|
Quantum Illumination
Quantum illumination is a paradigm for target detection that employs quantum entanglement between a signal electromagnetic mode and an idler electromagnetic mode, as well as joint measurement of these modes. The signal mode is propagated toward a region of space, and it is either lost or reflected, depending on whether a target is absent or present, respectively. In principle, quantum illumination can be beneficial even if the original entanglement is completely destroyed by a lossy and noisy environment. Introduction Many quantum information applications, such as quantum teleportation, quantum error correction, and superdense coding, rely on entanglement. However, entanglement is a fragile quantum property between particles and can be easily destroyed by loss and noise arising from interaction with the environment, leading to quantum decoherence. Entanglement is therefore considered very hard to use in lossy and noisy environment. Lloyd, Shapiro and collaborators showed that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Entanglement
Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon that occurs when a group of particles are generated, interact, or share spatial proximity in a way such that the quantum state of each particle of the group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, including when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic of quantum entanglement is at the heart of the disparity between classical and quantum physics: entanglement is a primary feature of quantum mechanics not present in classical mechanics. Measurements of physical properties such as position, momentum, spin, and polarization performed on entangled particles can, in some cases, be found to be perfectly correlated. For example, if a pair of entangled particles is generated such that their total spin is known to be zero, and one particle is found to have clockwise spin on a first axis, then the spin of the other particle, measured on the same axis, is found to be anticlockwise. However, this behavior gives ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bayesian
Thomas Bayes (/beɪz/; c. 1701 – 1761) was an English statistician, philosopher, and Presbyterian minister. Bayesian () refers either to a range of concepts and approaches that relate to statistical methods based on Bayes' theorem, or a follower of these methods. A number of things have been named after Thomas Bayes, including: Bayes *Bayes action *Bayes Business School * Bayes classifier * Bayes discriminability index *Bayes error rate *Bayes estimator *Bayes factor * Bayes Impact *Bayes linear statistics * Bayes prior * Bayes' theorem / Bayes-Price theorem -- sometimes called Bayes' rule or Bayesian updating. *Empirical Bayes method *Evidence under Bayes theorem *Hierarchical Bayes model * Laplace–Bayes estimator *Naive Bayes classifier * Random naive Bayes Bayesian *Approximate Bayesian computation * Bayesian average *Bayesian Analysis (journal) *Bayesian approaches to brain function * Bayesian bootstrap *Bayesian control rule *Bayesian cognitive science *Bayesian e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature (journal)
''Nature'' is a British weekly scientific journal founded and based in London, England. As a multidisciplinary publication, ''Nature'' features peer-reviewed research from a variety of academic disciplines, mainly in science and technology. It has core editorial offices across the United States, continental Europe, and Asia under the international scientific publishing company Springer Nature. ''Nature'' was one of the world's most cited scientific journals by the Science Edition of the 2019 ''Journal Citation Reports'' (with an ascribed impact factor of 42.778), making it one of the world's most-read and most prestigious academic journals. , it claimed an online readership of about three million unique readers per month. Founded in autumn 1869, ''Nature'' was first circulated by Norman Lockyer and Alexander Macmillan as a public forum for scientific innovations. The mid-20th century facilitated an editorial expansion for the journal; ''Nature'' redoubled its efforts in exp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secure Communication
Secure communication is when two entities are communicating and do not want a third party to listen in. For this to be the case, the entities need to communicate in a way that is unsusceptible to eavesdropping or interception. Secure communication includes means by which people can share information with varying degrees of certainty that third parties cannot intercept what is said. Other than spoken face-to-face communication with no possible eavesdropper, it is probably safe to say that no communication is guaranteed to be secure in this sense, although practical obstacles such as legislation, resources, technical issues (interception and encryption), and the sheer volume of communication serve to limit surveillance. With many communications taking place over long distance and mediated by technology, and increasing awareness of the importance of interception issues, technology and its compromise are at the heart of this debate. For this reason, this article focuses on communicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sensor
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon. In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends the information to other electronics, frequently a computer processor. Sensors are always used with other electronics. Sensors are used in everyday objects such as touch-sensitive elevator buttons (tactile sensor) and lamps which dim or brighten by touching the base, and in innumerable applications of which most people are never aware. With advances in micromachinery and easy-to-use microcontroller platforms, the uses of sensors have expanded beyond the traditional fields of temperature, pressure and flow measurement, for example into Attitude and heading reference system, MARG sensors. Analog sensors such as potentiometers and force-sensing resistors are still widely used. Their applications include manufacturing and machinery, airplane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Imaging
Biological imaging may refer to any imaging technique used in biology. Typical examples include: * Bioluminescence imaging, a technique for studying laboratory animals using luminescent protein * Calcium imaging, determining the calcium status of a tissue using fluorescent light * Diffuse optical imaging, using near-infrared light to generate images of the body * Diffusion-weighted imaging, a type of MRI that uses water diffusion * Fluorescence lifetime imaging, using the decay rate of a fluorescent sample * Gallium imaging, a nuclear medicine method for the detection of infections and cancers * Imaging agent, a chemical designed to allow clinicians to determine whether a mass is benign or malignant * Imaging studies, which includes many medical imaging techniques * Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), a non-invasive method to render images of living tissues * Magneto-acousto-electrical tomography (MAET), is an imaging modality to image the electrical conductivity of biological tissu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Signal-to-noise Ratio
Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR or S/N) is a measure used in science and engineering that compares the level of a desired signal to the level of background noise. SNR is defined as the ratio of signal power to the noise power, often expressed in decibels. A ratio higher than 1:1 (greater than 0 dB) indicates more signal than noise. SNR, bandwidth, and channel capacity of a communication channel are connected by the Shannon–Hartley theorem. Definition Signal-to-noise ratio is defined as the ratio of the power of a signal (meaningful input) to the power of background noise (meaningless or unwanted input): : \mathrm = \frac, where is average power. Both signal and noise power must be measured at the same or equivalent points in a system, and within the same system bandwidth. Depending on whether the signal is a constant () or a random variable (), the signal-to-noise ratio for random noise becomes: : \mathrm = \frac where E refers to the expected value, i.e. in this case ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nature Physics
''Nature Physics'' is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It was first published in October 2005 (volume 1, issue 1). The chief editor is Andrea Taroni, who is a full-time professional editor employed by this journal. Scope ''Nature Physics'' publishes both pure and applied research from all areas of physics. Subject areas covered by the journal include quantum mechanics, condensed-matter physics, optics, thermodynamics, particle physics, and biophysics. Abstracting and indexing The journal is indexed in the following databases: *Chemical Abstracts Service – CASSI *Science Citation Index * Science Citation Index Expanded *Current Contents – Physical, Chemical & Earth Sciences According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2021 impact factor The impact factor (IF) or journal impact factor (JIF) of an academic journal is a scientometric index calculated by Clarivate that reflects the yearly mean number of citati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Physical Review A
''Physical Review A'' (also known as PRA) is a monthly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Physical Society covering atomic, molecular, and optical physics and quantum information. the editor was Jan M. Rost (Max Planck Institute for the Physics of Complex Systems). History In 1893, the ''Physical Review'' was established at Cornell University. It was taken over by the American Physical Society (formed in 1899) in 1913. In 1970, ''Physical Review'' was subdivided into ''Physical Review A'', ''B'', ''C'', and ''D''. At that time section ''A'' was subtitled ''Physical Review A: General Physics''. In 1990 a process was started to split this journal into two, resulting in the creation of ''Physical Review E'' in 1993. Hence, in 1993, ''Physical Review A'' changed its statement of scope to ''Atomic, Molecular and Optical Physics.'' In January 2007, the section of ''Physical Review E'' that published papers on classical optics was merged into ''Physical Review ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rayleigh Fading
Rayleigh fading is a statistical model for the effect of a propagation environment on a radio signal, such as that used by wireless devices. Rayleigh fading models assume that the magnitude of a signal that has passed through such a transmission medium (also called a communication channel) will vary randomly, or fade, according to a Rayleigh distribution — the radial component of the sum of two uncorrelated Gaussian random variables. Rayleigh fading is viewed as a reasonable model for tropospheric and ionospheric signal propagation as well as the effect of heavily built-up urban environments on radio signals. Rayleigh fading is most applicable when there is no dominant propagation along a line of sight between the transmitter and receiver. If there is a dominant line of sight, Rician fading may be more applicable. Rayleigh fading is a special case of two-wave with diffuse power (TWDP) fading. The model Rayleigh fading is a reasonable model when there are many objects in the en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
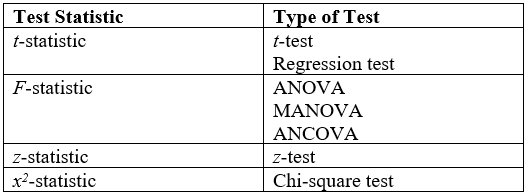
Hypothesis Testing
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of statistical inference used to decide whether the data at hand sufficiently support a particular hypothesis. Hypothesis testing allows us to make probabilistic statements about population parameters. History Early use While hypothesis testing was popularized early in the 20th century, early forms were used in the 1700s. The first use is credited to John Arbuthnot (1710), followed by Pierre-Simon Laplace (1770s), in analyzing the human sex ratio at birth; see . Modern origins and early controversy Modern significance testing is largely the product of Karl Pearson ( ''p''-value, Pearson's chi-squared test), William Sealy Gosset ( Student's t-distribution), and Ronald Fisher ("null hypothesis", analysis of variance, "significance test"), while hypothesis testing was developed by Jerzy Neyman and Egon Pearson (son of Karl). Ronald Fisher began his life in statistics as a Bayesian (Zabell 1992), but Fisher soon grew disenchanted with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Radar
Quantum radar is a speculative Remote sensing, remote-sensing technology based on quantum-mechanical effects, such as the uncertainty principle or quantum entanglement. Broadly speaking, a quantum radar can be seen as a device working in the microwave range, which exploits quantum features, from the point of view of the radiation source and/or the output detection, and is able to outperform a classical counterpart. One approach is based on the use of input quantum correlations (in particular, quantum entanglement) combined with a suitable interferometric quantum detection at the receiver (strongly related to the protocol of quantum illumination). Paving the way for a technologically-viable prototype of a quantum radar involves the resolution of a number of experimental challenges as discussed in some review articles, the latter of which pointed out "inaccurate reporting" in the media. Current experimental designs seem to be limited to very short ranges, of the order of one meter, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |