|
Question
A question is an utterance which serves as a request for information. Questions are sometimes distinguished from interrogatives, which are the grammar, grammatical forms, typically used to express them. Rhetorical questions, for instance, are interrogative in form but may not be considered wiktionary:bona fide, bona fide questions, as they are not expected to be answered. Questions come in a number of varieties. For instance; ''Polar questions'' are those such as the English language, English example "Is this a polar question?", which can be answered with yes and no, "yes" or "no". ''Alternative questions'' such as "Is this a polar question, or an alternative question?" present a list of possibilities to choose from. ''Open-ended question, Open questions'' such as "What kind of question is this?" allow many possible resolutions. Questions are widely studied in linguistics and philosophy of language. In the subfield of pragmatics, questions are regarded as illocutionary acts whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
A Question Of Honor (1922) - 7
Question of Honor may refer to: * ''A Question of Honor'' (1915 film), an American short film directed by B. Reeves Eason * ''A Question of Honor'' (1922 film), an American romance film directed by Edwin Carewe * ''A Question of Honour'' (film), English title of the 1965 Italian comedy-drama film ''Una questione d'onore'' directed by Luigi Zampa * ''A Question of Honor'' (1982 film), TV film directed by Jud Taylor Judson Taylor (February 25, 1932August 6, 2008) was an American actor, television director, and television producer. Early years Born in New York City, Taylor graduated from the University of California, Berkeley. Career Taylor is perhaps best ... * "A Question of Honour" (song), a 1995 single by Sarah Brightman from her album ''Fly'' {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Question
In linguistics, a yes–no question, also known as a binary question, a polar question, or a general question, is a closed-ended question whose expected answer is one of two choices, one that provides an affirmative answer to the question versus one that provides a negative answer to the question. Typically, the choices are either "yes" or "no" in English. Yes–no questions present an exclusive disjunction, namely a pair of alternatives of which only one is a felicitous answer. In English, such questions can be formed in both positive and negative forms: * positive yes/no question: "Will you be here tomorrow?" * negative yes/no question: "Won't you be here tomorrow?" Yes–no questions are in contrast with non-polar wh-questions. The latter are also called content questions, and are formed with the five Ws plus an H ("who", "what", "where", "when", "why", "how"). Rather than restricting the range of possible answers to two alternatives, content questions are compatible with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interrogative
An interrogative clause is a clause whose form is typically associated with question-like meanings. For instance, the English sentence (linguistics), sentence "Is Hannah sick?" has interrogative syntax which distinguishes it from its Declarative sentence, declarative counterpart "Hannah is sick". Also, the additional question mark closing the statement assures that the reader is informed of the interrogative mood. Interrogative clauses may sometimes be embedded within a phrase, for example: "Paul knows who is sick", where the interrogative clause "who is sick" serves as complement (linguistics), complement of the embedding verb "know". Languages vary in how they form interrogatives. When a language has a dedicated interrogative inflectional form, it is often referred to as interrogative grammatical mood. Interrogative mood or other interrogative forms may be denoted by the list of glossing abbreviations, glossing abbreviation . Question types Interrogative sentences are generally ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formal Semantics (natural Language)
Formal semantics is the scientific study of linguistic meaning through formal tools from logic and mathematics. It is an interdisciplinary field, sometimes regarded as a subfield of both linguistics and philosophy of language. Formal semanticists rely on diverse methods to analyze natural language. Many examine the meaning of a sentence by studying the circumstances in which it would be true. They describe these circumstances using abstract mathematical models to represent entities and their features. The principle of compositionality helps them link the meaning of expressions to abstract objects in these models. This principle asserts that the meaning of a compound expression is determined by the meanings of its parts. Propositional and predicate logic are formal systems used to analyze the semantic structure of sentences. They introduce concepts like singular terms, predicates, quantifiers, and logical connectives to represent the logical form of natural language expres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open-ended Question
An open-ended question is a question that cannot be answered with a "yes" or "no" response, or with a static response. Open-ended questions are phrased as a statement which requires a longer answer. They can be compared to closed-ended questions which demand a “yes”/“no” or short answer. Examples Examples of open-ended questions include: *Tell me about your relationship with your supervisor. *How do you see your future? *Tell me about the children in this photograph. *What is the purpose of government? *Why did you choose that answer? In education The received wisdom in education is that open questions are broadly speaking 'good' questions. They invite students to give longer responses that demonstrate their understanding. They are preferable to closed questions (i.e. one that demands a yes/no answer) because they are better for discussions or enquiries, whereas closed questions are only good for testing. Peter Worley argues that this is a false assumption. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhetorical Question
A rhetorical question is a question asked for a purpose other than to obtain information. In many cases it may be intended to start a discourse, as a means of displaying or emphasizing the speaker's or author's opinion on a topic. A simple example is the question "Can't you do anything right?" This question is not intended to ask about the listener's competence but rather to insinuate their lack of it. Forms Negative assertions A rhetorical question may be intended as a challenge. The question is often difficult or impossible to answer. In the example, "What have the Romans ever done for us?" (''Monty Python's Life of Brian'') the question functions as a negative assertion. It is intended to mean "The Romans have never done anything for us!" When Shakespeare's Mark Antony exclaims, "Here was a Caesar! When comes such another?" it functions as an assertion that Caesar possesses such rare qualities they may never be seen again. (''Julius Caesar'', Act 3, scene 2, 257) Rhetorical qu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
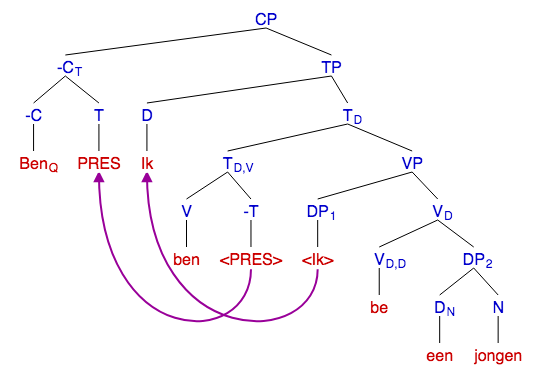
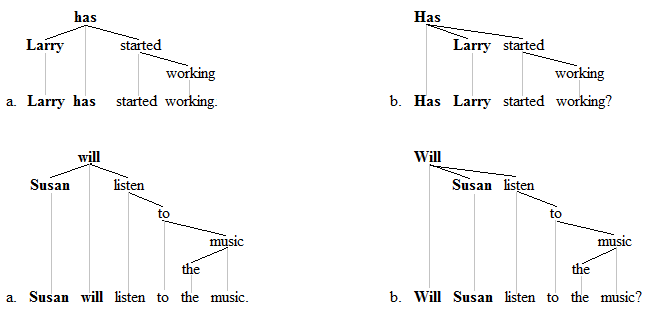
Subject–auxiliary Inversion
Subject–auxiliary inversion (SAI; also called subject–operator inversion) is a frequently occurring type of inversion (linguistics), inversion in the English language whereby a finite auxiliary verb – taken here to include finite forms of the copula (linguistics), copula ''be'' – appears to "invert" (change places) with the subject (grammar), subject. The word order is therefore Aux-S (auxiliary–subject), which is the opposite of the canonical SV (Subject–verb–object word order, subject–verb) order of declarative clauses in English. The most frequent use of subject–auxiliary inversion in English is in the formation of questions, although it also has other uses, including the formation of condition clauses, and in the syntax of sentences beginning with negative expressions (negative inversion). In certain types of English sentences, inversion is also possible with verbs other than auxiliaries; these are described in the article on the subject–verb inversion in En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language that developed in early medieval England and has since become a English as a lingua franca, global lingua franca. The namesake of the language is the Angles (tribe), Angles, one of the Germanic peoples that Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, migrated to Britain after its End of Roman rule in Britain, Roman occupiers left. English is the list of languages by total number of speakers, most spoken language in the world, primarily due to the global influences of the former British Empire (succeeded by the Commonwealth of Nations) and the United States. English is the list of languages by number of native speakers, third-most spoken native language, after Mandarin Chinese and Spanish language, Spanish; it is also the most widely learned second language in the world, with more second-language speakers than native speakers. English is either the official language or one of the official languages in list of countries and territories where English ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yes And No
''Yes'' and ''no'', or similar word pairs, are expressions of the affirmative and the negative, respectively, in several languages, including English. Some languages make a distinction between answers to affirmative versus negative questions and may have three-form or four-form systems. English originally used a four-form system up to and including Early Middle English. Modern English uses a two-form system consisting of ''yes'' and ''no''. It exists in many facets of communication, such as: eye blink communication, head movements, Morse code, and sign language. Some languages, such as Latin, do not have yes-no word systems. Answering a "yes or no" question with single words meaning ''yes'' or ''no'' is by no means universal. About half the world's languages typically employ an echo response: repeating the verb in the question in an affirmative or a negative form. Some of these also have optional words for ''yes'' and ''no'', like Hungarian, Russian, and Portuguese. Ot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alternative Semantics
Alternative semantics (or Hamblin semantics) is a framework in formal semantics and logic. In alternative semantics, expressions denote ''alternative sets'', understood as sets of objects of the same semantic type. For instance, while the word "Lena" might denote Lena herself in a classical semantics, it would denote the singleton set containing Lena in alternative semantics. The framework was introduced by Charles Leonard Hamblin in 1973 as a way of extending Montague grammar to provide an analysis for questions. In this framework, a question denotes the set of its possible answers. Thus, if P and Q are propositions, then \ is the denotation of the question whether P or Q is true. Since the 1970s, it has been extended and adapted to analyze phenomena including focus, scope, disjunction In logic, disjunction (also known as logical disjunction, logical or, logical addition, or inclusive disjunction) is a logical connective typically notated as \lor and read aloud as "o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pragmatics
In linguistics and the philosophy of language, pragmatics is the study of how Context (linguistics), context contributes to meaning. The field of study evaluates how human language is utilized in social interactions, as well as the relationship between the interpreter and the interpreted. Linguists who specialize in pragmatics are called pragmaticians. The field has been represented since 1986 by the International Pragmatics Association (IPrA). Pragmatics encompasses phenomena including implicature, speech acts, relevance theory, relevance and Conversation analysis, conversation,Mey, Jacob L. (1993) ''Pragmatics: An Introduction''. Oxford: Blackwell (2nd ed. 2001). as well as nonverbal communication. Theories of pragmatics go hand-in-hand with theories of semantics, which studies aspects of meaning, and syntax, which examines sentence structures, principles, and relationships. The ability to understand another speaker's intended meaning is called ''pragmatic competence''. In 1938 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |