published under the titles ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', and ''Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians''; the work has gone through several editions since the 19th century and is widely used. In recent years it has been made available as an electronic resource called ''Grove Music Online'', which is now an important part of ''Oxford Music Online''. ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' was first published in London by Macmillan and Co. in four volumes (1879, 1880, 1883, 1889) edited by George Grove with an Appendix edited by J. A. Fuller Maitland in the fourth volume. An Index edited by Mrs. E. Wodehouse was issued as a separate volume in 1890. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Tone
In Schenkerian analysis, the primary tone or head tone (german: Kopfton) is the starting tone of the fundamental line In Schenkerian analysis, the fundamental structure (german: Ursatz) describes the structure of a tonal work as it occurs at the most remote (or "background") level and in the most abstract form. A basic elaboration of the tonic triad, it cons .... The fundamental line itself originates as an arpeggiation of the tonic chord, filled by passing tones: :In accordance with the arpeggiation from which it stems, the fundamental line exhibits the space of a third, fifth, or octave. These spaces are filled by passing tones. The primary tone therefore necessarily is one of the higher tones of the tonic chord, , or . The fundamental line descends from its primary tone to the tonic, : :To man is given the experience of ending, the cessation of all tensions and efforts. In this sense, we feel by nature that the fundamental line must lead downward until it reaches , and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Schenkerian Ursatz
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schenkerian Analysis
Schenkerian analysis is a method of analyzing tonal music based on the theories of Heinrich Schenker (1868–1935). The goal is to demonstrate the organic coherence of the work by showing how it relates to an abstracted deep structure, the ''Ursatz''. This primal structure is roughly the same for any tonal work, but a Schenkerian analysis shows how, in an individual case, that structure develops into a unique work at the "foreground", the level of the score itself. A key theoretical concept is "tonal space". The intervals between the notes of the tonic triad in the background form a ''tonal space'' that is filled with passing and neighbour tones, producing new triads and new tonal spaces that are open for further elaborations until the "surface" of the work (the score) is reached. The analysis uses a specialized symbolic form of musical notation. Although Schenker himself usually presents his analyses in the generative direction, starting from the fundamental structure (''Ursatz'') t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Progression
In music, a linear progression (''Auskomponierungszug'' or ''Zug'', abbreviated: ''Zg.'') is a passing note elaboration involving stepwise melodic motion in one direction between two harmonic tones. "The compositional unfolding of a specific interval, one of the intervals of the chord of nature."Jonas, Oswald (1982). ''Introduction to the Theory of Heinrich Schenker'', p.62. (1934: ''Das Wesen des musikalischen Kunstwerks: Eine Einführung in Die Lehre Heinrich Schenkers''). Trans. John Rothgeb. . The mention of the "chord of nature" in this context reflects Jonas' own opinion, which Schenker would not have shared, if only because the minor chord cannot be a "chord of nature". See Klang (music). For example: -- over the tonic. According to Schenker: "A linear progression always presupposes a passing note; there can be no linear progression without a passing note, no passing note without a linear progression." In German ''Zug'' may be combined with prefixes to create related word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luigi Cherubini
Luigi Cherubini ( ; ; 8 or 14 SeptemberWillis, in Sadie (Ed.), p. 833 1760 – 15 March 1842) was an Italian Classical and Romantic composer. His most significant compositions are operas and sacred music. Beethoven regarded Cherubini as the greatest of his contemporaries. His operas were heavily praised and interpreted by Rossini. Early years Cherubini was born Maria Luigi Carlo Zenobio Salvatore Cherubini in Florence in 1760. There is uncertainty about his exact date of birth. Although 14 September is sometimes stated, evidence from baptismal records and Cherubini himself suggests the 8th is correct. Perhaps the strongest evidence is his first name, Maria, which is traditional for a child born on 8 September, the feast-day of the Nativity of the Virgin. His instruction in music began at the age of six with his father, Bartolomeo, '' maestro al cembalo'' ("Master of the harpsichord", in other words, ensemble leader from the harpsichord). Considered a child prodigy, Cherubini st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anton Bruckner
Josef Anton Bruckner (; 4 September 182411 October 1896) was an Austrian composer, organist, and music theorist best known for his symphonies, masses, Te Deum and motets. The first are considered emblematic of the final stage of Austro-German Romanticism because of their rich harmonic language, strongly polyphonic character, and considerable length. Bruckner's compositions helped to define contemporary musical radicalism, owing to their dissonances, unprepared modulations, and roving harmonies. Unlike other musical radicals such as Richard Wagner and Hugo Wolf, Bruckner showed extreme humility before other musicians, Wagner in particular. This apparent dichotomy between Bruckner the man and Bruckner the composer hampers efforts to describe his life in a way that gives a straightforward context for his music. Hans von Bülow described him as "half genius, half simpleton". Bruckner was critical of his own work and often reworked his compositions. There are several version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon Sechter
Simon Sechter (11 October 1788 – 10 September 1867) was an Austrian music theorist, teacher, organist, conductor and composer. He was one of the most prolific composers who ever lived, although his music is largely forgotten and he is now mainly remembered as a strict music teacher, most notably of Anton Bruckner. Carl Christian Müller (18311914) compiled and adapted Sechter's ''Die richtige Folge der Grundharmonien'' as ''The Correct Order of Fundamental Harmonies: A Treatise on Fundamental Basses, and their Inversions and Substitutes'' (Wm. A. Pond, 1871; G. Schirmer, 1898). Biography Sechter was born in Friedberg (Frymburk), Bohemia, then part of the Austrian Empire, and moved to Vienna in 1804, succeeding Jan Václav Voříšek as court organist there in 1824. In 1810 he began teaching piano and voice at an academy for blind students. In 1828 the ailing Franz Schubert had one counterpoint lesson with him. In 1851 Sechter was appointed professor of composition at the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gottfried Weber
Jacob Gottfried Weber (March 1, 1779 – September 21, 1839) was a prominent German writer on music (especially on music theory), composer, and jurist. Biography Weber was born at Freinsheim. From 1824 to 1839, he was the editor of ''Cäcilia'', a musical periodical published in Mainz, which influenced musical thought in Germany during the early Romantic era. His most important work is his ''Versuch einer geordneten Theorie der Tonsetzkunst'' ("Theory of Musical Composition") (Mainz: B. Schott, 1817–21), which introduced several concepts that have since become important in the study of music theory. In this work, Weber develops the idea of "Mehrdeutigkeit" (that is, "multiple meaning"), a term initially introduced by Georg Joseph Vogler. Weber's "multiple meaning" refers to individual tones and harmonies, based on their context in a piece of music. For example, a C major triad may serve as I in C major, IV in G major, V in F major, etc. "To analyze a chord, a theorist must ask ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georg Joseph Vogler
Abbé Vogler Georg Joseph Vogler, also known as Abbé Vogler (June 15, 1749 – May 6, 1814), was a German composer, organist, teacher and theorist. In a long and colorful career extending over many more nations and decades than was usual at the time, Vogler established himself as a foremost experimenter in baroque and early classic music. His greatest successes came as performer and designer for the organ at various courts and cities around Europe, as well as a teacher, attracting highly successful and devoted pupils such as Carl Maria von Weber. His career as a music theorist and composer however was mixed, with contemporaries such as Mozart believing Vogler to have been a charlatan. Despite his mixed reception in his own life, his highly original contributions in many areas of music (particularly musicology and organ theory) and influence on his pupils endured, and combined with his eccentric and adventurous career, prompted one historian to summarize Vogler as "one of the most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)