|
Radio Access Technology
A Radio Access Technology or (RAT) is the underlying physical connection method for a radio based communication network. Many modern mobile phones support several RATs in one device such as Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and GSM, UMTS, LTE or 5G NR. The term RAT was traditionally used in mobile communication network interoperability, for example, in Virtej et al., or in the example provided on the Wiki page for radio access network. More recently, the term RAT is used in discussions of heterogeneous wireless networks. The term is used when a user device selects between the type of RAT being used to connect to the Internet. This is often performed similar to access point selection in IEEE 802.11 (Wi-Fi) based networks. Inter-RAT (IRAT) handover A mobile terminal, while connected using a RAT, performs neighbour cell measurements and sends measurement report to the network. Based on this measurement report provided by the mobile terminal, the network can initiate handover from one RAT to anoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is limited to 2.5 milliwatts, giving it a very short range of up to . It employs UHF radio waves in the ISM bands, from 2.402GHz to 2.48GHz. It is mainly used as an alternative to wire connections, to exchange files between nearby portable devices and connect cell phones and music players with wireless headphones. Bluetooth is managed by the Bluetooth Special Interest Group (SIG), which has more than 35,000 member companies in the areas of telecommunication, computing, networking, and consumer electronics. The IEEE standardized Bluetooth as IEEE 802.15.1, but no longer maintains the standard. The Bluetooth SIG oversees development of the specification, manages the qualification program, and protects the trademarks. A manufacturer must meet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi () is a family of wireless network protocols, based on the IEEE 802.11 family of standards, which are commonly used for local area networking of devices and Internet access, allowing nearby digital devices to exchange data by radio waves. These are the most widely used computer networks in the world, used globally in home and small office networks to link desktop and laptop computers, tablet computers, smartphones, smart TVs, printers, and smart speakers together and to a wireless router to connect them to the Internet, and in wireless access points in public places like coffee shops, hotels, libraries and airports to provide visitors with Internet access for their mobile devices. ''Wi-Fi'' is a trademark of the non-profit Wi-Fi Alliance, which restricts the use of the term ''Wi-Fi Certified'' to products that successfully complete interoperability certification testing. the Wi-Fi Alliance consisted of more than 800 companies from around the world. over 3.05 billion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
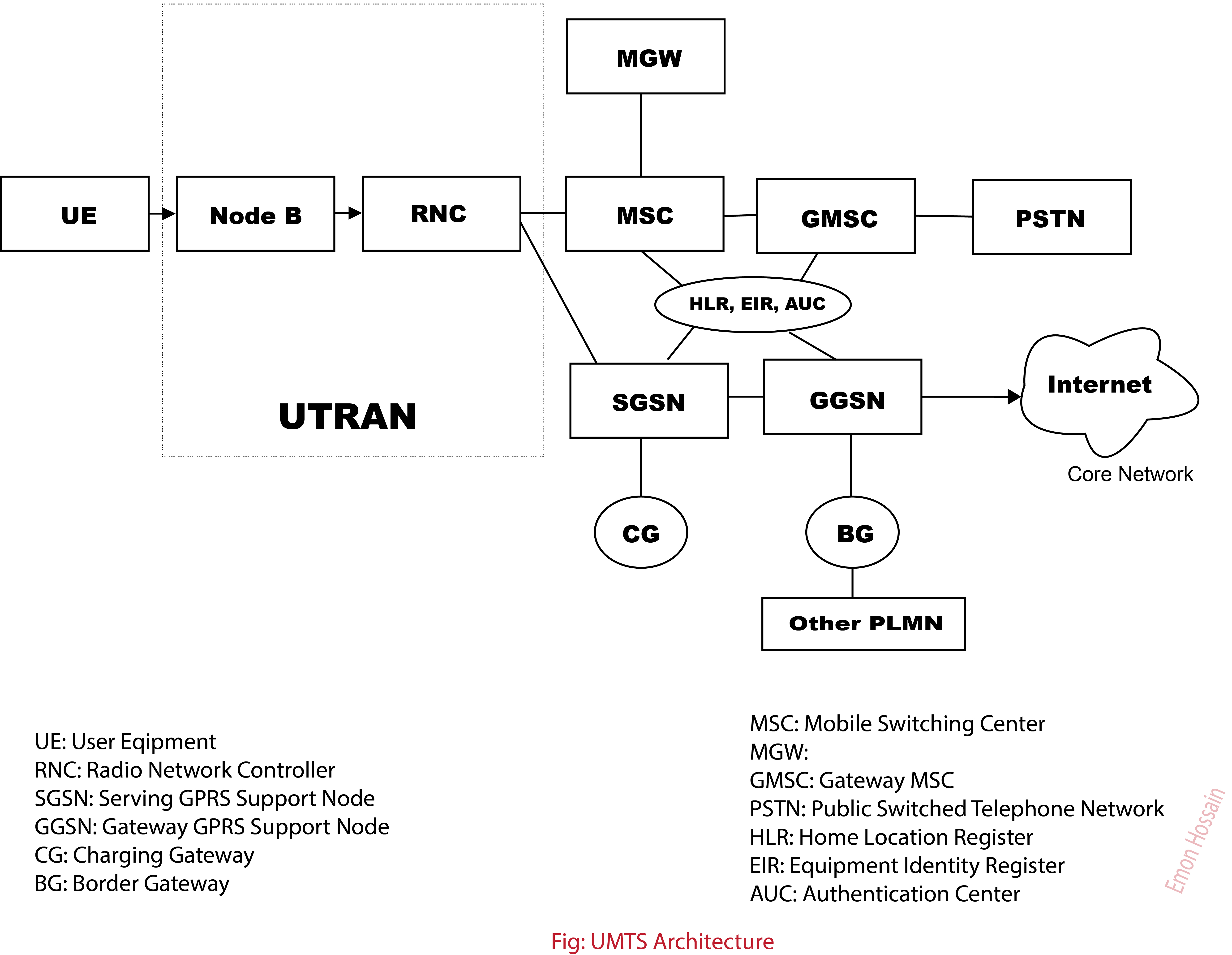
UMTS
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators. UMTS specifies a complete network system, which includes the radio access network (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network, or UTRAN), the core network (Mobile Application Part, or MAP) and the authentication of users via SIM (subscriber identity module) cards. The technology described in UMTS is sometimes also referred to as Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access (FOMA) or 3GSM. Unlike EDGE (IMT Single-Carrier, based on GSM) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LTE (telecommunication)
In telecommunications, long-term evolution (LTE) is a standard for wireless broadband communication for mobile devices and data terminals, based on the GSM/EDGE and UMTS/HSPA standards. It improves on those standards' capacity and speed by using a different radio interface and core network improvements. LTE is the upgrade path for carriers with both GSM/UMTS networks and CDMA2000 networks. Because LTE frequencies and bands differ from country to country, only multi-band phones can use LTE in all countries where it is supported. The standard is developed by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) and is specified in its Release 8 document series, with minor enhancements described in Release 9. LTE is also called 3.95G and has been marketed as "4G LTE" and "Advanced 4G"; but it does not meet the technical criteria of a 4G wireless service, as specified in the 3GPP Release 8 and 9 document series for LTE Advanced. The requirements were set forth by the ITU-R organisation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5G NR
5G NR (New Radio) is a new radio access technology (RAT) developed by 3GPP for the 5G (fifth generation) mobile network. It was designed to be the global standard for the air interface of 5G networks. As with 4G (LTE), it is based on OFDM. The 3GPP specification 38 series provides the technical details behind 5G NR, the successor of LTE. The study of NR within 3GPP started in 2015, and the first specification was made available by the end of 2017. While the 3GPP standardization process was ongoing, the industry had already begun efforts to implement infrastructure compliant with the draft standard, with the first large-scale commercial launch of 5G NR having occurred in the end of 2018. Since 2019, many operators have deployed 5G NR networks and handset manufacturers have developed 5G NR enabled handsets. Frequency bands 5G NR uses frequency bands in two frequency ranges: # Frequency Range 1 (FR1), for bands within 410 MHz – 7125 MHz # Frequency Range 2 (FR2), for bands ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radio Access Network
A radio access network (RAN) is part of a mobile telecommunication system. It implements a radio access technology. Conceptually, it resides between a device such as a mobile phone, a computer, or any remotely controlled machine and provides connection with its core network (CN). Depending on the standard, mobile phones and other wireless connected devices are varyingly known as user equipment (UE), terminal equipment, mobile station (MS), etc. RAN functionality is typically provided by a silicon chip residing in both the core network as well as the user equipment. See the following diagram: CN / ⧵ / ⧵ RAN RAN / ⧵ / ⧵ UE UE UE UE Examples of radio access network types are: * GRAN: GSM radio access network * GERAN: essentially the same as GRAN but specifying the inclusion of EDGE packet radio services * UTRAN: UMTS radio access network * E-UTRAN: The Long Term Evolution (LTE) high speed and low latency radio access network It is also possible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous Wireless Networks
In computer networking, a heterogeneous network is a network connecting computers and other devices where the operating systems and protocols have significant differences. For example, local area networks (LANs) that connect Microsoft Windows and Linux based personal computers with Apple Macintosh computers are heterogeneous. ''Heterogeneous network'' also describes wireless networks using different access technologies. For example, a wireless network that provides a service through a wireless LAN and is able to maintain the service when switching to a cellular network is called a wireless heterogeneous network. HetNet Reference to a HetNet often indicates the use of multiple types of access nodes in a wireless network. A Wide Area Network can use some combination of macrocells, picocells, and femtocells in order to offer wireless coverage in an environment with a wide variety of wireless coverage zones, ranging from an open outdoor environment to office buildings, homes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IEEE 802
IEEE 802 is a family of Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) standards for local area networks (LAN), personal area network (PAN), and metropolitan area networks (MAN). The IEEE 802 LAN/MAN Standards Committee (LMSC) maintains these standards. The IEEE 802 family of standards has had twenty-four members, numbered 802.1 through 802.24, with a working group of the LMSC devoted to each. However, not all of these working groups are currently active. The IEEE 802 standards are restricted to computer networks carrying variable-size packets, unlike cell relay networks, for example, in which data is transmitted in short, uniformly sized units called cells. Isochronous signal networks, in which data is transmitted as a steady stream of octets, or groups of octets, at regular time intervals, are also outside the scope of the IEEE 802 standards. The number 802 has no significance: it was simply the next number in the sequence that the IEEE used for standards projects. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handover
In cellular telecommunications, handover, or handoff, is the process of transferring an ongoing call or data session from one channel connected to the core network to another channel. In satellite communications it is the process of transferring satellite control responsibility from one earth station to another without loss or interruption of service. Terminology American English uses the term ''handoff'', and this is most commonly used within some American organizations such as 3GPP2 and in American originated technologies such as CDMA2000. In British English the term ''handover'' is more common, and is used within international and European organisations such as ITU-T, IETF, ETSI and 3GPP, and standardised within European originated standards such as GSM and UMTS. The term handover is more common in academic research publications and literature, while handoff is slightly more common within the IEEE and ANSI organisations. Purpose In telecommunications there may be diffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WCDMA
The Universal Mobile Telecommunications System (UMTS) is a third generation mobile cellular system for networks based on the GSM standard. Developed and maintained by the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), UMTS is a component of the International Telecommunication Union IMT-2000 standard set and compares with the CDMA2000 standard set for networks based on the competing cdmaOne technology. UMTS uses wideband code-division multiple access (W-CDMA) radio access technology to offer greater spectral efficiency and bandwidth to mobile network operators. UMTS specifies a complete network system, which includes the radio access network (UMTS Terrestrial Radio Access Network, or UTRAN), the core network (Mobile Application Part, or MAP) and the authentication of users via SIM (subscriber identity module) cards. The technology described in UMTS is sometimes also referred to as Freedom of Mobile Multimedia Access (FOMA) or 3GSM. Unlike EDGE (IMT Single-Carrier, based on GSM) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |