|
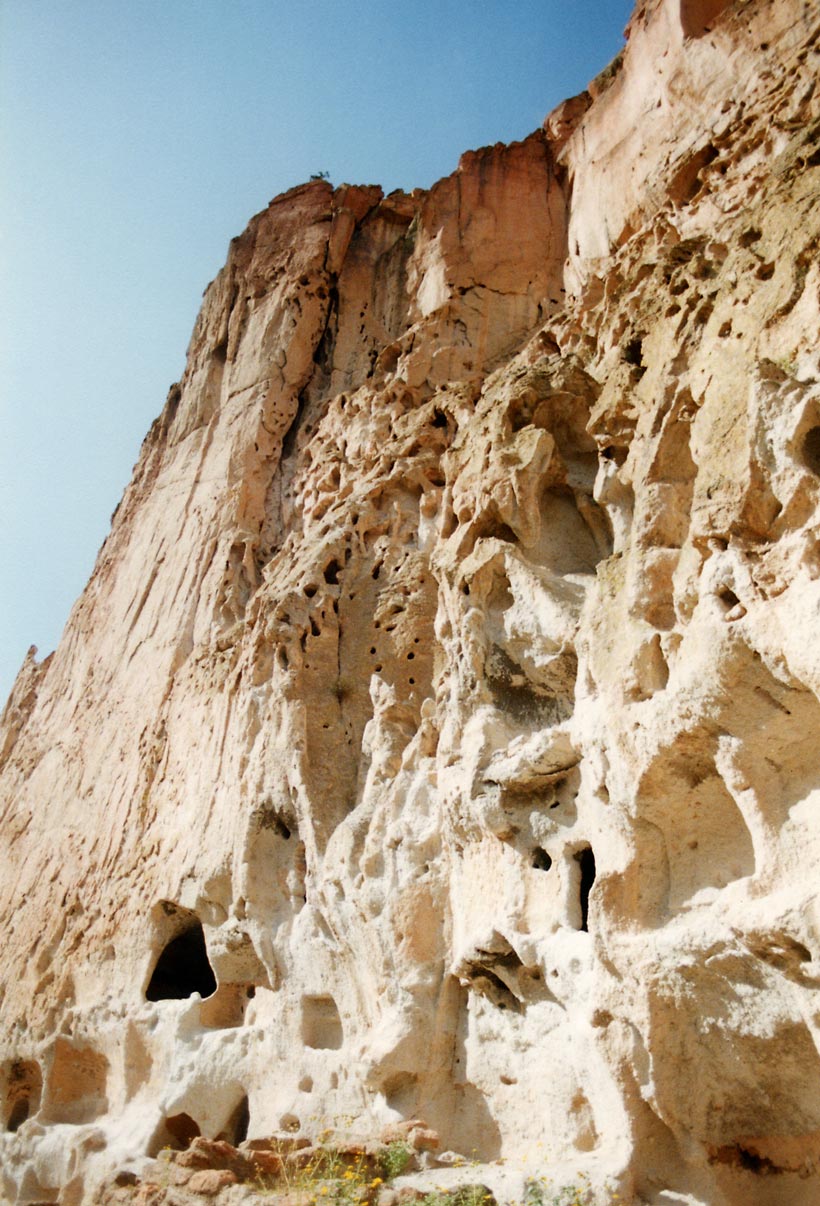
Puy
Puy () is a geological term used locally in the Auvergne, France for a volcanic hill. The word derives from the Provençal ''puech'', meaning an isolated hill, coming from Latin ''podium'', which has given also ''puig'' in Catalan, ''poggio'' in Italian, ''poio'' in Galician and Portuguese. Most of the puys of central France are small cinder cones, with or without associated lava, whilst others are domes of trachytic rock, like the of the Puy-de-Dôme. The puys may be scattered as isolated hills, or, as is more usual, clustered together, sometimes in lines. The chain of puys in central France probably became extinct in late prehistoric time. Other volcanic hills more or less like those of Auvergne are also known to geologists as puys; examples may be found in the Eifel and in the small cones on the Bay of Naples, whilst the relics of puys denuded by erosion are numerous in the Swabian Alps of Württemberg, as pointed out by W. Branco. Sir A. Geikie has shown that the puy typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puy-de-Dôme (mountain)
Puy-de-Dôme (; oc, label=Auvergnat, lo Puèi de Doma or ''lo Puèi Domat'') is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in the centre of France. In 2019, it had a population of 662,152.Populations légales 2019: 63 Puy-de-Dôme INSEE Its is and subprefectures are , [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auvergne (région)
Auvergne (; ; oc, label=Occitan, Auvèrnhe or ) is a former administrative region in central France, comprising the four departments of Allier, Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal and Haute-Loire. Since 1 January 2016, it has been part of the new region Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes.. The administrative region of Auvergne is larger than the historical province of Auvergne, one of the seven counties of Occitania, and includes provinces and areas that historically were not part of Auvergne. The Auvergne region is composed of the following old provinces: * Auvergne: departments of Puy-de-Dôme, Cantal, northwest of Haute-Loire, and extreme south of Allier. The province of Auvergne is entirely contained inside the Auvergne region * Bourbonnais: department of Allier. A small part of Bourbonnais lies outside Auvergne, in the neighbouring Centre-Val de Loire region (south of the department of Cher). * Velay: centre and southeast of department of Haute-Loire. Velay is entirely contained inside the Auvergne re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puy Montjuger Pourcharet 2A
Puy () is a geological term used locally in the Auvergne, France for a volcanic hill. The word derives from the Provençal ''puech'', meaning an isolated hill, coming from Latin ''podium'', which has given also ''puig'' in Catalan, ''poggio'' in Italian, ''poio'' in Galician and Portuguese. Most of the puys of central France are small cinder cones, with or without associated lava, whilst others are domes of trachytic rock, like the of the Puy-de-Dôme. The puys may be scattered as isolated hills, or, as is more usual, clustered together, sometimes in lines. The chain of puys in central France probably became extinct in late prehistoric time. Other volcanic hills more or less like those of Auvergne are also known to geologists as puys; examples may be found in the Eifel and in the small cones on the Bay of Naples, whilst the relics of puys denuded by erosion are numerous in the Swabian Alps of Württemberg, as pointed out by W. Branco. Sir A. Geikie has shown that the puy typ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puig (other)
Puig () is a word of Catalan origin, meaning "hill". Hence, in Catalan-speaking areas, it appears in the names of numerous people and geographical features: Geographical features * Puig-l'agulla, a mountain of Catalonia *Puig de l'Àliga (Sant Pere de Torelló), a mountain of Catalonia *Puig d'Arques, a mountain of Catalonia *Puig de Bassegoda, a mountain of Catalonia *Puig Campana, a mountain of Alicante, Spain *Puig Castellar (Balenyà), a mountain of Catalonia *Puig Cerverís, a mountain of Catalonia *Puig de la Collada Verda, a mountain of Catalonia * Puig Cornador (Les Llosses), a mountain of Catalonia * Puig Cornador (Ribes de Freser), a mountain of Catalonia * Puig Cornador (Sant Sadurní d'Osormort), a mountain of Catalonia * Puig Cornador (Vilanova de Sau), a mountain of Catalonia *Puig de Dòrria, a mountain of Catalonia *Puig Drau, a mountain of Catalonia * Puig Estela, a mountain of Catalonia *Puig de Fontlletera, a mountain of Catalonia *Puig de Fontnegra, a mountain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its Metropolitan France, metropolitan area extends from the Rhine to the Atlantic Ocean and from the Mediterranean Sea to the English Channel and the North Sea; overseas territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the North Atlantic, the French West Indies, and many islands in Oceania and the Indian Ocean. Due to its several coastal territories, France has the largest exclusive economic zone in the world. France borders Belgium, Luxembourg, Germany, Switzerland, Monaco, Italy, Andorra, and Spain in continental Europe, as well as the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Netherlands, Suriname, and Brazil in the Americas via its overseas territories in French Guiana and Saint Martin (island), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hill
A hill is a landform that extends above the surrounding terrain. It often has a distinct Summit (topography), summit. Terminology The distinction between a hill and a mountain is unclear and largely subjective, but a hill is universally considered to be not as tall, or as Grade (slope), steep as a mountain. Geographers historically regarded mountains as hills greater than above sea level, which formed the basis of the plot of the 1995 film ''The Englishman who Went up a Hill but Came down a Mountain''. In contrast, hillwalkers have tended to regard mountains as peaks above sea level. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' also suggests a limit of and Whittow states "Some authorities regard eminences above as mountains, those below being referred to as hills." Today, a mountain is usually defined in the UK and Ireland as any summit at least high, while the official UK government's definition of a mountain is a summit of or higher. Some definitions include a topographical pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Von Branca
Carl Wilhelm Franz von Branca Until 1895: Wilhelm Branco; 1895-1907: Wilhelm von Branco (9 September 1844 – 12 March 1928) was a German geologist and paleontologist. Biography Von Branca was born in Potsdam. After having been an officer, and then a farmer, Branca studied geology in Halle and Heidelberg, receiving his doctorate in 1876. He did postdoctoral work in Straßburg, Berlin, Munich, and in Rome with Karl Alfred von Zittel. In 1881 he received his habilitation from the Friedrich-Wilhelms-University Berlin (today's Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin), where he then worked as a lecturer. After a short stint as a lecturer in Aachen, von Branca became State Geologist at the Prussian Geological State Service in Berlin. From 1887 to 1890 he served as professor for geology and paleontology in Königsberg, until 1895 in Tübingen, then for four years (until 1899) in Hohenheim, until finally settling down in Berlin, where he was professor of geology until 1917, doubling as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agglomerate
Agglomerate (from the Latin ''agglomerare'' meaning "to form into a ball") is a coarse accumulation of large blocks of volcanic material that contains at least 75% bombs. Volcanic bombs differ from volcanic blocks in that their shape records fluidal surfaces: they may, for example, have ropy, cauliform, scoriaceous, folded, spindle, spatter, ribbon, ragged, or amoeboid shapes. Globular masses of lava may have been shot from the crater at a time when partly molten lava was exposed, and was frequently shattered by sudden outbursts of steam. These bombs were viscous at the moment of ejection and by rotation in the air acquired their shape. They are commonly in diameter, but specimens as large as have been observed. There is less variety in their composition at any one volcanic centre than in the case of the lithic blocks, and their composition indicates the type of magma being erupted. Agglomerates are typically found near volcanic vents and within volcanic conduits, where they m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock containing 25% to 75% ash is described as tuffaceous (for example, ''tuffaceous sandstone''). Tuff composed of sandy volcanic material can be referred to as volcanic sandstone. Tuff is a relatively soft rock, so it has been used for construction since ancient times. Because it is common in Italy, the Romans used it often for construction. The Rapa Nui people used it to make most of the ''moai'' statues on Easter Island. Tuff can be classified as either igneous or sedimentary rock. It is usually studied in the context of igneous petrology, although it is sometimes described using sedimentological terms. Tuff is often erroneously called tufa in guidebooks and in television programmes. Volcanic ash The material that is expelled in a volcanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Denudation
Denudation is the geological processes in which moving water, ice, wind, and waves erode the Earth's surface, leading to a reduction in elevation and in relief of landforms and landscapes. Although the terms erosion and denudation are used interchangeably, erosion is the transport of soil and rocks from one location to another, and denudation is the sum of processes, including erosion, that result in the lowering of Earth's surface. Endogenous processes such as volcanoes, earthquakes, and tectonic uplift can expose continental crust to the exogenous processes of weathering, erosion, and mass wasting. The effects of denudation have been recorded for millennia but the mechanics behind it have been debated for the past 200 years and have only begun to be understood in the past few decades. Description Denudation incorporates the mechanical, biological, and chemical processes of erosion, weathering, and mass wasting. Denudation can involve the removal of both solid particles and diss ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the north and west, the North Sea to the northeast and east, and the Irish Sea to the south. It also contains more than 790 islands, principally in the archipelagos of the Hebrides and the Northern Isles. Most of the population, including the capital Edinburgh, is concentrated in the Central Belt—the plain between the Scottish Highlands and the Southern Uplands—in the Scottish Lowlands. Scotland is divided into 32 administrative subdivisions or local authorities, known as council areas. Glasgow City is the largest council area in terms of population, with Highland being the largest in terms of area. Limited self-governing power, covering matters such as education, social services and roads and transportation, is devolved from the Scott ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)




