|
Quartic Equation
In mathematics, a quartic equation is one which can be expressed as a ''quartic function'' equaling zero. The general form of a quartic equation is :ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e=0 \, where ''a'' ≠ 0. The quartic is the highest order polynomial equation that can be solved by radicals in the general case. History Lodovico Ferrari is attributed with the discovery of the solution to the quartic in 1540, but since this solution, like all algebraic solutions of the quartic, requires the solution of a cubic to be found, it could not be published immediately. The solution of the quartic was published together with that of the cubic by Ferrari's mentor Gerolamo Cardano in the book '' Ars Magna'' (1545). The proof that this was the highest order general polynomial for which such solutions could be found was first given in the Abel–Ruffini theorem in 1824, proving that all attempts at solving the higher order polynomials would be futile. The notes left by Évariste Galois before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
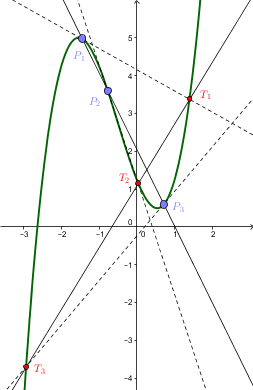
Quartic Function
In algebra, a quartic function is a function (mathematics), function of the form :f(x)=ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e, where ''a'' is nonzero, which is defined by a polynomial of Degree of a polynomial, degree four, called a quartic polynomial. A ''quartic equation'', or equation of the fourth degree, is an equation that equates a quartic polynomial to zero, of the form :ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e=0 , where . The derivative of a quartic function is a cubic function. Sometimes the term biquadratic is used instead of ''quartic'', but, usually, biquadratic function refers to a quadratic function of a square (or, equivalently, to the function defined by a quartic polynomial without terms of odd degree), having the form :f(x)=ax^4+cx^2+e. Since a quartic function is defined by a polynomial of even degree, it has the same infinite limit when the argument goes to positive or negative infinity. If ''a'' is positive, then the function increases to positive infinity at both ends; and thus the function ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biquadratic Equations
In algebra, a quartic function is a function of the form :f(x)=ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e, where ''a'' is nonzero, which is defined by a polynomial of degree four, called a quartic polynomial. A ''quartic equation'', or equation of the fourth degree, is an equation that equates a quartic polynomial to zero, of the form :ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e=0 , where . The derivative of a quartic function is a cubic function. Sometimes the term biquadratic is used instead of ''quartic'', but, usually, biquadratic function refers to a quadratic function of a square (or, equivalently, to the function defined by a quartic polynomial without terms of odd degree), having the form :f(x)=ax^4+cx^2+e. Since a quartic function is defined by a polynomial of even degree, it has the same infinite limit when the argument goes to positive or negative infinity. If ''a'' is positive, then the function increases to positive infinity at both ends; and thus the function has a global minimum. Likewise, if ''a'' is ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartic Equation
In mathematics, a quartic equation is one which can be expressed as a ''quartic function'' equaling zero. The general form of a quartic equation is :ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e=0 \, where ''a'' ≠ 0. The quartic is the highest order polynomial equation that can be solved by radicals in the general case. History Lodovico Ferrari is attributed with the discovery of the solution to the quartic in 1540, but since this solution, like all algebraic solutions of the quartic, requires the solution of a cubic to be found, it could not be published immediately. The solution of the quartic was published together with that of the cubic by Ferrari's mentor Gerolamo Cardano in the book '' Ars Magna'' (1545). The proof that this was the highest order general polynomial for which such solutions could be found was first given in the Abel–Ruffini theorem in 1824, proving that all attempts at solving the higher order polynomials would be futile. The notes left by Évariste Galois before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartic Formula
In algebra, a quartic function is a function of the form :f(x)=ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e, where ''a'' is nonzero, which is defined by a polynomial of degree four, called a quartic polynomial. A ''quartic equation'', or equation of the fourth degree, is an equation that equates a quartic polynomial to zero, of the form :ax^4+bx^3+cx^2+dx+e=0 , where . The derivative of a quartic function is a cubic function. Sometimes the term biquadratic is used instead of ''quartic'', but, usually, biquadratic function refers to a quadratic function of a square (or, equivalently, to the function defined by a quartic polynomial without terms of odd degree), having the form :f(x)=ax^4+cx^2+e. Since a quartic function is defined by a polynomial of even degree, it has the same infinite limit when the argument goes to positive or negative infinity. If ''a'' is positive, then the function increases to positive infinity at both ends; and thus the function has a global minimum. Likewise, if ''a'' is n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is a field of study that discovers and organizes methods, Mathematical theory, theories and theorems that are developed and Mathematical proof, proved for the needs of empirical sciences and mathematics itself. There are many areas of mathematics, which include number theory (the study of numbers), algebra (the study of formulas and related structures), geometry (the study of shapes and spaces that contain them), Mathematical analysis, analysis (the study of continuous changes), and set theory (presently used as a foundation for all mathematics). Mathematics involves the description and manipulation of mathematical object, abstract objects that consist of either abstraction (mathematics), abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicspurely abstract entities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. Mathematics uses pure reason to proof (mathematics), prove properties of objects, a ''proof'' consisting of a succession of applications of in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Möbius Transformation
In geometry and complex analysis, a Möbius transformation of the complex plane is a rational function of the form f(z) = \frac of one complex number, complex variable ; here the coefficients , , , are complex numbers satisfying . Geometrically, a Möbius transformation can be obtained by first applying the inverse stereographic projection from the plane to the unit sphere, moving and rotating the sphere to a new location and orientation in space, and then applying a stereographic projection to map from the sphere back to the plane. These transformations preserve angles, map every straight line to a line or circle, and map every circle to a line or circle. The Möbius transformations are the projective transformations of the complex projective line. They form a group (mathematics), group called the Möbius group, which is the projective linear group . Together with its subgroups, it has numerous applications in mathematics and physics. Möbius geometry, Möbius geometries and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Converting To A Depressed Quartic
Conversion or convert may refer to: Arts, entertainment, and media * ''The Convert'', a 2023 film produced by Jump Film & Television and Brouhaha Entertainment * "Conversion" (''Doctor Who'' audio), an episode of the audio drama ''Cyberman'' * "Conversion" (''Stargate Atlantis''), an episode of the television series ''Stargate Atlantis'' * "The Conversion" (''The Outer Limits''), a 1995 episode of the television series ''The Outer Limits'' * " Chapter 19: The Convert", an episode of the television series ''The Mandalorian'' Business and marketing * Conversion funnel, the path a consumer takes through the web toward or near a desired action or conversion * Conversion marketing, when a website's visitors take a desired action * Converting timber to commercial lumber Computing, science, and technology * Conversion of units, conversion between different units of measurement Computing and telecommunication * CHS conversion of data storage, mapping cylinder/head/sector tuples to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Conjugate
In mathematics, the complex conjugate of a complex number is the number with an equal real part and an imaginary part equal in magnitude but opposite in sign. That is, if a and b are real numbers, then the complex conjugate of a + bi is a - bi. The complex conjugate of z is often denoted as \overline or z^*. In polar form, if r and \varphi are real numbers then the conjugate of r e^ is r e^. This can be shown using Euler's formula. The product of a complex number and its conjugate is a real number: a^2 + b^2 (or r^2 in polar coordinates). If a root of a univariate polynomial with real coefficients is complex, then its complex conjugate is also a root. Notation The complex conjugate of a complex number z is written as \overline z or z^*. The first notation, a vinculum, avoids confusion with the notation for the conjugate transpose of a matrix, which can be thought of as a generalization of the complex conjugate. The second is preferred in physics, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Complex Number
In mathematics, a complex number is an element of a number system that extends the real numbers with a specific element denoted , called the imaginary unit and satisfying the equation i^= -1; every complex number can be expressed in the form a + bi, where and are real numbers. Because no real number satisfies the above equation, was called an imaginary number by René Descartes. For the complex number is called the , and is called the . The set of complex numbers is denoted by either of the symbols \mathbb C or . Despite the historical nomenclature, "imaginary" complex numbers have a mathematical existence as firm as that of the real numbers, and they are fundamental tools in the scientific description of the natural world. Complex numbers allow solutions to all polynomial equations, even those that have no solutions in real numbers. More precisely, the fundamental theorem of algebra asserts that every non-constant polynomial equation with real or complex coefficie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Function
In mathematics, a cubic function is a function of the form f(x)=ax^3+bx^2+cx+d, that is, a polynomial function of degree three. In many texts, the ''coefficients'' , , , and are supposed to be real numbers, and the function is considered as a real function that maps real numbers to real numbers or as a complex function that maps complex numbers to complex numbers. In other cases, the coefficients may be complex numbers, and the function is a complex function that has the set of the complex numbers as its codomain, even when the domain is restricted to the real numbers. Setting produces a cubic equation of the form :ax^3+bx^2+cx+d=0, whose solutions are called roots of the function. The derivative of a cubic function is a quadratic function. A cubic function with real coefficients has either one or three real roots ( which may not be distinct); all odd-degree polynomials with real coefficients have at least one real root. The graph of a cubic function always has a single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labyrinth
In Greek mythology, the Labyrinth () is an elaborate, confusing structure designed and built by the legendary artificer Daedalus for King Minos of Crete at Knossos. Its function was to hold the Minotaur, the monster eventually killed by the hero Theseus. Daedalus had so cunningly made the Labyrinth that he could barely escape it after he built it. Although early Cretan coins occasionally exhibit branching (multicursal) patterns, the single-path (unicursal) seven-course "Classical" design without branching or dead ends became associated with the Labyrinth on coins as early as 430 BC, and similar non-branching patterns became widely used as visual representations of the Labyrinth – even though both logic and literary descriptions make it clear that the Minotaur was trapped in a complex branching maze. Even as the designs became more elaborate, visual depictions of the mythological Labyrinth from the Roman era until the Renaissance are almost invariably unicursal. Branching maz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quadratic Equation
In mathematics, a quadratic equation () is an equation that can be rearranged in standard form as ax^2 + bx + c = 0\,, where the variable (mathematics), variable represents an unknown number, and , , and represent known numbers, where . (If and then the equation is linear equation, linear, not quadratic.) The numbers , , and are the ''coefficients'' of the equation and may be distinguished by respectively calling them, the ''quadratic coefficient'', the ''linear coefficient'' and the ''constant coefficient'' or ''free term''. The values of that satisfy the equation are called ''solution (mathematics), solutions'' of the equation, and ''zero of a function, roots'' or ''zero of a function, zeros'' of the quadratic function on its left-hand side. A quadratic equation has at most two solutions. If there is only one solution, one says that it is a double root. If all the coefficients are real numbers, there are either two real solutions, or a single real double root, or two comple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |